Increased risk of hearing impairment with new thyroid eye disease treatment
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--More patients than previously reported may experience hearing symptoms such as hearing loss or muffled hearing from a new treatment for thyroid eye disease, teprotumumab (Tepezza), according to a small study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
Teprotumumab, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in January 2020, is the first and only drug to be approved for thyroid eye disease. In two clinical trials conducted prior to FDA approval of the drug, otologic symptoms were reported in 10 percent of patients. The new study found the rate could be as high as 65 percent.
The treatment is administered to patients once every three weeks for a total of eight infusions. It ...
Tubeless automated insulin delivery system improves blood glucose outcomes
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--People with type 1 diabetes can improve their blood sugar control while reducing time with low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, using Insulet Corporation's Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System compared to their standard insulin therapy. Results from an industry-sponsored study of the latest Omnipod, the first tubeless, wearable insulin pump, will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
The Omnipod 5 System underwent three months of at-home testing in 128 adults and adolescents ages 14 to 70 years and 112 children ages 6 to less than 14 years. All study participants have type 1 diabetes and were first followed for two weeks using their standard therapy, either multiple daily insulin injections ...
'Hunger hormone' ghrelin affects monetary decision making
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Higher levels of the stomach-derived hormone ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, predict a greater preference for smaller immediate monetary rewards over larger delayed financial rewards, a new study finds. The study results will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
This research presents novel evidence in humans that ghrelin, the so-called "hunger hormone," affects monetary decision making, said co-investigator Franziska Plessow, Ph.D., assistant professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. She said recent research findings in rodents suggested that ghrelin may play a part in impulsive choices and behaviors.
"Our results indicate that ghrelin might play a broader role than ...
Spanish-speaking children experience higher rate of obesity than English-speaking children
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Nearly one in five U.S. children and teenagers has obesity, and statistics show a higher prevalence of obesity in certain ethnicities, such as Hispanics and Blacks. Now results of a study being presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, suggest that Spanish as a family's primary language is a predictor of childhood obesity, regardless of ethnicity.
The prevalence of obesity among children and teens from Spanish-speaking households in the nation was 24.4 percent, approximately 50 percent higher than those from English-speaking households, according to results of a new analysis of the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. This survey examines a nationally representative sample ...
Real "doodles of light" in real-time mark leap for holograms at home
2021-03-20
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have devised and implemented a simplified algorithm for turning freely drawn lines into holograms on a standard desktop CPU. They dramatically cut down the computational cost and power consumption of algorithms that require dedicated hardware. It is fast enough to convert writing into lines in real-time, and makes crisp, clear images that meet industry standards. Potential applications include hand-written remote instructions superimposed on landscapes and workbenches.
Flying cars, robots, spaceships...whatever sci-fi future you can imagine, there is always a common feature: holograms. ...
An easy way to reduce socioeconomic disparities
2021-03-20
Researchers from Columbia University and Temple University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how choice architecture can reduce socioeconomic disparities.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Do Nudges Reduce Disparities? Choice Architecture Compensates for Low Consumer Knowledge" and is authored by Kellen Mrkva, Nathaniel Posner, Crystal Reeck, and Eric Johnson.
As Mrkva explains, "Our research demonstrates that people with low socioeconomic status (SES), low numerical ability, and low knowledge are most impacted by nudges. As a result, 'good nudges,' designed to encourage ...
How our microplastic waste becomes 'hubs' for pathogens, antibiotic-resistant bacteria
2021-03-19
It's estimated that an average-sized wastewater treatment plant serving roughly 400,000 residents will discharge up to 2,000,000 microplastic particles into the environment each day. Yet, researchers are still learning the environmental and human health impact of these ultra-fine plastic particles, less than 5 millimeters in length, found in everything from cosmetics, toothpaste and clothing microfibers, to our food, air and drinking water.
Now, researchers at New Jersey Institute of Technology have shown that ubiquitous microplastics can become 'hubs' for antibiotic-resistant bacteria ...
Lack of diversity in genomic databases may affect therapy selection for minority groups
2021-03-19
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Low representation of minority groups in public genomic databases may affect therapy selection for Black patients with cancer, according to new Mayo Clinic research published in npj Precision Oncology.
The researchers investigated the use of genomic databases and found that tumor mutation burden was significantly inflated in Black patients compared to White patients.
As a result of the study, clinicians who are using public genomic databases need to be aware of the potential for inflated tumor mutation burden values and how that may affect therapy selection and outcomes, especially for patients from underrepresented groups.
Clinicians use biomarkers, which are indicators of a disease or condition, to determine ...
Gene therapy using 'zinc fingers' may help treat Alzheimer's disease, animal study shows
2021-03-19
BOSTON - Researchers have used a genetic engineering strategy to dramatically reduce levels of tau--a key protein that accumulates and becomes tangled in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease--in an animal model of the condition. The results, which come from investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Sangamo Therapeutics Inc., could lead to a potentially promising treatment for patients with this devastating illness.
