Diabetes patients use of mobile health app found to improve health outcomes, lower medical costs
2021-02-24
Emerging smart mobile health (or mHealth) technologies are changing the way patients track information related to diagnosed conditions. A new study examined the health and economic impacts of mHealth technologies on the outcomes of diabetes patients in Asia. The study concluded that compared to patients who did not use mHealth applications, patients who used the apps had better health outcomes and were able to regulate their health behavior more effectively. They also had fewer hospital visits and lower medical costs.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and New York University ...
Study identifies strengths and challenges of responding to dual disasters
2021-02-24
New Orleans, LA -- A new study of how the 2020 major hurricanes and the COVID-19 pandemic affected each other as well as disaster response found that although prior experience enabled community-based organizations to respond to the pandemic, the pandemic is also creating new challenges to preparing for and responding to natural disasters. The research is published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, available here.
"Two major crises hit Louisiana and coastal communities in the Southeastern United States in 2020 - a significant increase in the frequency and severity of hurricanes, and the COVID-19 pandemic," says Benjamin Springgate, MD, MPH, Chief of Community & Population Medicine at ...
A combination therapy for treating severe neurological childhood disorders
2021-02-24
A study aiming to develop a new therapeutic technique could bring a revolution in our approach to treating rare, fatal Sanfilippo syndrome, a disorder that affects children as young as 2 years old and leads to childhood dementia and premature death.
"We are using a combination of gene therapy, stem cells and small molecules to restore metabolic defects in the patient's brain cells" says Dr. Alexey Pshezhetsky, Professor at CHU Ste-Justine and lead GlycoNet Investigator on this project. "First results in the mouse models of the disease are very encouraging."
Sanfilippo syndrome belongs to a group of rare diseases known as lysosomal storage disorders.
The syndrome occurs in ...
Bearded seals are loud - but not loud enough
2021-02-24
ITHACA, N.Y. - During mating season, male bearded seals make loud calls to attract a mate. How loud? Well, even their "quiet" call can still be as ear-rattling as a chainsaw.
These elaborate vocalizations are essential for bearded seal reproduction, and have to be loud enough to be heard over the cacophony of their equally loud brethren.
But in the rapidly changing Arctic soundscape, where noise from industrial activities is predicted to dramatically increase in the next 15 years, bearded seals may need to adjust their calling behavior if they are ...
New study charts the complexity of SARS-CoV-2 neutralization
2021-02-24
Washington, DC - February 24, 2021 - In the absence of effective treatments for COVID-19, many countries have approved the therapeutic use of blood plasma from recovering patients because it contains antibodies against the coronavirus. But not every type of antibody can neutralize the virus and render it noninfectious. New research published this week in mSphere, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, explores variation in virus neutralization capabilities, which can vary widely by type of antibody.
"What we need for plasma therapy is not only high levels of antibodies but also high neutralization capability," said virologist Michael Schindler, Ph.D, at University Hospital Tübingen, ...
Scientists suggested using 'defective' diamonds in x-ray optics
2021-02-24
X-rays are used to study the atomic and microstructure properties of matter. Such studies are conducted with special accelerator complexes called synchrotrons. A synchrotron source generates powerful electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength equal to fractions of a nanometer. Some X-rays are reflected from the atomic planes of a crystal and some go through the crystal plane that plays the role of a beam-splitter (or the so-called semitransparent mirror). If the radiation passes through monochromators-optical devices that consist of two or more ideal crystals - its optimal exit wavelength can be regulated. ...
Data transfer system connects silicon chips with a hair's-width cable
2021-02-24
Researchers have developed a data transfer system that can transmit information 10 times faster than a USB. The new link pairs high-frequency silicon chips with a polymer cable as thin a strand of hair. The system may one day boost energy efficiency in data centers and lighten the loads of electronics-rich spacecraft.
The research was presented at this month's IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. The lead author is Jack Holloway '03, MNG '04, who completed his PhD in MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) last fall and currently works for Raytheon. Co-authors include Ruonan Han, associate professor and Holloway's PhD adviser in EECS, and Georgios Dogiamis, ...
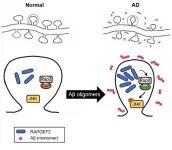
Uncovers the molecular mechanism behind synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease
2021-02-24
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, Pann-Ghill Suh (President)) announced that Dr. Kea Joo Lee and Dr. You-Na Jang of the Neural Circuits Research Group have identified the mechanism causing synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease as the aberrant expression of RAPGEF2, a synaptic protein.
- The results were published on January 2021, in the online Early View of Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.
