(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL - A new study of young U.S. veterans shows that the probability of having a high risk of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) increased with increasing severity of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms.
The study involved 195 Iraq and Afghanistan veterans who visited a VA outpatient PTSD clinic for evaluation. Results show that 69.2 percent of participants had a high risk for sleep apnea, and this risk increased with PTSD symptom severity. Every clinically significant increase in PTSD symptom severity was associated with a 40 percent increase in the probability of screening as high risk for sleep apnea.
"The implication is that veterans who come to PTSD treatment, even younger veterans, should be screened for obstructive sleep apnea so that they have the opportunity to be diagnosed and treated," said co-principal investigator Sonya Norman, PhD, researcher at the San Diego VA, director of the PTSD Consultation Program at the National Center for PTSD, and an associate professor of psychiatry at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. "This is critical information because sleep apnea is a risk factor for a long list of health problems such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease and diabetes, and psychological problems including depression, worsening PTSD and anxiety."
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine reports that obstructive sleep apnea is a common sleep disease afflicting at least 25 million adults in the U.S. Sleep apnea warning signs include snoring and choking, gasping or silent breathing pauses during sleep. The AASM and other partners in the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project, which is funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, urge anyone with symptoms of sleep apnea to visit http://www.stopsnoringpledge.org to pledge to "Stop the Snore" by talking to a doctor.
The study idea was initiated by Tonya Masino, MD, who was the first to recognize that a surprising number of younger veterans who were coming to the clinic for PTSD treatment also were presenting with sleep apnea symptoms. Study results are published in the May 15 issue of the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
Ninety-three percent of study participants were men, and their mean age was 33 years. Sleep apnea risk was evaluated using the Berlin Questionnaire, and PTSD was assessed using the PTSD Checklist Stressor Specific Version (PCL-S) questionnaire. Analyses controlled for potential confounders such as older age, smoking status, and use of central nervous system depressants.
According to the authors, younger veterans with PTSD are rarely screened for sleep apnea and frequently remain undiagnosed. They noted that the mechanism underlying the relationship between sleep apnea and PTSD in military veterans is unclear. However, potential factors that may connect the two disorders include disturbed sleep in combat, prolonged sleep deprivation, sleep fragmentation and hyperarousal due to the physical and psychological stressors of combat, the chronic stress from PTSD, or the sleep disturbances caused by OSA. Longitudinal studies are needed to examine the temporal relationship between sleep apnea and PTSD.
The study was led by Norman and co-principal investigator Abigail Angkaw, PhD. The lead author of the study is Peter Colvonen, PhD.
According to the National Center for PTSD of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, PTSD symptoms such as nightmares or flashbacks usually start soon after a traumatic event, but they may not appear until months or years later. Symptoms that last longer than four weeks, cause great distress or interfere with daily life may be a sign of PTSD. To get help for PTSD, veterans can call the Veterans Crisis Line at 1-800-273-8255 and press 1, text 838255, contact a local VA Medical Center, or use the online PTSD program locator on the VA website.
INFORMATION:
To request a copy of the study, "Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder among OEF/OIF/OND Veterans," or to arrange an interview with the study author or an AASM spokesperson, please contact Communications Coordinator Lynn Celmer at 630-737-9700, ext. 9364, or lcelmer@aasmnet.org.
The monthly, peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine is the official publication of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, a professional membership society that improves sleep health and promotes high quality patient centered care through advocacy, education, strategic research, and practice standards (http://www.aasmnet.org). The AASM encourages patients to talk to their doctor about sleep problems or visit http://www.sleepeducation.org for a searchable directory of AASM-accredited sleep centers.
WASHINGTON, D.C., May 19, 2015 -- Playing natural sounds such as flowing water in offices could boosts worker moods and improve cognitive abilities in addition to providing speech privacy, according to a new study from researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. They will present the results of their experiment at the 169th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, held May 18-22, 2015 in Pittsburgh.
An increasing number of modern open-plan offices employ sound masking systems that raise the background sound of a room so that speech is rendered unintelligible ...
