Pick up the pace!
2021-03-16
SLOW walkers are almost four times more likely to die from COVID-19, and have over twice the risk of contracting a severe version of the virus, according to a team of researchers from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Leicester Biomedical Research Centre led by Professor Tom Yates at the University of Leicester.
The study of 412,596 middle-aged UK Biobank participants examined the relative association of body mass index (BMI) and self-reported walking pace with the risk of contracting severe COVID-19 and COVID-19 mortality.
The analysis found slow walkers of a normal weight to be almost 2.5 times more likely to develop severe COVID-19 and 3.75 times more likely to die from the virus ...
BIDMC researchers model a safe new normal
2021-03-16
Boston, Mass. - Just one year after the World Health Organization declared the novel coronavirus a global pandemic, three COVID-19 vaccines are available in the United States, and more than 2 million Americans are receiving shots each day. Americans are eager to get back to business as usual, but experts caution that opening the economy prematurely could allow a potential resurgence of the virus. How foot traffic patterns in restaurants and bars, schools and universities, nail salons and barbershops affect the risk of transmission has been largely unknown.
In an article published ...
Leprosy drug holds promise as at-home treatment for COVID-19
2021-03-16
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - March 16, 2021 - A Nature study authored by scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and the University of Hong Kong shows that the leprosy drug clofazimine, which is FDA approved and on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, exhibits potent antiviral activities against SARS-CoV-2 and prevents the exaggerated inflammatory response associated with severe COVID-19. Based on these findings, a Phase 2 study evaluating clofazimine as an at-home treatment for COVID-19 could begin immediately.
"Clofazimine is an ideal candidate for a COVID-19 treatment. It is safe, affordable, easy to make, taken as a pill and can be made globally available," ...
More accurate method to predict long term outcomes for pre-invasive breast cancer
2021-03-16
A study by Queen Mary University of London researchers, funded by Cancer Research UK, confirms the role of the oestrogen receptor biomarker in ductal carcinoma in situ and presents a new and more accurate method to predict long term outcomes for this pre-invasive stage of breast cancer. The study is published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Oestrogen receptor (ER), a protein expressed in some breast cancer cells, is routinely tested in invasive breast cancer to predict long-term outcomes select treatment options. Its role in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) has been previously unclear, and it is not generally evaluated in this pre-invasive stage of breast cancer. The new research confirms the role of ER in predicting ...
Electronic cigarettes help smokers with schizophrenia quit
2021-03-16
A new study in Nicotine & Tobacco Research, published by Oxford University Press, finds that the use of high-strength nicotine e-cigarettes can help adults with schizophrenia spectrum disorders quit smoking.
Some 60-90% of people with schizophrenia smoke cigarettes, compared to 15-24% of the general population. The researchers from the University of Catania, in collaboration with colleagues from City University of New York and Weill Medical College of Cornell University, have assessed here the feasibility of using a high-strength nicotine e-cigarette to modify smoking behavior in people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders who smoke cigarettes. In this study ...
A promising breakthrough for a better design of electronic materials
2021-03-16
Finding the best materials for tomorrow's electronics is the goal of Professor Emanuele Orgiu of the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS). Among the materials in which Professor Orgiu is interested, some are made of molecules that can conduct electricity. He has demonstrated the role played by molecular vibrations on electron conductivity on crystals of such materials. This finding is important for applications of these molecular materials in electronics, energy and information storage. The study, conducted in collaboration with a team from the INRS and the ...
Non-invasive skin swab samples are enough to quickly detect COVID-19, a new study finds
2021-03-16
Researchers at the University of Surrey have found that non-invasive skin swab samples may be enough to detect COVID-19.
The most widely used approach to testing for COVID-19 requires a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test, which involves taking a swab of the back of the throat and far inside the nose.