* (Title) RAPGEF2 mediates oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic loss and cognitive dysfunction in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) accounts for about 75% of dementia cases and is the most common type of degenerative brain disease. AD is a devastating because disease progression can cause ...
Celebrating Black chemists and chemical engineers
2021-02-24
Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society (ACS), is celebrating Black chemists and chemical engineers with a special issue highlighting Black chemists who work across the fields of biotechnology, solar energy, pharmaceuticals and more. Guest edited by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) drug delivery pioneer Paula Hammond, Ph.D., this special issue showcases Black scientists, spotlighting their scientific passions and career accomplishments.
"In bringing into focus the unique lives of this set of accomplished Black scientists in chemistry and chemical engineering, ...
Study finds digital treatment for osteoarthritis is superior to traditional routine care
2021-02-24
The steadily increasing prevalence and high costs of treating chronic joint pain worldwide poses a challenge for healthcare systems and healthcare payers. New research published today in END ...
A gene provides both protection and destruction
2021-02-24
The family of ENDOU enzymes is found in most organisms, yet its functions are only poorly understood. In humans, it has been connected with cancer. RNA viruses, such as SARS-CoV2, contain a gene corresponding to ENDOU, and this is important for virus replication and the suppression of the immune response. However, so far only few details of the role of these enzymes are known. The research group led by the molecular geneticist Dr. Wenjing Qi from the University of Freiburg now contributes some more details to its function in a study published by the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications. They suggest that the gene ENDU-2 could ...
Pushing computing to the edge by rethinking microchips' design
2021-02-24
Responding to artificial intelligence's exploding demands on computer networks, Princeton University researchers in recent years have radically increased the speed and slashed the energy use of specialized AI systems. Now, the researchers have moved their innovation closer to widespread use by creating co-designed hardware and software that will allow designers to blend these new types of systems into their applications.
"Software is a critical part of enabling new hardware," said Naveen Verma, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Princeton and a leader of the research team. "The ...
Flu vaccination this season likely to be highest ever
2021-02-24
More U.S. adults reported receiving or planning to receive an influenza vaccination during the 2020-2021 flu season than ever before, according to findings from a national survey.
The survey of 1,027 adults, conducted by the University of Georgia, found that 43.5% of respondents reported having already received a flu vaccination with an additional 13.5% stating they "definitely will get one" and 9.3% stating they "probably will get one." Combined, 66.3% have received or intend to receive an influenza vaccination.
By comparison, 48.4% of adults 18 and older received the vaccine during the 2019-2020 flu season, according to the Centers for Disease ...
'Micropopulism' may be turning education into a battlefield in the culture wars
2021-02-24
A new analysis of education debates on both social media and in traditional media outlets suggests that the education sector is being increasingly influenced by populism and the wider social media 'culture wars'.
The study also suggests that the type of populism in question is not quite the same as that used to explain large-scale political events, such as the UK's 'Brexit' from the European Union, or Donald Trump's recent presidency in the United States.
Instead, the researchers - from the University of Cambridge, UK, and Queensland University of Technology, Australia - identify a phenomenon called 'micropopulism': a localised populism which spotlights an aspect of public ...
Study finds low rate of COVID-19 among dental hygienists
2021-02-24
CHICAGO, February 24, 2021 -- Despite having been designated as high risk for COVID-19 by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, a new study finds 3.1 percent of dental hygienists have had COVID-19 based on data collected in October 2020. This is in alignment with the cumulative infection prevalence rate among dentists and far below that of other health professionals in the U.S, although slightly higher than that of the general population.
The research, published by The Journal of Dental Hygiene, is the first large-scale collection and publication of U.S. dental hygienists' infection rates and infection control practices related to COVID-19. In partnership, the American Dental Hygienists' Association (ADHA) and the American Dental Association (ADA) ...
Sulfur: the consequences
2021-02-24
The transition from single-celled organisms to multicellular ones was a major step in the evolution of complex life forms. Multicellular organisms arose hundreds of millions of years ago, but the forces underlying this event remain mysterious. To investigate the origins of multicellularity, Erika Pearce's group at the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg turned to the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum, which can exist in both a unicellular and a multicellular state, lying on the cusp of this key evolutionary step. These dramatically different states depend on just one thing - food.
A core question of Pearce's lab is to answer how changes in metabolism drive cell function and differentiation. Usually, they study immune cells ...
NCI study finds people with SARS-CoV-2 antibodies may have low risk of future infection
2021-02-24
People who have had evidence of a prior infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, appear to be well protected against being reinfected with the virus, at least for a few months, according to a newly published study from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). This finding may explain why reinfection appears to be relatively rare, and it could have important public health implications, including decisions about returning to physical workplaces, school attendance, the prioritization of vaccine distribution, and other activities.
