New research shows substantially higher burden of COVID-19 compared to flu
2021-03-19
Boston, Mass. - In a paper published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, physician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) assessed the relative impact of COVID-19 on patients hospitalized with the viral infection in March and April 2020, versus patients hospitalized with influenza during the last five flu seasons at the medical center. Overall, the team demonstrated that COVID-19 cases resulted in significantly more weekly hospitalizations, more use of mechanical ventilation and higher mortality rates than influenza.
COVID-19 and influenza are both contagious respiratory viral diseases that can lead to pneumonia and acute respiratory failure in severe cases. However, detailed comparison of the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 ...
Difficulty learning nonsense words may indicate a child's high risk of dyslexia
2021-03-19
Researchers at Aalto University and the Niilo Mäki Institute have used neuroimaging to pinpoint where the brain activates - or doesn't activate - among children identified as having a high risk of dyslexia. Magnetoencephalography (MEG) has rarely been used to study the reading disorder in children.
The brain study was carried out at Aalto University by measuring brain activity with MEG, which measures the weak magnetic fields arising from electrical activity in the brain, over a period of two days. Earlier studies have shown that difficulties in processing sounds may be partly responsible for dyslexia, and that these challenges may relate to the left auditory cortex which processes language.
During the study, the children listened to nonsensical ...
Increasing neurodiversity within organisations can boost skill base
2021-03-19
At the start of Neurodiversity Celebration Week, new research from Cranfield University demonstrates the importance of organisations becoming more inclusive employers when it comes to neurodiversity.
It has been estimated that one in seven of the population of the UK is neurodiverse. However, according to research by the Institute of Leadership and Management, only half of managers would employ a neurodiverse person.
Last week, in an interview with The Times, The Second Sea Lord Vice Admiral Nick Hine, revealed that ten years ago he was diagnosed with autism.
Speaking to The Times, the Vice Admiral, said: ""The world is made for neuro-typical people by neuro-typical people, and therefore it's not surprising that people who are not neuro-typical have a ...
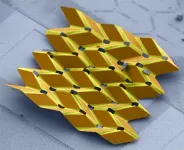
Advancement creates nanosized, foldable robots
2021-03-19
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Army-funded researchers created nanosized robots that could enable locomotion, novel metamaterial design and high-fidelity sensors.
Cornell University researchers created micron-sized shape memory actuators that fold themselves into 3D configurations and allow atomically thin 2D materials with just a quick jolt of voltage. Once the material is bent, it holds its shape, even after the voltage is removed.
To demonstrate the technology, the team created what is potentially the world's smallest self-folding origami bird.
"The research team is pushing the boundary of how quickly and precisely we can control motion at the micro- and even nano-scales," said Dr. Dean Culver, program manager for Complex Dynamics and Systems at Army Research Office, ...
COVID-19 in pregnancy associated with adverse outcomes for mother and baby
2021-03-19
Infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in pregnancy is associated with preeclampsia, stillbirth, preterm birth and other adverse outcomes, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) .
"Our findings suggest that pregnant people with COVID-19 have an increased risk of high blood pressure, stillbirth and preterm birth. Their newborns are more likely to need intensive care. Pregnant people with severe COVID-19 symptoms have a particularly high risk of these complications," says Dr. Nathalie ...
Is grant review feedback perceived as fair or useful? AIBS publication investigates
2021-03-19
An important function of the grant peer review process is to provide constructive feedback to applicants for their resubmissions. However, little is known about whether review feedback achieves this goal.
The American Institute of Biological Sciences (AIBS), in collaboration with Washington State University, has published findings on a multi-methods analysis of responses from grant applicants regarding their perceptions of the usefulness and appropriateness of peer review feedback they received from grant submissions.
The analysis focused on responses ...
Demonstrating the world's fastest spintronics p-bit
2021-03-19
Tohoku University researchers have, for the first time, developed the technology for the nanosecond operation of the spintronics-based probabilistic bit (p-bit) - dubbed the poor man's quantum bit (q-bit).
The late physicist R.P. Feynman envisioned a probabilistic computer: a computer that is capable of dealing with probabilities at scale to enable efficient computing.