As described in Science Advances, the strategy involves a gene regulation technology called zinc finger protein transcription ...
Tiny machine poised to unlock brain's mysteries
2021-03-19
A team of scientists, led by researchers at Northwestern University, Shirley Ryan AbilityLab and the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), has developed novel technology promising to increase understanding of how brains develop, and offer answers on repairing brains in the wake of neurotrauma and neurodegenerative diseases.
Their research is the first to combine the most sophisticated 3-D bioelectronic systems with highly advanced 3-D human neural cultures. The goal is to enable precise studies of how human brain circuits develop and repair themselves in vitro. The study is the cover story for ...
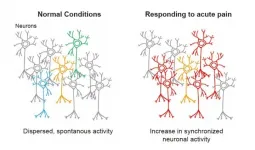
Holographic microscopy illuminates pain-driven changes in neuronal network activity
2021-03-19
In a world first, a cross-institutional research collaboration has used a two-photon microscope (*1) with a combination of calcium imaging (*2) and holographic stimulation (*3) to reveal that the functional connectivity between neurons located in the primary somatosensory cortex is increased in response to acute pain.
Pain occurs as a result of injury, such as peripheral neuron damage or inflammation stemming from peripheral tissue violation. Research findings have been published on the involvement of central nervous system abnormalities in the onset of pain and sustained pain. The primary somatosensory cortex ...
New technology 'retrains' cells to repair damaged brain tissue in mice after stroke
2021-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Most stroke victims don't receive treatment fast enough to prevent brain damage. Scientists at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, College of Engineering and College of Medicine have developed technology to "retrain" cells to help repair damaged brain tissue. It's an advancement that may someday help patients regain speech, cognition and motor function, even when administered days after an ischemic stroke.
Engineering and medical researchers use a process created by Ohio State called tissue nanotransfection (TNT) to introduce genetic material into cells. This allows them to reprogram skin cells to become something ...
Building tough 3D nanomaterials with DNA
2021-03-19
New York, NY--March 19, 2020--Columbia Engineering researchers, working with Brookhaven National Laboratory, report today that they have built designed nanoparticle-based 3D materials that can withstand a vacuum, high temperatures, high pressure, and high radiation. This new fabrication process results in robust and fully engineered nanoscale frameworks that not only can accommodate a variety of functional nanoparticle types but also can be quickly processed with conventional nanofabrication methods.
"These self-assembled nanoparticles-based materials are so resilient that they could fly in space," says Oleg Gang, professor ...
Researchers identify immune cells that contribute to transplant rejection
2021-03-19
PITTSBURGH, March 19, 2021 - Non-circulating memory T cells, whose main function is to provide local protection against re-infection, contribute to chronic transplant rejection, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers reveal in a paper published today in Science Immunology.
The scientists show that these "tissue-resident memory T cells" are harmful in situations where antigens that the cells recognize are present in the body for a long time, such as in cases of an organ or tissue transplant. This finding is an important step toward improving therapies to help prevent organ rejection in transplant recipients.
"Tissue-resident memory T cells serve an important surveillance function," said co-senior author Martin Oberbarnscheidt, ...
Vaccination by inhalation
2021-03-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Many viruses infect their hosts through mucosal surfaces such as the lining of the respiratory tract. MIT researchers have now developed a vaccination strategy that can create an army of T cells that are ready and waiting at those surfaces, offering a quicker response to viral invaders.
The researchers showed that they could induce a strong memory T cell response in the lungs of mice by giving them a vaccine modified to bind to a protein naturally present in mucus. This can help ferry the vaccine across mucosal barriers, such as the lining of the lungs.
"In this paper, we specifically focused on T cell responses that would be useful against viruses or cancer, and our idea was to use this protein, albumin, as sort of a Trojan horse to ...
Better batteries start with basics -- and a big computer
2021-03-19
To understand the fundamental properties of an industrial solvent, chemists with the University of Cincinnati turned to a supercomputer.
UC chemistry professor and department head Thomas Beck and UC graduate student Andrew Eisenhart ran quantum simulations to understand glycerol carbonate, a compound used in biodiesel and as a common solvent.
They found that the simulation provided detail about hydrogen bonding in determining the structural and dynamic properties of the liquid that was missing from classical models. The study was published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry B.
Glycerol carbonate could be a more environmentally ...
Importance of crisis standards of care for equitable allocation of scarce medical re
2021-03-19
During a public health crisis like the COVID-19 pandemic, U.S. hospitals need to allocate scarce medical resources in an equitable manner, according to clinicians and ethicists at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
"Significant concerns have been raised that crisis standards of care may be biased against certain patients based on race or ethnicity," said Hayley Gershengorn, M.D., associate professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine. "To examine that issue, we analyzed over a thousand medical records from two academic hospitals where University of Miami faculty see patients and found no disparities ...