Children born since the 1980s are two to three times more likely than older generations to be overweight or obese by the age of 10, according to new research published in PLOS Medicine. The study, conducted by researchers from CLOSER, a consortium of UK longitudinal studies, characterized population shifts in body mass index (BMI) using data from more than 56,000 people born in Britain from 1946 to 2001.
The findings will be relevant to policymakers and health care professionals, who predict the obesity epidemic will cost the UK's National Health Service (NHS) £22.9 ...
Large-scale screening for diabetes in India using currently available survey- and glucometer- based screening tools is unlikely to meet effectiveness criteria, according to a modeling study published this week in PLOS Medicine. The predictions of this simulation, conducted by Sanjay Basu of Stanford University and colleagues, suggest that large numbers of false positive results would waste financial resources, and that focusing on symptom-based screening and on improvements to diabetes treatment might better serve India's population.
Diabetes is becoming increasingly ...
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have identified the role of an enzyme in muscle wasting, and associated age-related problems. They believe that inhibiting it could hold the key to developing ways of preventing, or reversing, the adverse effects.
The research, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, is a significant step in understanding the role played by the enzyme '11β-HSD1' in the degenerative effects of ageing - including sarcopenia (age related muscle wasting).
The expression of 11β-HSD1, responsible for activating ...
Use of cholesterol lowering drugs is associated with a one third lower risk of stroke in older adults without previous disease, finds a study published in The BMJ this week.
In high income countries, a growing proportion of heart disease and stroke occur in the oldest people. In France, for instance, people aged 85 years and over accounted for 43% of deaths from coronary heart disease and 49% of deaths from stroke in 2010.
Yet very few people over the age of 70 take part in trials testing cardiovascular drugs, so their benefit in the oldest people remains uncertain. ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study in animals suggests that skipping meals sets off a series of metabolic miscues that can result in abdominal weight gain.
In the study, mice that ate all of their food as a single meal and fasted the rest of the day developed insulin resistance in their livers - which scientists consider a telltale sign of prediabetes. When the liver doesn't respond to insulin signals telling it to stop producing glucose, that extra sugar in the blood is stored as fat.
These mice initially were put on a restricted diet and lost weight compared to controls ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Many of those who should get it, don't. And many of those who shouldn't, do. That's the story of a common screening test for osteoporosis, according to new research from UC Davis Health System.
The study, published online today in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, found that screening rates increased sharply among women at age 50, despite guidelines suggesting screening at age 65 unless risk factors are present. The presence of risk factors only had a modest influence on screening decisions.
Osteoporosis causes bone density to diminish ...
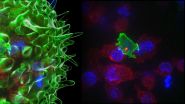
A dramatic video has captured the behaviour of cytotoxic T cells - the body's 'serial killers' - as they hunt down and eliminate cancer cells before moving on to their next target.
In a study published today in the journal Immunity, a collaboration of researchers from the UK and the USA, led by Professor Gillian Griffiths at the University of Cambridge, describe how specialised members of our white blood cells known as cytotoxic T cells destroy tumour cells and virally-infected cells. Using state-of-the-art imaging techniques, the research team, with funding from the ...
Decades' worth of textbook precepts about how our immune systems manage to avoid attacking our own tissues may be wrong.
Contradicting a long-held belief that self-reactive immune cells are weeded out early in life in an organ called the thymus, a new study by Stanford University School of Medicine scientists has revealed that vast numbers of these cells remain in circulation well into adulthood.
"This overturns 25 years of what we've been teaching," said Mark Davis, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology and director of Stanford's Institute for Immunity, Transplantation ...
Scientists are reporting development of a new way to modify interleukin-2 (IL-2), a substance known as a cytokine that plays key roles in regulating immune system responses, in order to fine-tune its actions. Harnessing the action of IL-2 in a controllable fashion is of clinical interest with potential benefit in a range of situations, including transplantation and autoimmune disease. The modified IL-2 molecules inhibited the actions of endogenous IL-2, potentially more effectively than existing agents, as well as inhibited the actions of another interleukin, IL-15, with ...