"Using spintronics, our latest technology made the first step in realizing Feynman's vision," said Shun Kanai, professor at the Research Institute of Electrical Communication at Tohoku University and lead author of the study.
Magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) are the key component of non-volatile ...
The shape of things to come: Shifting rewards are encoded using special neuronal patterns
2021-03-19
Tsukuba, Japan - Animals must make predictions about future rewards when making decisions during daily life. Specific reward-related patterns of neuronal activity are known to underlie such decisions. But now, researchers from Japan have found a new pattern of neural activity that occurs when responding to rewards that are changing over time.
In a study published this month in eLife, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that dopamine neurons, which process information about rewards, are activated in a previously undetected way when an animal considers a reward that is changing in value.
Previous studies have highlighted ...
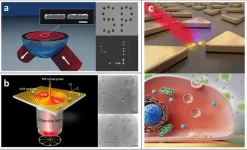
Plasmonic tweezers: For nanoscale optical trapping and beyond
2021-03-19
Optical tweezers and associated manipulation tools in the far field have had a major impact on scientific and engineering research by offering precise manipulation of small objects. More recently, the near-field manipulation with surface plasmons has opened opportunities not feasible with conventional far-field optical methods. The use of surface plasmon techniques enables excitation of hotspots much smaller than the free-space wavelength; with this confinement, the plasmonic field facilitates trapping of various nanostructures and materials with higher precision. It has become commonly used in trapping of micro- and nanometre-sized objects in various fields of science.
In a new review paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor ...
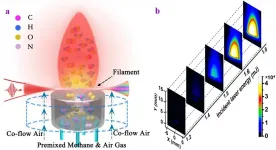
Robust and ultralow-energy-threshold ignition of lean fuels by an ultrashort-pulsed laser
2021-03-19
Laser ignition (LI) is a promising electrode-less alternative to electronic spark ignition of lean fuel/air mixtures, offering high thermal efficiency with low harmful emissions. One of the most widely adopted LI methods is nanosecond laser-induced spark ignition (ns-LISI), in which combustible mixtures undergo multiphoton ionization followed by avalanche breakdown, resulting in high-temperature and high-pressure plasma along with shockwaves. However, inevitable shot-to-shot energy fluctuations resulting from ns light sources lead to the stochastic nature of the breakdown, influencing reaction routes and producing potential misfiring.
Although LI is not a new concept, it is commonly deemed that igniting lean-fuel mixtures by an ultrashort femtosecond (fs) ...
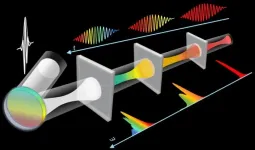
High-efficiency pulse compression established on solitons in nonlinear Kerr resonators
2021-03-19
Generating intense ultrashort pulses with high spatial quality has opened up possibilities for ultrafast and strong-field science. It is so important that the Nobel Prize in Physics 2018 was given to Dr. Strickland and Dr. Mourou for inventing a technique called chirped pulse amplification, which drives numerous ultrafast lasers worldwide. With the great advancement in the last decade, Yb-based ultrafast lasers have become highly popular, because they exhibit exceptional thermal efficiency, are low in cost and are highly flexible in adjusting pulse energies and repetition rates. However, the pulse durations from these lasers are usually not shorter than 100 fs or even 1 ps, which requires external ...
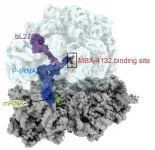
New antibiotic clears multi-drug resistant gonorrhea in mice in single dose
2021-03-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A new antibiotic compound clears infection of multi-drug resistant gonorrhea in mice in a single oral dose, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State and Emory University. The compound targets a molecular pathway found in bacteria but not humans and could lead to new treatments for gonorrhea and infections from other bacteria, such as tuberculosis and MRSA.
The research team, which also includes scientists from the biopharmaceutical company Microbiotix, the Uniformed Services University, and Florida State, published their results in a paper appearing March 19 ...
