(Press-News.org) DANVILLE, Pa. and GAITHERSBURG, Md. - Researchers have discovered a strong link between genetic changes known to cause neurodevelopmental disabilities and cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy affects movement and posture and often co-occurs with other neurodevelopmental disorders, including intellectual disability, epilepsy and autism spectrum disorder. Individual cases of cerebral palsy are often attributed to birth asphyxia, although recent studies indicate that asphyxia accounts for less than 10% of cases. A growing body of research indicates that cerebral palsy may be caused by genetic changes, as is the case in other neurodevelopmental disorders.
The research team, which included investigators from Geisinger and GeneDx Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of BioReference Laboratories Inc., an OPKO Health company and global leader in genetic diagnostics, studied the DNA sequence of 1,526 children and adults with cerebral palsy. The team found disease-causing changes in 229 genes, several of which have been previously identified in people with both cerebral palsy and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Disease-causing genetic changes were found in 32.7% of a primarily pediatric group of patients from GeneDx and in 10.5% of a primarily adult group from Geisinger.
"Finding a genetic cause for cerebral palsy not only provides an answer to the family, but also informs recurrence risk estimates for future children born to the same parents," said Christa Martin, Ph.D., senior co-author of the study and professor and director of Geisinger's Autism & Developmental Medicine Institute.
"Previous studies in families with children with CP have found a risk of recurrence of 1-2%. Identifying a genetic change that causes the CP in a child and is not present in either parent decreases the risk to less than 1% for future children born to the same parents. When the genetic change that causes CP is inherited from one or both of the parents, that risk increases to 50% and 25%, respectively," Martin said.
"At GeneDx, we were able to test three-fourths of patients along with both parents, allowing us to establish the inheritance of the genetic changes," said Francisca Millan, M.D., co-first author of the study and associate director of neurogenetics at GeneDx. "For approximately a third of the families where a causative genetic change was identified, the family recurrence risk increased to 25% to 50%."
The identification of these genetic changes in multiple patients and replication of these findings across different settings and cohort types provided strong evidence for their role in cerebral palsy, the research team wrote. The findings were published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
"DNA sequencing is recommended as a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders, which are known to co-occur with cerebral palsy," said Andres Moreno De Luca, M.D., physician-scientist and clinical neuroradiologist at Geisinger and co-first author of the study. "Since cerebral palsy can be identified earlier than other neurodevelopmental disorders, such as intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder, genetic testing for individuals with cerebral palsy may allow for quicker identification of genetic changes and facilitate early interventions and treatment."
"This study re-iterates the value of genetic testing for neurodevelopmental disorders and highlights the utility of genetic testing for cerebral palsy patients," said Kyle Retterer, senior co-author of the study and senior vice president and chief technology officer at GeneDx. "Increasing utilization of and access to DNA sequencing for these patients will lead to earlier diagnoses and improved care in many cases."
INFORMATION:
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institute of Mental Health.
About Geisinger
Geisinger is committed to making better health easier for the more than 1 million people it serves. Founded more than 100 years ago by Abigail Geisinger, the system now includes nine hospital campuses, a 550,000-member health plan, two research centers and the Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. With nearly 24,000 employees and more than 1,600 employed physicians, Geisinger boosts its hometown economies in Pennsylvania by billions of dollars annually. Learn more at geisinger.org or connect with us on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and Twitter.
About GeneDx, Inc.
GeneDx, Inc. is a global leader in genomics, providing testing to patients and their families from more than 55 countries. Led by its world-renowned clinical genomics program, GeneDx has an acknowledged expertise in rare and ultra-rare genetic disorders, as well as one of the broadest menus of sequencing services available among commercial laboratories. GeneDx offers a suite of additional genetic testing services, including diagnostic testing for hereditary cancers, cardiac, mitochondrial, neurological disorders, prenatal diagnostics and targeted variant testing. GeneDx is a subsidiary of BioReference Laboratories, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of OPKO Health, Inc. To learn more, please visit http://www.genedx.com.
BOSTON -- Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have typically excluded diverse and minority individuals in the search for gene variants that confer risk of disease. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and other institutions around the world have now developed a free-access software package called Tractor that increases the discovery power of genomics in understudied populations. A study of Tractor's performance and accuracy was published in END ...
