Treating rheumatoid arthritis with micromotors
2021-02-24
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder marked by joint pain, swelling and damage. Although medications, such as steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants, can help slow joint destruction and relieve pain, they have side effects and aren't completely successful. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have developed magnesium-based micromotors propelled by hydrogen bubbles, which improved rheumatoid arthritis symptoms when injected into the joints of rats.
Scientists have linked rheumatoid arthritis development to the excess production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can oxidize and degrade cartilage and bone, as well as activate the expression of inflammatory cytokines. A new type of therapy, hydrogen gas, can neutralize ROS ...
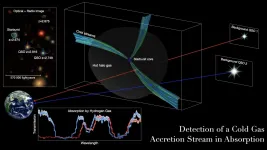
Researchers detect cold gas pipelines feeding early, massive galaxies
2021-02-24
To come into being, galaxies need a steady diet of cold gases to undergo gravitational collapse. The larger the galaxy, the more cold gas it needs to coalesce and to grow.
Massive galaxies found in the early universe needed a lot of cold gas--a store totaling as much as 100 billion times the mass of our sun.
But where did these early, super-sized galaxies get that much cold gas when they were hemmed in by hotter surroundings?
In a new study, astronomers led by the University of Iowa report direct, observational evidence of streams of cold gas they believe provisioned these early, massive galaxies. They detected cold gas pipelines that knifed through the hot atmosphere in the dark matter halo of an early massive galaxy, supplying the materials ...
Evidence that Earth's first cells could have made specialized compartments
2021-02-24
New research by the University of Oslo provides evidence that the "protocells" that formed around 3.8 billion years ago, before bacteria and single-celled organisms, could have had specialized bubble-like compartments that formed spontaneously, encapsulated small molecules, and formed "daughter" protocells.
ROCKVILLE, MD - Scientists have long speculated about the features that our long-ago single-celled ancestors might have had, and the order in which those features came about. Bubble-like compartments are a hallmark of the superkingdom to which we, and many other species including yeast, belong. But the cells in today's superkingdom have a host of specialized molecules that help make and shape these bubbles inside our ...
One-third of cancer survivors worried about treatment and healthcare disruptions during the pandemic
2021-02-24
ATLANTA - FEBRUARY 24, 2021 - New study reports that early in the 2020 pandemic in the United States, one-third of cancer survivors worried about treatment and cancer care disruptions. Using a mixed methods approach, investigators utilized survivors' own words to more deeply describe their experiences and worries about the pandemic's impact on their overall health.
The article, appearing in the Journal of Psychosocial Oncology, finds the impact of the pandemic on cancer survivors and the broader health care system is widespread and exacerbated serious gaps in the health care system. For this study, investigators led by Corinne Leach, MPH, MS, PhD, from the American ...
Jumping frost crystals: Boreyko lab works toward electrostatic de-icing
2021-02-24
If you have ever gotten up on a winter morning and thrown yourself into the arduous task of scraping frost from a windshield, a Virginia Tech lab is engaging science [IS1] that could make your life much easier. In research funded by the National Science Foundation, Associate Professor END ...
Older women who ate more plant protein had lower risk of premature, dementia-related death
2021-02-24
DALLAS, Feb. 24, 2021 -- Postmenopausal women who ate high levels of plant protein had lower risks of premature death, cardiovascular disease and dementia-related death compared with women who ate less plant proteins, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
Previous research has shown an association between diets high in red meat and cardiovascular disease risk, yet the data is sparse and inconclusive about specific types of proteins, the study authors ...
International team identifies 127 glaucoma genes in largest study of its kind
2021-02-24
In the largest genome-wide association study of glaucoma comparing the genes of 34,179 people with the disease to 349,321 control subjects, an international consortium of researchers identified 44 new gene loci and confirmed 83 previously reported loci linked to glaucoma. Loci are considered "genetic street addresses," denoting a specific location on a gene.
The study's authors hope the identification of these genes will lead to new treatment targets for this incurable eye disease that is a leading cause of blindness worldwide.
"These new findings come out of the highest-powered genome-wide association study of glaucoma to date, and show the power of team science and using big data to answer questions when research groups around the world join forces," said co-senior study author ...
Sound-frequency map for inner ear created with advanced X-ray technology
2021-02-24
Peer review/Experimental study/Cells
Researchers at Uppsala University have created the first 3D map of the hearing nerve showing where the various sound frequencies are captured. Using what is known as synchrotron X-ray imaging, they were able to trace the fine nerve threads and the vibrating auditory organ, the cochlea, and find out exactly how the frequencies of incoming sound are distributed. The study is published in Scientific Reports.
"This can make treatment with cochlea implants for the hearing-impaired more effective," says Helge Rask-Andersen, Professor of Experimental Otology at Uppsala ...