In a paper published by Lancet E Clinical Medicine, chemists from Surrey teamed up with Frimley NHS Trust and the Universities of Manchester and Leicester to collect sebum samples from 67 hospitalised patients - 30 who had tested positive for COVID-19 and 37 who had tested negative. The samples were collected by gently swabbing a skin area rich in sebum - an oily, waxy substance produced by the body's sebaceous glands - such as the face, neck or back.
The researchers analysed ...
Abuse in childhood and adolescence linked to higher likelihood of conduct problems
2021-03-16
Children who are exposed to abuse before they are eleven years old, and those exposed to abuse both in childhood and adolescence may be more likely to develop conduct problems (such as bullying or stealing) than those exposed to abuse in adolescence only and those who are not exposed to abuse, according to a study published in the open access journal BMC Psychiatry.
A team of researchers at the Universities of Bath and Bristol examined data on 13,793 children and adolescents (51.6% boys), who were followed from ages four to 17 years, included in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children, ...
Use of AI to fight COVID-19 risks harming 'disadvantaged groups', experts warn
2021-03-16
Rapid deployment of artificial intelligence and machine learning to tackle coronavirus must still go through ethical checks and balances, or we risk harming already disadvantaged communities in the rush to defeat the disease.
This is according to researchers at the University of Cambridge's Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (CFI) in two articles, published today in the British Medical Journal, cautioning against blinkered use of AI for data-gathering and medical decision-making as we fight to regain some normalcy in 2021.
"Relaxing ...
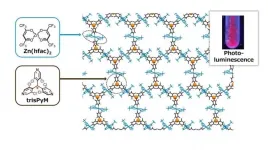
A novel recipe for air-stable and highly-crystalline radical-based coordination polymer
2021-03-16
Coordination polymers (CPs) composed of organic radicals have been the focus of much research attention in recent years due to their potential application to a wide variety of next-generation electronics, from more flexible devices to 'spintronics' storage of information. Sadly, they often suffer from their limited stability and poor crystallinity. Researchers from Japan's Institute for Molecular Science (IMS), National Institute of Natural Sciences (NINS) have developed a novel recipe that not only produces a stable material, but offers a variety of other useful attributes.
Their findings appear in the journal ...
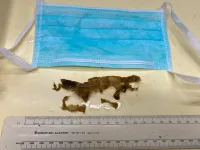
COVID waste: Archaeologists have a role to play in informing environmental policy
2021-03-16
The 2020 COVID-19 pandemic is creating a viral archive, an archaeological record of history in the making. One aspect of this archive is increased environmental pollution, not least through discarded face-masks and gloves, collectively known as PPE, that characterise the pandemic.
These items of plastic waste have become symbolic of the pandemic and have now entered the archaeological record, in particular face-masks.
In the UK alone, 748 million items of PPE, amounting to 14 million items a day, were delivered to hospitals in the two or so months from ...
New research reveals possible cause of mystery condition that leaves people paralysed
2021-03-16
Researchers believe they may have discovered a possible cause of a mystery condition that can leave sufferers suddenly unable to walk, talk or see.
It's hoped the study - led by the University of York and Hull York Medical School and supported by Tees, Esk and Wear Valley NHS Trust - will pave the way for new treatments for Conversion disorder which affects around 800,000 people in the UK alone.
The condition, also known as functional neurological disorder (FND), causes physical symptoms that would appear neurological but doctors can't find an injury or physical condition to explain them.
Professor Christina van der Feltz-Cornelis from the Department of Health Sciences is leading the Conversion And Neuro-inflammation ...
Vulnerable newborns being separated from their mothers in COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-16
Two-thirds of 1,120 healthcare workers surveyed worldwide would separate mothers and babies with a positive or unknown COVID-19 status.
Implementing Kangaroo Mother Care and keeping mothers and babies together could save more than 125,000 newborn lives, representing 65x decreased risk of newborn death compared to the risk of newborn deaths from COVID-19.
