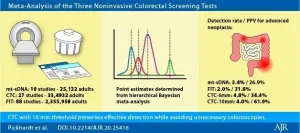
CT colonography most effective noninvasive colorectal cancer screening test
2021-03-12
Leesburg, VA, March 12, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), compared with multi-target stool-DNA (mt-sDNA) and fecal immunochemical test (FIT), CT colonography (CTC) with 10 mm threshold most effectively targets advanced neoplasia (AN)--preserving detection while decreasing unnecessary colonoscopies.
"CTC performed with a polyp size threshold for colonoscopy referral set at 10 mm represents the most effective and efficient non-invasive screening test for colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention and detection," clarified first author Perry J. Pickhardt from the department of radiology ...
New machine learning model could remove bias from social network connections
2021-03-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Did you ever wonder how social networking applications like Facebook and LinkedIn make recommendations on the people you should friend or pages you should follow?
Behind the scenes are machine learning models that classify nodes based on the data they contain about users -- for example, their level of education, location or political affiliation. The models then use these classifications to recommend people and pages to each user. But there is significant bias in the recommendations made by these models -- known as graph neural networks (GNNs) ...
Study finds adolescents with autism may engage neural control systems differently
2021-03-12
A new study by UC Davis MIND Institute researchers suggests that executive control differences in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be the result of a unique approach, rather than an impairment.
Executive control difficulties are common in individuals with autism and are associated with challenges completing tasks and managing time. The study, published in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, sought to tease out whether these difficulties represent a disruption in proactive executive control (engaged and maintained before a ...
Use of perovskite will be a key feature of the next generation of electronic appliances
2021-03-12
Quantum dots are manmade nanoparticles of semiconducting material comprising only a few thousand atoms. Because of the small number of atoms, a quantum dot's properties lie between those of single atoms or molecules and bulk material with a huge number of atoms. By changing the nanoparticles' size and shape, it is possible to fine-tune their electronic and optical properties - how electrons bond and move through the material, and how light is absorbed and emitted by it.
Thanks to increasingly refined control of the nanoparticles' size and shape, the number ...
Artificial intelligence calculates suicide attempt risk
2021-03-12
A machine learning algorithm that predicts suicide attempt recently underwent a prospective trial at the institution where it was developed, Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Over the 11 consecutive months concluding in April 2020, predictions ran silently in the background as adult patients were seen at VUMC. The algorithm, dubbed the Vanderbilt Suicide Attempt and Ideation Likelihood (VSAIL) model, uses routine information from electronic health records (EHRs) to calculate 30-day risk of return visits for suicide attempt, and, by extension, suicidal ideation.
Suicide has been on the rise in the U.S. for a generation ...
Association of acute symptoms of COVID-19, symptoms of depression in adults
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether acute COVID-19 symptoms are associated with the probability of subsequent depressive symptoms.
Authors: Roy H. Perlis, M.D., M.Sc., of the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3223)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
Well-child visits with out-of-pocket costs before, after ACA
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: National claims data were used to look at changes in well-child care visits with out-of-pocket costs before and after passage of the Affordable Care Act.
Authors: Paul R. Shafer, Ph.D., of Boston University, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1248)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
Association between preterm birth, psychotropic drug use in adolescence, young adulthood
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: Researchers compared rates of psychotropic drug prescriptions during adolescence and young adulthood between individuals born preterm and at term.
Authors: Christine S. Bachmann, M.D., of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology in Trondheim, Norway, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1420)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Poor survival after heart attack linked to excess levels of signaling protein in heart
2021-03-12
(Philadelphia, PA) - About 6.2 million Americans suffer from heart failure, an incurable disease with a staggering mortality rate - some 40 percent of patients die within five years of diagnosis. Heart failure is one form of heart disease, for which new therapies are desperately needed.
Now, in new work, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University identify a path to a promising novel therapeutic strategy, taking aim at a molecule in the heart known as G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5). In a study published online in the journal Cardiovascular Research, the scientists show in mice that reducing GRK5 levels can significantly improve survival ...
Astronomers detect a black hole on the move
2021-03-12
Scientists have long theorized that supermassive black holes can wander through space--but catching them in the act has proven difficult.
Now, researchers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian have identified the clearest case to date of a supermassive black hole in motion. Their results are published today in the Astrophysical Journal.
"We don't expect the majority of supermassive black holes to be moving; they're usually content to just sit around," says Dominic Pesce, an astronomer at the Center for Astrophysics who led the study. "They're just so heavy that it's tough to get them going. Consider how much more ...
