Strict environmental laws 'push' firms to pollute elsewhere
2021-03-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Multinational companies headquartered in countries with tougher environmental policies tend to locate their polluting factories in countries with more lax regulations, a new study finds.
While countries may hope their regulations will reduce emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, these results show that these policies can lead to "carbon leakage" to other nations, said Itzhak Ben-David, co-author of the study and professor of finance at The Ohio State University's Fisher College of Business.
"Firms decide strategically where to locate their production based ...
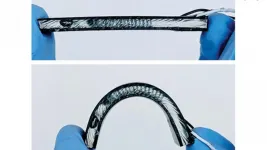
Reduced heat leakage improves wearable health device
2021-03-08
North Carolina State University engineers continue to improve the efficiency of a flexible device worn on the wrist that harvests heat energy from the human body to monitor health.
In a paper published in npj Flexible Electronics, the NC State researchers report significant enhancements in preventing heat leakage in the flexible body heat harvester they first reported in 2017 and updated in 2020. The harvesters use heat energy from the human body to power wearable technologies - think of smart watches that measure your heart rate, blood oxygen, glucose and other health parameters - that never need to have their batteries recharged. The technology relies on the same principles ...
Allelica's polygenic risk score data published in <i>Circulation</i>
2021-03-08
Rome, Italy, March 8, 2021 - Allelica, a leading genomics software company specialising in developing polygenic risk scores (PRS) for personalised medicine, today announced publication of a study in Circulation (Vol. 143, Issue 10) showing that the effect of LDL cholesterol on a person's risk of having a heart attack depends on their genes. Using Allelica's proprietary PRS analysis software, the data showed that combining information on an individual's genetic risk of heart attack with their LDL level helps determine those at most risk from heart attack, including those potentially in need of treatment with statins or PCSK9 inhibitors. The PRS was also able to identify individuals eligible for therapeutic intervention based on current ...
Irrigation management key for bioenergy production to mitigate climate change
2021-03-08
To avoid a substantial increase in water scarcity, biomass plantations for energy production need sustainable water management, a new study shows. Bioenergy is frequently considered one of the options to reduce greenhouse gases for achieving the Paris climate goals, especially if combined with capturing the CO2 from biomass power plants and storing it underground. Yet growing large-scale bioenergy plantations worldwide does not just require land, but also considerable amounts of freshwater for irrigation - which can be at odds with respecting Earth's ...
Diphtheria risks becoming major global threat again as it evolves antimicrobial resistance
2021-03-08
Diphtheria - a relatively easily-preventable infection - is evolving to become resistant to a number of classes of antibiotics and in future could lead to vaccine escape, warn an international team of researchers from the UK and India.
The researchers, led by scientists at the University of Cambridge, say that the impact of COVID-19 on diphtheria vaccination schedules, coupled with a rise in the number of infections, risk the disease once more becoming a major global threat.
Diphtheria is a highly contagious infection that can affect the nose and throat, and sometimes the skin. If left untreated it can prove fatal. In the UK and other high-income countries, babies are vaccinated against ...
Cardiac arrest from opioid overdose has unique features affecting prevention and treatment
2021-03-08
DALLAS, March 8, 2021 -- Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests triggered by opioid overdose are a significant cause of death among adults 25 to 64, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, the nation's largest voluntary health organization focused on heart and brain health for all. The statement published today in the Association's flagship journal Circulation.
In the U.S., opioid use disorder affects an estimated 2 million people each year and costs more than $78 billion in health care expenses. The opioid epidemic, ...
Stroke affecting the eye requires immediate treatment, can signal future vascular events
2021-03-08
DALLAS, March 8, 2021 - While most people think of strokes affecting the brain, they can also affect the eye. Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a rare form of acute ischemic stroke that occurs when blood flow is blocked to the main artery of the eye. It typically causes painless, immediate vision loss in the impacted eye, with fewer than 20% of people regaining functional vision in that eye.
Today, the American Heart Association published a new scientific statement, "Management of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion," in Stroke, an American Heart Association ...
Immune cells in cerebrospinal fluid predict response to immunotherapy
2021-03-08
The analysis of immune cells infiltrating cerebrospinal fluid enables the characterization of the tumor microenvironment in brain metastases.
Findings reported today in Nature Communications* confirm that these cells recapitulate the characteristics of those detected in brain metastases, and could act as novel and non-invasive biomarkers to predict patient responsiveness to immune-based therapies.
Results from a study led by Joan Seoane, Director of Preclinical and Translational Research co-program at VHIO and ICREA Professor, show that immune cells accessing cerebrospinal fluid faithfully recapitulate the characteristics of cells identified in brain metastasis, and could therefore constitute novel ...