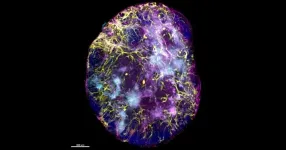
Three-dimensional imaging provides valuable insight to immune responses
2021-03-19
A new imaging technique is shining a light on immune responses and setting the scene for enhancing immune memory to optimise vaccine strategies.
By imaging intact lymphoid organs in three dimensions, researchers have been able to identify specialised niches, which can determine how immune T cells function.
The research, published in Nature Immunology, is a step forward in understanding the differentiation of T cells - critical cells for developing strong immune responses - and how we can use these crucial findings to inform and optimise vaccine strategies.
At a glance
Three-dimensional imaging has enabled researchers to identify the factors that play a role in determining where immune memory cells locate ...
Scientists identify genetic pathway that suppresses Lou Gehrig's Disease
2021-03-19
Professor Chunghun Lim and his research team in the Department of Biological Sciences unveiled a neuroprotective pathway that suppresses Lou Gehrig's Disease (ALS).
Nucleocytoplasmic transport (NCT) defects have been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, such as C9ORF72-associated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (C9-ALS/FTD). In this study, the research team has identified a neuroprotective pathway of like-Sm protein 12 (LSM12) and exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP 1 (EPAC1) that sustains the nucleocytoplasmic ...
Reactive boride infusion stabilizes ni-rich cathodes for lithium-ion batteries
2021-03-19
A new coating for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), developed by scientists at UNIST promises extended driving for future electric vehicles (EVs). The coating, described in a paper published in the journal Nature Energy, when applied to LIBs is shown to have improved cycling stability even after being charged and discharged more than 500 times. As a result, the development of EV batteries that can drive longer distances with a single battery charge has gained considerable momentum.
Distinguished Professor Jaephil Cho and his research team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST unveiled ...
Binge drinking in adolescence is linked to changes in the cerebellum in young adulthood
2021-03-19
Binge drinking in adolescence is associated with changes in the volume of the cerebellum in young adulthood, a new study from the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital shows. Earlier studies have shown that excessive, long-term alcohol consumption causes damage to the cerebellum in adults, but there is very little data on the effects of adolescent drinking on the cerebellum. The findings were published in Alcohol.
The study included 58 young adults aged 21 to 28 years, whose alcohol consumption had been monitored for the previous ten years. Of the participants, 33 had been heavy drinkers since adolescence, while 25 were light drinkers, consuming little or no alcohol at all. All of them were highly functional and had normal ...
How do humpback whales rest?
2021-03-19
An international research collaboration has used an omnidirectional camera attached to humpback whale to reveal how these creatures rest underwater. These findings demonstrate how wide-angle lens cameras can be useful tools for illuminating the ecology of difficult-to-observe animals in detail.
The research group consisted of Assistant Professor Takashi Iwata of Kobe University's Graduate School of Maritime Sciences, Researcher Martin Biuw of the Norwegian Institute of Marine Research, Assistant Professor Kagari Aoki and Professor Katsufumi Sato of the Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, the University of Tokyo, and Professor Patrick Miller of the University of St. Andrews.
These research results ...
Endocrine disruptors threatens semen quality
2021-03-19
A growing number of studies show that the environmental factors and lifestyle habits of pregnant women play an important role in the health of their child. But how about the semen quality of young men? Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, showed two years ago that only 38% of Swiss men had semne parameters above the thresholds set by the World Health Organisation (WHO) for fertile men. Epidemiologists from the Institut de recherche en santé, environnement et travail (IRSET, Rennes, France), in collaboration with the UNIGE team analyzed the potential impact of endocrine disruptors on semen quality of men whose mothers were working at the early ...
Hidden genetic defects contain real risks for serious diseases
2021-03-19
For the first time researchers from Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Radboudumc, Maastricht UMC+ and international colleagues have gained insight into the "hidden genetic defects" of the general European population. This is important because these defects, if inherited from both father and mother, can lead to all kinds of illnesses in their children. Research in the Dutch and Estonian population shows that every person has two to four such hidden genetic defects. In 1 in 100 couples, this leads to a situation with an increased risk of a genetic disease for future children. In the case of consanguinity, even 20 percent of the couples appear to be at high risk. This research is published in The American Journal of Human Genetics and Genetics in Medicine.