Study uncovers clues to COVID-19 using imaging
2021-03-12
Since the pandemic hit, researchers have been uncovering ways COVID-19 impacts other parts of the body, besides the lungs.
Now, for the first time, a visual correlation has been found between the severity of the disease in the lungs using CT scans and the severity of effects on patient's brains, using MRI scans. This research is published in the American Journal of Neuroradiology. It will be presented at the 59th annual meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR) and has also been selected as a semifinalist for that organization's Cornelius Dyke Award.
The results show that by looking at lung CT scans of patients diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians may be able to predict just how badly they'll experience other ...
Yeast epigenome map reveals details of gene regulation
2021-03-12
ITHACA, N.Y. - A new Penn State and Cornell study describes an effort to produce the most comprehensive and high-resolution map yet of chromosome architecture and gene regulation in yeast, a major step toward improving understanding of development, evolution and environmental responses in higher organisms.
Specifically, the study mapped precise binding sites of more than 400 different chromosomal proteins in the yeast genome, most of which regulate the expression of genes.
Yeast cells provide a simple model system with 6,000 genes, most of which are found in other organisms, including humans, making them excellent candidates for studying fundamental genetics and complex biological pathways.
The paper, "A High-Resolution Protein Architecture of the Budding Yeast ...
Are there differences in the brains of autistic men and women?
2021-03-12
Around three times as many males are diagnosed with autism than females. This suggests that biological sex factors may play a role in the development and presentation of autism.
Studies on the neurobiology (brain biology) of males and females with autism have begun to examine brain networks but results have been mixed. This is largely due to the limited availability of data from autistic females.
In response, researchers from END ...
Extinction cascading through ecosystems could spell trouble for humans
2021-03-12
Humans rely on nature extensively for everything from food production to coastal protection, but those contributions might be more threatened than previously thought, according to new findings from the University of Colorado Boulder.
This research, out today in Nature Communications, looked at three different coastal food webs that include those services provided to humans, or ecosystem services, and found that even if the services themselves aren't directly threatened, they can become threatened when other species around them go extinct--often called secondary ...
Using AI to assess surgical performance
2021-03-12
More than one million operations are performed in Switzerland every year. A surgeon's skill has a direct impact on the outcome of the operation. Training and experience, as well as momentary fatigue and other influencing factors all play a role. At present, skill is tested by experts, either directly during an operation or by evaluating video footage. This approach is very costly and only a limited number of experts are available. Moreover, the assessment may vary and is not always fully reproducible. For some time, attempts have been made to automate and objectify the assessment of surgeons' skills.
Proof of feasibility
The key result of the study is the proof of the fundamental feasibility of an ...
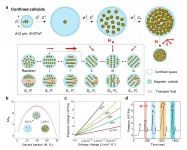
Confined magnetic colloidal system for controllable fluid transport
2021-03-12
Colloidal suspensions of microscopic particles show complex and interesting collective behaviors. In particular, the collective dynamics of colloids is fundamental and ubiquitous for materials assembly, robotic motion, microfluidic control, and in several biological scenarios. The collective dynamics of confined colloids can be completely different from that of free colloids: for instance, confined colloids can self-organize into vortex structures, coherent motion, or different phase behaviors. On one hand, due to the complexity of colloidal suspensions, how to finely tune the ...
New review explores effective sampling techniques for collecting airborne viruses and ultrafine part
2021-03-12
As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, an international team of researchers have published a review of the best techniques to collect airborne aerosols containing viruses.
In the review, which was published by the Science of the Total Environment journal, a team led by the University of Surrey concluded that the most effective way to collect and detect airborne pathogens, particularly viruses, was to use cyclone sampling techniques.
For example, the sampler draws the air through the cyclone separator. It then uses centrifugal forces to collect the particles on a sterile cone containing the liquid collection vessel, such as DMEM (Dulbecco's minimal essential ...
Shedding light on perovskite films
2021-03-12
Photovoltaics decisively contributes to sustainable energy supply. The efficiency of solar cells in directly converting light energy into electrical energy depends on the material used. Metal-halide perovskites are considered very promising materials for solar cells of the next generation. With these semiconductors named after their special crystal structure, a considerable increase in efficiency was achieved in the past years. Meanwhile, perovskite solar cells have reached an efficiency of up to 25.5 percent, which is quite close to that of silicon ...