Virtual avatar coaching with community context for adult-child dyads
2021-03-08
Philadelphia, March 8, 2021 - Virtual reality avatar-based coaching shows promise to increase access to and extend the reach of nutrition education programs to children at risk for obesity, according to a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier.
Researchers introduced 15 adult-child dyads to a virtual avatar-based coaching program that incorporated age-specific information on growth; physical, social, and emotional development; healthy lifestyles; common nutrition concerns; and interview questions around eating behaviors and food resources and counseling.
"We developed a virtual reality avatar computer program ...
Globalization of cancer clinical trials linked to lower enrollment of Black patients
2021-03-08
For the drug approval process in the United States, investigators have been expanding clinical trials to sites outside the country. However, a new study indicates that this trend may be widening racial disparities in patient enrollment in cancer clinical trials. The study is published by Wiley early online in END ...
Drug to treat hypoactive sexual desire disorder in women of 'very limited use'
2021-03-08
An independent analysis of the medical trials which formed the final basis of approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) strongly suggests the drug bremelanotide has very limited effectiveness as a treatment for hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in women, and that trial participants preferred a placebo.
The analysis, published today in the peer-reviewed Journal of Sex Research, also highlights issues with the validity of HSDD as a diagnosis. The condition was removed from the American Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) in 2013.
Professor Glen Spielmans, of Metropolitan State University, USA, examined data from bremelanotide's FDA New Drug Application, ...
Investigating youth suicides among children involved with the welfare system
2021-03-08
Suicide is the second leading cause of death among youth aged 5 to 21 years in the United States. Between 2010 and 2019, suicide rates among this group increased 40%.
Youth involved in the child welfare system experience an even greater risk of suicidal behavior, yet research on this vulnerable population is minimal.
To better understand and prevent suicide in this at-risk group, researchers at Nationwide Children's Hospital conducted the first study to compare characteristics and health service utilization patterns of youth suicide decedents (those ...
Study suggests wearing a face mask during intense exercise is safe for healthy people
2021-03-08
Wearing a protective face mask has only a modest effect on the ability of healthy people to do vigorous exercise, according to a study published today (Monday) in the European Respiratory Journal [1].
Researchers carried out detailed testing on breathing, heart activity and exercise performance in a group of 12 people while they were using an exercise bike with and without a mask.
Although they found differences in some measurements between wearing a mask and not wearing a mask, they say that none of their results indicate any risk to health. This suggests that masks could be worn safely during intense exercise, for example to reduce COVID-19 transmission between ...
One size doesn't fit all when it comes to products for preventing HIV from anal sex
2021-03-06
The initial insights from the study, aptly named DESIRE (Developing and Evaluating Short-acting Innovations for Rectal Use), are being reported on March 6 in a Science Spotlight session at the virtual meeting of the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), March 6-10. The presentation will be available for registered participants and media to view throughout the meeting.
Conducted by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded Microbicide Trials Network (MTN), DESIRE focused on potential delivery methods for rectal microbicides - topical products being developed and tested to reduce ...
"Magic sand" might help us understand the physics of granular matter
2021-03-06
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have studied the properties of mixtures of silicone-coated "magic sand", a popular kid's toy, and normal sand. Silicone-coated sand particles were found to interact with each other only, and not with other sand particles. The team discovered that adding silicone-coated sand beyond a certain threshold leads to an abrupt change in clustering and rigidity, a simple, useful way to potentially tune the flow of granular materials for industry.
Sand is a fascinating material. It can flow and be poured like a liquid, ...
WRAIR, Duke scientists find evidence of monoclonal antibodies activity against malaria
2021-03-05
Scientists at Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, in a collaboration with Duke University, have confirmed that monoclonal antibodies can be an effective tool in the global fight against malaria.
The study, led by Dr. Sheetij Dutta, chief of the Structural Vaccinology Laboratory at WRAIR, showed that mAbs such as CIS43 were most effective in a culture-based assay that measured malaria parasites' ability to infect a human liver cell, while another mAb 317 showed the best activity in a mouse infection model. Dutta added "difference in assay outcomes for mAbs could reflect distinct sites on the circumsporozoite protein that can be exploited for developing improved vaccines." The ...
Physics camp has proven benefits for high school girls
2021-03-05
HOUSTON - (March 5, 2021) - Even a small effort up front can boost the abilities and confidence of girls as they anticipate taking challenging science courses.
A long-running summer program at Rice University and elsewhere that trains high school girls in basic physics concepts has proven successful in helping them thrive when they take on full courses the next year.
When leaders of Rice's two-week day camp looked at similar programs beyond Houston, they found participants scored 3% better in high school physics than their counterparts who did not have the equivalent summer experience.