New research underscores the need for decision-makers and providers, particularly in LMICs, to protect and strengthen care for small and sick newborns during the pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the quality of care given to small and sick newborn babies in all regions of the world and threatening implementation of life-saving interventions, ...
Switching from TDF- to TAF-containing ART associated with the development of obesity in people living with HIV
2021-03-15
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Switching from TDF- to TAF-containing ART associated with the development of obesity in people living with HIV
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-4853
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
Switching from antiretroviral therapy ...
HIV research: Increased weight gain with TAF medication
2021-03-15
In Switzerland about 17 000 people are living with an HIV infection, worldwide there are about 38 million. Today, the disease can be treated so successfully that a normal life can be ensured to a great extent. However, weight increases are often observed at the beginning of HIV therapy due to adaptations of the metabolism, which are part of a successful therapy. Therefore, body weight control plays an important role in HIV therapy. It is important, for example, to avoid metabolic problems that can lead to heart attacks or diabetes over the long term.
Tenofovir is the drug used as part of the standard HIV therapies. The previously, widely used TDF-based therapy (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, TDF) has been associated with renal side effects and ...
An ancient Maya ambassador's bones show a life of privilege and hardship
2021-03-15
An important Maya man buried nearly 1,300 years ago led a privileged yet difficult life. The man, a diplomat named Ajpach' Waal, suffered malnutrition or illness as a child, but as an adult he helped negotiate an alliance between two powerful dynasties that ultimately failed. The ensuing political instability left him in reduced economic circumstances, and he probably died in relative obscurity.
During excavations at El Palmar, a small plaza compound in Mexico near the borders of Belize and Guatemala, archaeologists led by Kenichiro Tsukamoto, an assistant professor of anthropology at UC Riverside, discovered a hieroglyph-adorned stairway ...
Criteria published for diagnosing the clinical syndrome of CTE during life
2021-03-15
(Boston)-- Newly published National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Traumatic Encephalopathy Syndrome (TES) are the first expert consensus criteria developed for the clinical disorder associated with Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) brain pathology. CTE is a degenerative brain disease associated with a history of repetitive head impacts, including those sustained in contact and collision sports such as American football and boxing. At this time, CTE can only be diagnosed after death through a neuropathological examination of brain tissue. There has been no accepted approach or agreed upon criteria for the diagnosis of CTE and its clinical manifestations during life until now.
"The publication of these criteria ...
Exercise during pregnancy may save kids from health problems as adults
2021-03-15
Exercise during pregnancy may let mothers significantly reduce their children's chances of developing diabetes and other metabolic diseases later in life, new research suggests.
A study in lab mice has found that maternal exercise during pregnancy prevented the transmission of metabolic diseases from an obese parent - either mother or father - to child. If the finding holds true in humans, it will have "huge implications" for helping pregnant women ensure their children live the healthiest lives possible, the researchers report in a new scientific paper.
This means that one day soon, a woman's first trip to the doctor after conceiving might include a prescription for an exercise ...
Community banks a key resource for small businesses when crises arise
2021-03-15
The $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan, a stimulus package introduced by the Biden Administration, recently received Congress' approval. The stimulus package, like its two predecessors aimed at providing relief for individuals and businesses hindered by the COVID-19 pandemic, includes another round of funding for the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP).
The American Rescue Plan includes $7.25 billion for PPP loans as well as a number of changes to make it easier for the smallest of businesses to gain access to the funding. With billions on the table for struggling small businesses, new research from the University of Florida Warrington College of ...
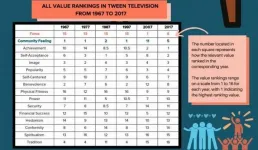
Tweens and TV: UCLA's 50-year survey reveals the values kids learn from popular shows
2021-03-15
How important is fame? What about self-acceptance? Benevolence? The messages children between the ages of 8 and 12 glean from TV play a significant role in their development, influencing attitudes and behaviors as they grow into their teenage years and beyond, UCLA psychologists say.