New proteins 'out of nothing'
2021-03-12
Proteins are the key component in all modern forms of life. Haemoglobin, for example, transports the oxygen in our blood; photosynthesis proteins in the leaves of plants convert sunlight into energy; and fungal enzymes help us to brew beer and bake bread. Researchers have long been examining the question of how proteins mutate or come into existence in the course of millennia. That completely new proteins - and, with them, new properties - can emerge practically out of nothing, was inconceivable for decades, in line with what the Greek philosopher Parmenides said: "Nothing can emerge from nothing" (ex nihilo nihil fit). Working with colleagues from the USA and ...
Evaluating the rehabilitation of an old mine waste rock pile
2021-03-12
The Cabeza de los Gatos waste rock pile, left from mining activities in the town of Tharsis (Huelva), underwent a rehabilitation process consisting of remodelling the slope of the pile, applying liming materials and then a layer of soil. Finally, trees and shrubs typical of the area were planted and a hydroseeding with a mixture of shrub and herbaceous seeds was applied. Twelve years later, a study led by researchers from IRNAS-CSIC, in collaboration with Sabina Rossini Oliva, a researcher from the University of Seville and the Environment and Water Agency of Andalusia (AMAYA), has proven the effectiveness of this sort of rehabilitation.
"The results obtained show that the steps taken were successful. Now, ...
High emotional intelligence 'can help to identify fake news'
2021-03-12
People with high levels of emotional intelligence are less likely to be susceptible to 'fake news', according to research at the University of Strathclyde.
The study invited participants to read a series of news items on social media and to ascertain whether they were real or fictitious, briefly describing the reasons for their answers. They were also asked to complete a test to determine their levels of emotional intelligence (EQ or emotional quotient) and were asked a number of questions when considering the veracity of each news item.
Researchers found that those who identified the types of news correctly were most likely to score highly in the EQ tests. There was a similar correlation between correct identification and educational attainment.
The ...
Release of serotonin from mast cells contribute to airway hyperresposivness in asthma
2021-03-12
In asthma, the airways become hyperresponsive. Researchers from Uppsala University have found a new mechanism that contributes to, and explains, airway hyperresponsiveness. The results are published in the scientific journal Allergy.
Some 10 per cent of Sweden's population suffer from asthma. In asthmatics, the airways are hyperresponsive (overreactive) to various types of stimuli, such as cold air, physical exertion and chemicals. The airways become constricted, making breathing difficult.
To diagnose asthma, a "methacholine test" is commonly used to determine whether a person is showing signs of airway hyperresponsiveness. Methacholine binds to what are known as muscarinic receptors in the smooth muscle cells lining the inside ...
'Magical' fire suppressant kills zombie fires 40% faster than water alone
2021-03-12
The researchers say this is a big step in tackling smouldering peat fires, which are the largest fires on Earth. They ignite very easily, are notoriously difficult to put out, and release up to 100 times more carbon into the atmosphere than flaming fires, contributing to climate change.
The fires, known as 'zombie fires' for their ability to hide and smoulder underground and then reanimate as new flames days or weeks after the wildfire had been extinguished, are prevalent in regions like Southeast Asia, North America, and Siberia.
They are driven by the burning of soils rich in organic content like peat, which is a large natural reservoir of carbon. Worldwide, peat fires account for millions of tonnes of carbon released into the atmosphere each year.
Firefighters currently use millions ...
Beyond genes and environment, random variations play important role in longevity
2021-03-12
A new model of aging takes into account not only genetics and environmental exposures but also the tiny changes that randomly arise at the cellular level.
University Professor Caleb Finch introduced the "Tripartite Phenotype of Aging" as a new conceptual model that addresses why lifespan varies so much, even among human identical twins who share the same genes. Only about 10 to 35 percent of longevity can be traced to genes inherited from our parents, Finch mentioned.
Finch authored the paper introducing the model with one of his former graduate students, Amin Haghani, who received his PhD in the Biology of Aging from the USC ...
New clinical method could lower risk of recurring heart attacks
2021-03-12
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden can now show that a new examination method identifies high-risk plaques in the blood vessels surrounding the heart, that cannot be seen solely with traditional angiograms. This type of plaque, rich in fat, could potentially cause recurring heart attacks in patients with heart disease. The study is published in the The Lancet.
"We have been working on this study for ten years. This creates a unique opportunity to treat plaques before they cause a heart attack", says David Erlinge, professor of cardiology at Lund University and Consultant in ...
[1] ... [2536]
[2537]
[2538]
[2539]
[2540]
[2541]
[2542]
[2543]
2544
[2545]
[2546]
[2547]
[2548]
[2549]
[2550]
[2551]
[2552]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.