The genes of a every ...
New discoveries on deadly fungus - might be a key for treatment
2021-03-19
Aspergillus fumigatus kills as many people as malaria and tuberculosis, but is less known. It is found "everywhere", for example in the soil or in our compost, but is not normally dangerous to healthy people.
Those who die from it often have a poor immune system or are hospitalized for lung infections, such as covid-19.
Aspergillus also constitutes an increasing problem in agriculture, because the fungus causes deadly infections in both plants and animals. In the same way that many bacteria are resistant to antibiotics, also this fungus is now becoming more and more resistant to the limited repertoire of treatments. It is therefore important to find new ways to fight fungal ...
Vape aerosol and gene expression in human lung tissue compared to cigarette sm
2021-03-19
March 19, 2021, Bristol, UK - A new peer-reviewed study published in the journal Toxicological Research & Application shows acute exposure of a 3D human bronchial tissue model to e-cigarette aerosol has minimal impact on gene expression compared to smoke from combustible cigarettes.
The research involved sub-cytotoxic exposure to cells in a 3D human bronchial model (MucilAirTM) to nicotine-containing vape aerosol, combustible cigarette smoke and fresh air control under strict laboratory conditions.
The highly sensitive Toxicity Testing in the Twenty-First Century (TT21C)-based technique allows researchers to gain a ...
80% of Spanish health professionals were willing to be vaccinated during the second COVID-19 wave
2021-03-19
Approximately 8 out of every 10 health professionals in Spain are willing to be vaccinated against COVID-19, according to a study led by researchers from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC). Published in the open-access journal Vaccines, the study assessed for the first time this population segment's willingness to be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 and concluded that the level of acceptance is higher among physicians than among nursing staff. Among the reasons given by health personnel for not wanting to be immunized, fears about the vaccines' safety and the potential side effects stood out.
Although vaccination is considered to the most effective method for preventing and eradicating viral infections and stopping ...
Foreign-born run greater risk of workplace bullying
2021-03-19
The risk of being bullied at work is twice as high if you were born abroad. And if you come from a culture that is culturally dissimilar to Sweden's, the risk is even higher. These are the results of a Swedish study from Linköping University that was recently published in The International Journal of Human Resource Management.
Employers in Sweden have a duty to ensure that the workplace is safe, with a healthy atmosphere. Despite this, some employees are treated poorly, excluded and ignored. When such treatment has continued for a longer period, it is defined as bullying.
Researchers at Linköping University wanted to see if people born abroad run a greater risk of being bullied at work.
"Our results show an increased risk of bullying ...
The eukaryotic cell nucleus resembles the layout of a superstore
2021-03-19
The headquarter of a eukaryotic cell is the nucleus, and most of the cell's information and instructions are stored there in the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). The DNA, which is twisted, rolled and bundled two-meter-long chain, together with protein molecules, makes up the chromatin fiber that lays inside the nucleus. For years, scientists were curious how these components are organized. How is it possible that proteins necessary in biochemical reactions move efficiently within the nucleus full of DNA? Recent studies have finally solved the mystery. Findings describing it in detail were published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters on December 21st, 2020.
Molecules ...
ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021: Myths and facts about the prevention of heart disease
2021-03-19
Stay tuned for the hottest science in the prevention of heart disease at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC), a branch of the ESC, takes place 15 to 17 April online.
Preventive cardiology covers how to avoid first and subsequent heart attacks and strokes. It also includes sports cardiology, primary care, epidemiology and population science, basic and translational research, and rehabilitation after an event. Explore the scientific programme.
Novel research will be presented including new insights into the connections between diet, exercise, and cardiovascular health. How does shift work affect the body? And are there links between climate ...
[1] ... [2513]
[2514]
[2515]
[2516]
[2517]
[2518]
[2519]
[2520]
2521
[2522]
[2523]
[2524]
[2525]
[2526]
[2527]
[2528]
[2529]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.