Now, a new report by UCLA's Center for Scholars and Storytellers assesses the values emphasized by television programs popular with tweens over each decade from 1967 to 2017, charting how 16 values have waxed and waned in importance during that 50-year span.
Among the key findings is that fame, after nearly 40 years of ranking near the bottom (it was 15th in 1967, 1987 and 1997), rose to become the No. 1 ...
Blight may increase public health risk from mosquito-borne diseases
2021-03-15
Louisiana State University researchers recently published findings that blight leads to an increased abundance of disease-carrying mosquitoes. The researchers investigated the presence of several mosquito species in two adjacent but socio-economically contrasting neighborhoods in Baton Rouge: the historic Garden District, a high-income neighborhood, and the Old South neighborhood, a low-income area. They found significantly higher adult and larvae abundance of the Asian tiger mosquito (a carrier of Zika and dengue) and higher mosquito habitat availability--particularly discarded tires--in the Old South neighborhood. This indicates that environmental conditions in the low-income neighborhood were most ideal for this mosquito to breed and proliferate.
"These ...
When 'eradicated' species bounce back with a vengeance
2021-03-15
Some invasive species targeted for total eradication bounce back with a vengeance, especially in aquatic systems, finds a study led by the University of California, Davis.
The study, published today in the journal PNAS, chronicles the effort --and failure -- to eradicate invasive European green crabs from a California estuary. The crabs increased 30-fold after about 90 percent had been removed. The study is the first experimental demonstration in a coastal ecosystem of a dramatic population increase in response to full eradication.
"A failure in science often leads to ...
Study predicts the oceans will start emitting ozone-depleting CFCs
2021-03-15
The world's oceans are a vast repository for gases including ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs. They absorb these gases from the atmosphere and draw them down to the deep, where they can remain sequestered for centuries and more.
Marine CFCs have long been used as tracers to study ocean currents, but their impact on atmospheric concentrations was assumed to be negligible. Now, MIT researchers have found the oceanic fluxes of at least one type of CFC, known as CFC-11, do in fact affect atmospheric concentrations. In a study appearing today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team reports that the global ocean will reverse its longtime role as a sink for the potent ozone-depleting chemical.
The researchers ...
Scientists stunned to discover plants beneath mile-deep Greenland ice
2021-03-15
In 1966, US Army scientists drilled down through nearly a mile of ice in northwestern Greenland--and pulled up a fifteen-foot-long tube of dirt from the bottom. Then this frozen sediment was lost in a freezer for decades. It was accidentally rediscovered in 2017.
In 2019, University of Vermont scientist Andrew Christ looked at it through his microscope--and couldn't believe what he was seeing: twigs and leaves instead of just sand and rock. That suggested that the ice was gone in the recent geologic past--and that a vegetated landscape, perhaps a boreal forest, stood where a mile-deep ice sheet as big ...
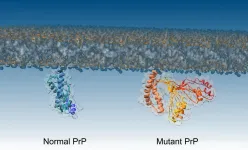
Crucial step in formation of deadly brain diseases discovered
2021-03-15
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed what causes normal proteins to convert to a diseased form, causing conditions like CJD and Kuru.
The research team, from Imperial College London and the University of Zurich, also tested a way to block the process, which could lead to new drugs for combatting these diseases.
The research concerned prion diseases - a group of brain diseases caused by proteins called prions that malfunction and 'misfold', turning into a form that can accumulate and kill brain cells. These diseases can take decades to manifest, but are then are aggressive and fatal.
They include Kuru, mad cow disease and its human equivalent Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), and a heritable condition called fatal familial ...
[1] ... [2530]
[2531]
[2532]
[2533]
[2534]
[2535]
[2536]
[2537]
2538
[2539]
[2540]
[2541]
[2542]
[2543]
[2544]
[2545]
[2546]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.