"That doesn't seem like a lot, but it's really hard to move the needle on student outcomes, so 3% is significant," said Carolyn Nichol, an assistant ...
With unfair police treatment, the tragedy is not limited to the incident itself
2021-03-05
BUFFALO, N.Y. - New research using a nationally representative sample of more than 12,000 participants shows the collateral consequences victims are likely to confront following unfair treatment by police.
Michael Brown, George Floyd and Tamir Rice are just some of those who have died recently at the hands of police.
Their names are now tragically familiar, but thousands of other people who are unjustly stopped, searched or questioned by law enforcement will likely experience a range of detrimental outcomes associated with unfair police treatment, including depression, suicidal thoughts, drug use, and a loss of self-efficacy, according to Christopher ...
Building networks not enough to expand rural broadband
2021-03-05
ITHACA, N.Y. - Public grants to build rural broadband networks may not be sufficient to close the digital divide, new Cornell University research finds.
High operations and maintenance costs and low population density in some rural areas result in prohibitively high service fees - even for a subscriber-owned cooperative structured to prioritize member needs over profits, the analysis found.
Decades ago, cooperatives were key to the expansion of electric and telephone service to underserved rural areas, spurred by New Deal legislation providing low-interest government grants and loans. Public funding for rural ...
Rapid 3D printing method moves toward 3D-printed organs
2021-03-05
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- It looks like science fiction: A machine dips into a shallow vat of translucent yellow goo and pulls out what becomes a life-sized hand.
But the seven-second video, which is sped-up from 19 minutes, is real.
The hand, which would take six hours to create using conventional 3D printing methods, demonstrates what University at Buffalo engineers say is progress toward 3D-printed human tissue and organs -- biotechnology that could eventually save countless lives lost due to the shortage of donor organs.
"The technology we've developed is 10-50 times faster than the industry standard, and it works with large ...
Online dating: Super effective, or just... superficial?
2021-03-05
According to the Pew Research Center, 1 in 10 American adults have landed a long-term relationship from an online dating app, such as Tinder, OKCupid and Match.com. But what compels people to "swipe right" on certain profiles and reject others?
New research from William Chopik, an associate professor in the Michigan State University Department of Psychology, and Dr. David Johnson from the University of Maryland, finds that people's reason for swiping right is based primarily on attractiveness and the race of a potential partner, and that decisions are often made in less than a second.
"Despite online dating becoming an increasingly popular way for people to meet one another, ...
New 'split-drive' system puts scientists in the (gene) driver seat
2021-03-05
Powerful new genetic engineering methods have given scientists the potential to revolutionize several sectors of global urgency.
So-called gene drives, which leverage CRISPR technology to influence genetic inheritance, carry the promise of rapidly spreading specific genetic traits throughout populations of a given species. Gene-drive technologies applied in insects, for example, are being designed to halt the spread of devastating diseases such as malaria and dengue by preventing mosquito hosts from becoming infected. In agricultural fields, gene-drives are being developed to help control or eliminate economically ...
Survey identifies factors in reducing clinical research coordinator turnover
2021-03-05
Strong, collaborative relationships with principal investigators are a key factor of longevity in clinical research coordinator positions -- an essential, but increasingly transient job in executing treatment-advancing clinical trials, Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers found.
Danielle Buchanan, BS, clinical translational research coordinator III in the Department of Neurology, and Daniel Claassen, MD, MS, chief of the Division of Cognitive Disorders and associate professor of Neurology, found the top factor for retention is a close working relationship between clinical research coordinators (CRCs) and the study's principal investigator that emphasizes respect and collaboration. Salary followed as the next factor for retention among 85 former or current CRCs who responded to ...
Study reveals how egg cells get so big
2021-03-05
Egg cells are by far the largest cells produced by most organisms. In humans, they are several times larger than a typical body cell and about 10,000 times larger than sperm cells.
There's a reason why egg cells, or oocytes, are so big: They need to accumulate enough nutrients to support a growing embryo after fertilization, plus mitochondria to power all of that growth. However, biologists don't yet understand the full picture of how egg cells become so large.
A new study in fruit flies, by a team of MIT biologists and mathematicians, reveals that the process through which the oocyte ...
Vision impairment is associated with mortality
2021-03-05
The global population is aging, and so are their eyes. In fact, the number of people with vision impairment and blindness is expected to more than double over the next 30 years. ...
[1] ... [2565]
[2566]
[2567]
[2568]
[2569]
[2570]
[2571]
[2572]
2573
[2574]
[2575]
[2576]
[2577]
[2578]
[2579]
[2580]
[2581]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.