New research has found that men who have the Western world's most common genetic disorder are more likely to develop dementia, compared to those without the faulty genes.
Researchers at the University of Exeter and the University of Connecticut have previously found that men with two faulty genes that cause the iron overload condition haemochromatosis are more likely to develop liver cancer, arthritis and frailty, compared to those without the faulty genes.
Now, the team's new analysis of more than 335,000 people of European ancestry in UK Biobank, ...
WASHINGTON, February 2, 2021 -- Scientists are hoping advances in cancer research could lead to a day when a patient's own immune system could be used to fight and destroy a wide range of tumors.
Cancer immunotherapy has some remarkable successes, but its effectiveness has been limited to a relatively small handful of cancers. In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, a team from Stanford University and Genentech describes how advances in engineering models of tumors can greatly expand cancer immunotherapy's effectiveness to a wider range of cancers.
"One of the biggest breakthroughs we've had in cancer research in decades is that we can modify the cells in your own immune system to make them kill cancer cells," said author Joanna Lee.
Using ...
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Feb. 2, 2021) -- What does bile acid production in the digestive tract have to do with Parkinson's disease?
Quite a lot, according to a sweeping new analysis published in the journal Metabolites. The findings reveal that changes in the gut microbiome -- the rich population of helpful microbes that call the digestive tract home -- may in turn alter bile acid production by favoring synthesis of toxic forms of the acids.
These shifts were seen only in people with Parkinson's and not in healthy controls, a critical difference that suggests bile acids may be a viable biomarker for diagnosing Parkinson's early and tracking its progression. The insights also may provide new avenues for developing therapies ...
Colorectal cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality among men and women in the United States, according to the American Cancer Society. At-home tests, which measure blood in stool as a potential marker for colon cancer, are often used for colorectal cancer screening.
Usage of these tests has increased during the COVID-19 pandemic as people try to avoid clinical visits. However, effectiveness of these screening tools, along with all colon cancer screenings, requires a follow-up colonoscopy if an abnormal test result occurs. The problem is ...
Researchers at the George Washington University and University of California, Los Angeles, have developed and demonstrated for the first time a photonic digital to analog converter without leaving the optical domain. Such novel converters can advance next-generation data processing hardware with high relevance for data centers, 6G networks, artificial intelligence and more.
Current optical networks, through which most of the world's data is transmitted, as well as many sensors, require a digital-to-analog conversion, which links digital systems synergistically to analog components.
Using a silicon photonic chip platform, Volker J. Sorger, an associate professor of electrical and computer ...
DeKalb, Ill. -- If you build it, they might not come. That's the key finding of a END ...
DENVER (Feb. 2, 2021) - Jongeun You, a researcher at the University of Colorado Denver, recently END ...
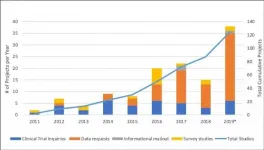
Amsterdam, February 2, 2021 - The Canadian Neuromuscular Disease Registry (CNDR) was launched in 2010 to increase efficient patient access to cutting-edge research and clinical trials, to increase understanding of the natural history and epidemiology of neuromuscular disease across Canada, and to facilitate research collaboration. An assessment of CNDR's accomplishments, published in the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, found that it has been successful in securing funding and engaging the community over the past 10 years. With more than 4,000 enrolled patients, data from the registry have been used in over 125 research projects as of 2019, including clinical trial and research notifications, patient questionnaires, and data analyses around ...
The mesmerizing flow of a sidewinder moving obliquely across desert sands has captivated biologists for centuries and has been variously studied over the years, but questions remained about how the snakes produce their unique motion. Sidewinders are pit vipers, specifically rattlesnakes, native to the deserts of the southwestern United State and adjacent Mexico.
Scientists had already described the microstructure of the skin on the ventral, or belly, surface of snakes. Many of the snakes studied, including all viper species, had distinctive rearward facing "microspicules" (micron-sized protrusions on scales) that had been interpreted in the context of reducing ...