For the study, researchers at NCI, part of the National Institutes of Health, collaborated with ...
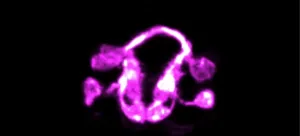
Yale scientists capture the choreography of a developing brain
2021-02-24
The formation of a brain is one of nature's most staggeringly complex accomplishments. The intricate intermingling of neurons and a labyrinth of connections also make it a particularly difficult feat for scientists to study.
Now, Yale researchers and collaborators have devised a strategy that allows them to see this previously impenetrable process unfold in a living animal -- the worm Caenorhabditis elegans, they report February 24 in the journal Nature.
"Before, we were able to study single cells, or small groups of cells, in the context of the living C. elegans, and for relatively short periods of time," said Mark Moyle, an associate research scientist in neuroscience at Yale School of Medicine and first author of the study. "It has been a breathtaking experience to ...
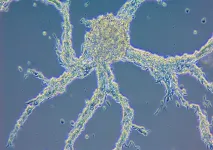
Building a brain: Pioneering study reveals principles of brain tissue structure, assembly
2021-02-24
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Understanding how the brain works is a paramount goal of medical science. But with its billions of tightly packed, intermingled neurons, the human brain is dauntingly difficult to visualize and map, which can provide the route to therapies for long-intractable disorders.
In a major advance published next week in Nature, scientists for the first time report the structure of a fundamental type of tissue organization in brains, called neuropil, as well as the developmental pathways that lead to neuropil assembly in the roundworm C. elegans. This multidisciplinary study ...
Costs associated with delirium in older adults after elective surgery
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: Medicare claims and clinical data were used to estimate health care costs associated with delirium in older adults one year after major elective surgery.
Authors: Tammy T. Hshieh, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2020.7260)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
Association of SARS-CoV-2 seropositive antibody test with risk of future infection
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: Researchers use a large set of clinical laboratory data linked to other clinical information such as claims to investigate the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 antibody status and subsequent nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) results in an effort to understand how serostatus may predict risk of reinfection.
Authors: Lynne T. Penberthy, M.D., M.P.H., of the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health in Rockville, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.0366)
Editor's ...
Researchers take aim at the evolution of traditional technologies
2021-02-24
In the last 60,000 years, humans have emerged as an ecologically dominant species and have successfully colonized every terrestrial habitat. Our evolutionary success has been facilitated by a heavy reliance on an ever-advancing technology. Understanding how human technology evolves is crucial to understanding why humans have enjoyed such unprecedented evolutionary success.
ASU doctoral graduate Jacob Harris, working with ASU researcher Robert Boyd and Brian Wood from the University of California Las Angeles and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, are interested in the role of causal ...
Childhood ADHD, risk of developing psychotic disorder
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: This study combined the results of 12 studies with 1.8 million participants to examine the association between attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in childhood and adolescence and the subsequent risk of developing a psychotic disorder.
Authors: Mikaïl Nourredine, M.D., M.Sc., of the Hospices Civils de Lyon in Lyon, France, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4799)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Study shows economic impact of post-op delirium
2021-02-24
BOSTON (February 24, 2021) - Results of a study published today in JAMA Surgery reveal the impact post-operative delirium has on health care costs in the U.S. Data from the study shows that if delirium were prevented or made less severe for patients, it could reduce health care costs by $33 billion per year, that is, $44,300 per patient per year. Severe delirium resulted in an additional $56,500 per patient per year, as compared to routine health care costs for older post-operative patients.
Tammy Hshieh, M.D., M.P.H., Adjunct Scientist, and Ray Yun Gou, M.A., Data Scientist II, both with the Aging Brain Center in the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife, are co-first authors. Sharon K. Inouye, M.D., M.P.H., Director ...
Daily emails about chemicals in tobacco lead some smokers to consider quitting
2021-02-24
CHAPEL HILL, N.C.--For the last decade, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has required tobacco manufacturers and importers to report the levels of harmful and potentially harmful chemicals found in their tobacco products and tobacco smoke. The idea was to educate the public and ultimately to decrease tobacco use, but little research has demonstrated if such information can impact on people's decisions to quit smoking.
A new study from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found that smokers who saw messages about tobacco chemicals with associated ...
[1] ... [2610]
[2611]
[2612]
[2613]
[2614]
[2615]
[2616]
[2617]
2618
[2619]
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
[2623]
[2624]
[2625]
[2626]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.