COVID-19 transmission rare in schools with masking, distancing, contact tracing
2021-03-19
In-school COVID-19 transmission is rare - even among close school contacts of those who test positive for the virus - when schools heed public health precautions such as mandatory masking, social distancing and frequent hand-washing, according to results of a pilot study in Missouri aimed at identifying ways to keep elementary and secondary schools open and safe during the pandemic. A close contact is anyone who has been within 6 feet for more than 15 minutes in a 24-hour period with someone infected with COVID-19.
The study is part of a larger, ongoing collaboration involving the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, ...
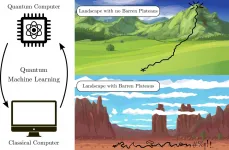
Solving 'barren plateaus' is the key to quantum machine learning
2021-03-19
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 19, 2021--Many machine learning algorithms on quantum computers suffer from the dreaded "barren plateau" of unsolvability, where they run into dead ends on optimization problems. This challenge had been relatively unstudied--until now. Rigorous theoretical work has established theorems that guarantee whether a given machine learning algorithm will work as it scales up on larger computers.
"The work solves a key problem of useability for quantum machine learning. We rigorously proved the conditions under which certain architectures of variational quantum algorithms will or will not have barren plateaus as they are scaled up," said Marco Cerezo, lead author on the paper published in Nature Communications ...
Tropical species are moving northward in U.S. as winters warm
2021-03-19
Notwithstanding last month's cold snap in Texas and Louisiana, climate change is leading to warmer winter weather throughout the southern U.S., creating a golden opportunity for many tropical plants and animals to move north, according to a new study appearing this week in the journal Global Change Biology.
Some of these species may be welcomed, such as sea turtles and the Florida manatee, which are expanding their ranges northward along the Atlantic Coast. Others, like the invasive Burmese python -- in the Florida Everglades, the largest measured 18 feet, end-to-end --maybe less so.
Equally unwelcome, and among the quickest to spread into warming areas, are ...
Emphasizing urgency alone won't increase support for major climate policies, study finds
2021-03-19
In light of recent extreme climate events--from wildfires blazing through the western US to snowstorms sweeping Texas into a blackout--climate scientists and media outlets have repeatedly called out the urgency of tackling the climate crisis. But in a new study published March 19 in the journal One Earth, researchers found that emphasizing urgency alone is not enough to kindle public support for climate change policies.
"We had the impression that policymakers shy away from enacting ambitious, stringent climate policy because they're afraid of ...
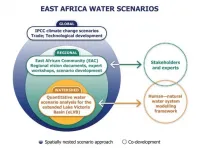
Strengthening water resources planning in East Africa
2021-03-19
IIASA researchers worked with local stakeholders from the East African Community to explore and co-develop regional water scenarios that can enhance understanding of the up- and downstream water sector interactions in the extended Lake Victoria Basin to facilitate rational water resource planning.
East Africa is the world's fastest growing region outside of Asia, with an estimated growth of 5% and above over the last decade. Part of this success can likely be attributed to the East Africa Vision 2050, which was launched in 2015 by the Heads of States of the East African Community (EAC) - an intergovernmental organization composed of six countries in the African Great Lakes ...
Hospital surge capacity survey before COVID-19 gives insight into pandemic preparedness
2021-03-19
PITTSBURGH, March 19, 2021 - A University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine-led survey of dozens of surge capacity managers at hospitals nationwide captures the U.S. health care system's pandemic preparedness status in the months before the first COVID-19 cases were identified in China.
Published today in the journal JAMA Network Open, the investigation details the strain experienced by U.S. hospitals during the 2017-18 influenza season, which was marked by severe illness and the highest infectious disease-related hospitalization rates in at least a decade. At the time, pandemic planning ...
High vitamin D levels may protect against COVID-19, especially for Black people
2021-03-19
A new research study at the University of Chicago Medicine has found that when it comes to COVID-19, having vitamin D levels above those traditionally considered sufficient may lower the risk of infection, especially for Black people.
The study, published March 19 in JAMA Open Network, retrospectively examined the relationship between vitamin D levels and likelihood of testing positive for COVID-19. While levels of 30 ng/ml or more are usually considered "sufficient," the authors found that Black individuals who had levels of 30 to 40 ng/ml had a 2.64 times higher risk of testing ...
Outcomes, risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in North American registry of patients with MS
2021-03-19
What The Study Did: This analysis examined how patients with multiple sclerosis who have COVID-19 fare and what patient and disease characteristics are associated with worse outcomes.
Authors: Amber Salter, Ph.D., of Washington University in St Louis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0688)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
[1] ... [2511]
[2512]
[2513]
[2514]
[2515]
[2516]
[2517]
[2518]
2519
[2520]
[2521]
[2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.