Open data on malaria genomes will help combat drug resistance
2021-02-24
Genome variation data on more than 7,000 malaria parasites from 28 endemic countries is released today (24 February) in Wellcome Open Research. It has been produced by MalariaGEN, a data-sharing network of groups around the world who are working together to build high-quality data resources for malaria research and disease control.
This open data release represents the world's largest resource of genomic data on malaria parasite evolution and drug resistance. It provides benchmark data on parasite genome variation that is needed in the search for new drugs and vaccines, and in the development of surveillance tools for malaria control and elimination.
Malaria is a major global ...
„Fat jam" in the cell
2021-02-24
In the journal Nature Communications, scientists of the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) report new findings on the mechanisms of "Niemann-Pick type C disease" (NPC). This rare brain disorder mainly manifests in childhood and includes severe neurological and psychiatric symptoms. Researchers led by Dr. Sabina Tahirovic have now found evidence that already at an early stage, NPC is associated with neuroinflammation and that this condition is triggered by impaired intracellular lipid transport. In addition, they identified pathological features in the blood of affected individuals that in the future could assist to better monitor the course of the disease and response to therapy.
NPC is a hereditary metabolic disorder ...
One in five people in south London live with multiple long-term conditions
2021-02-24
New research has found one in five people in the south London live with multimorbidity.
The study, published today in the Lancet Regional Health by researchers from King's College London and the NIHR Guy's and St Thomas' Biomedical Research Centre and supported by Impact on Urban Health, examined the prevalence of multimorbidity - two or more long-term diseases at once - and identified key relationships between diseases.
Researchers analysed electronic health records from participants aged 18 and over between April 2005 and May 2020 in one London borough. The borough has a deprived, ...
Machine learning tool can predict malignancy in patients with multiple pulmonary nodules
2021-02-24
PHILADELPHIA - A machine learning-based tool was able to predict the risk of malignancy among patients presenting with multiple pulmonary nodules and outperformed human experts, previously validated mathematical models, and a previously established artificial intelligence tool, according to results published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Tools currently available can predict malignancy in patients with single nodules; predictive tools for patients presenting with multiple nodules are limited.
"With the adoption of widespread use of thoracic computed tomography (CT) for lung cancer screening, the detection of multiple pulmonary nodules has become increasingly ...
Self-monitoring using digital health tools is associated with weight loss
2021-02-24
SILVER SPRING, Md.--A systematic review of multiple randomized controlled studies among adults with overweight or obesity showed that greater engagement in self-monitoring using digital health tools was associated with significant weight loss, according to a paper published online in Obesity, The Obesity Society's flagship journal. This is the first comprehensive systematic review to examine the relationship between digital self-monitoring and weight loss.
"Digital health tools have flourished in the past decade," said Michele L. Patel, PhD, post-doctoral ...
Red light put moths in the mood
2021-02-24
Do you dim the lighting and turn on the red light for a romantic night in with your partner? It turns out moths aren't so different in that regard. A new study published in END ...
Mangrove forests store more carbon when they're more diverse
2021-02-24
Mangrove forests with greater species diversity can store more carbon, according to new research published in the British Ecological Society journal Functional Ecology.
Researchers studying mangrove forests in Hainan Island, China, have found that species diversity in mangrove forests enhances both biomass production (the quantity of organic matter) and soil carbon storage. The findings highlight the impotence of conserving mangrove biodiversity as a nature-based solution to mitigate climate change.
The East side of the island was found to have the highest mangrove biomass, diversity and carbon storage, with a mean of 537 tonnes of carbon per hectare (Mg C ha-1). ...
Vaginal pessaries prove effective in treating pelvic organ prolapse long-term
2021-02-24
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Feb 24, 2021)--The aging population combined with increasing obesity rates has resulted in more women experiencing pelvic organ prolapse. Common treatment options include pelvic reconstructive surgery or the use of pessaries to prop up descending organs. A new study evaluated the long-term effectiveness of pessaries, as well as reasons why women discontinued their use. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Despite the fact that vaginal pessaries have existed in some form for thousands of years to help treat pelvic organ prolapse, few studies have been published regarding their long-term use and effectiveness. Pessaries are devices inserted into the vagina ...
Buckyballs on DNA for harvesting light
2021-02-24
Organic molecules that capture photons and convert these into electricity have important applications for producing green energy. Light-harvesting complexes need two semiconductors, an electron donor and an acceptor. How well they work is measured by their quantum efficiency, the rate by which photons are converted into electron-hole pairs.
Quantum efficiency is lower than optimal if there is "self-quenching", where one molecule excited by an incoming photon donates some of its energy to an identical non-excited molecule, yielding two molecules at an intermediate energy state too low ...
Ancestry estimation perpetuates racism, white supremacy
2021-02-24
BINGHAMTON, NY -- Ancestry estimation -- a method used by forensic anthropologists to determine ancestral origin by analyzing bone structures -- is rooted in "race science" and perpetuates white supremacy, according to a new paper by a forensic anthropologist at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
By themselves, bones seem somewhat uniform to the untrained eye. They lack the traits we so often use to categorize fellow humans: hair texture, the shape of nose and eye, skin pigmentation.
Forensic anthropologists know that race isn't based in biological fact, but in a history and culture that assigns meaning to physical traits that occur among different ...
Measuring carbon nanotubes taken up by plants
2021-02-24
Carbon nanotubes are tiny. They can be a hundred thousand times smaller than the width of a human hair. But they have huge potential.
Products manufactured using carbon nanotubes include rebar for concrete, sporting goods, wind turbines, and lithium batteries, among others.
Potential uses of carbon nanotubes could extend to diverse fields, such as agriculture, biomedicine and space science.
But as we use more carbon nanotubes to make things, we also increase the chances that these nanotubes enter different environments and ecosystems.
"That makes it important to understand how ...
Mushrooms add important nutrients when included in the typical diet
2021-02-24
February 24, 2021 - The second study published in as many months has identified another reason to add more mushrooms to the recommended American diet. The new research , published in Food & Nutrition Research (February 2021), examined the addition of mushrooms to U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Food Patterns resulting in the increase of several micronutrients including shortfall nutrients, while having a minimal to zero impact on overall calories, sodium or saturated fat.
Dr. Victor L. Fulgoni III and Dr. Sanjiv Agarwal looked at the nutritional ...
Changes in writing style provide clues to group identity
2021-02-24
Small changes to people's writing style can reveal which social group they "belong to" at a given moment, new research shows.
Groups are central to human identity, and most people are part of multiple groups based on shared interests or characteristics - ranging from local clubs to national identity.
When one of these group memberships becomes relevant in a particular situation, behaviour tends to follow the norms of this group so that people behave "appropriately".
The new study - by the University of Exeter, Imperial College London, University College London and Lancaster University - demonstrates that group normative behaviour is reflected in a person's writing style.
It also shows that assessing ...
Recycle anaesthetics to reduce carbon emission of healthcare, study concludes
2021-02-24
New research has highlighted the value of recycling general anaesthetic used in routine operations.
In the UK, healthcare accounts for more than five per cent of national greenhouse gas emissions, and as much as 10 per cent in the US. Inhaled general anaesthetics are particularly potent greenhouse gases and as little is metabolised almost all that is administered is breathed out to end up in the atmosphere. The commonly used anaesthetic agents have been considered to vary considerably from as little as 1.5 for sevoflurane to more than 60 kg carbon dioxide equivalence for an hour's anaesthetic with desflurane. However, research led by a team from the University of ...
How "ugly" labels can increase purchase of unattractive produce
2021-02-24
Researchers from University of British Columbia published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines whether and how the use of 'ugly' labeling for unattractive produce increases sales and profit margins.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "From Waste to Taste: How "Ugly" Labels Can Increase Purchase of Unattractive Produce" and is authored by Siddhanth (Sid) Mookerjee, Yann Cornil, and JoAndrea Hoegg.
According to a recent report by the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine (2020), each year in the U.S. farmers throw away up to 30% of their crops, equal to 66.5 million tons of edible produce, ...
Tissue-engineered implants provide new hope for vocal injuries
2021-02-24
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New technology from Purdue University and Indiana University School of Medicine innovators may one day help patients who suffer devastating vocal injuries from surgery on the larynx.
A collaborative team consisting of Purdue biomedical engineers and clinicians from IU has tissue-engineered component tissue replacements that support reconstruction of the larynx. The team's work is published in The Laryngoscope.
The larynx is a very complex human organ consisting of outer cartilage for structural support, inner muscle that contracts to permit voicing, swallowing, and breathing, and inner vibratory lining.
Currently, thousands of patients each year with laryngeal cancer ...
Oktoberfest memories increase life-satisfaction, customer loyalty
2021-02-24
RICHLAND, Wash. - No one went to Oktoberfest in 2020, but chances are those who attended in the past are still thinking about it.
In a case study of the famous German beer festival, researchers tested the theory that events which create memorable experiences can increase life-satisfaction. This deep connection with customers has big benefits for associated businesses, according to Robert Harrington, lead author of the study recently published online in the International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
"If you can do something that transforms people even a little bit, it can have a huge impact on the success of your company and your brand," said Harrington, professor and director of the School ...
[1] ... [2601]
[2602]
[2603]
[2604]
[2605]
[2606]
[2607]
[2608]
2609
[2610]
[2611]
[2612]
[2613]
[2614]
[2615]
[2616]
[2617]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.