42,000-year-old trees allow more accurate analysis of last Earth's magnetic field reversal
2021-02-19
The last complete reversal of the Earth's magnetic field, the so-called Laschamps event, took place 42,000 years ago. Radiocarbon analyses of the remains of kauri trees from New Zealand now make it possible for the first time to precisely time and analyse this event and its associated effects, as well as to calibrate geological archives such as sediment and ice cores from this period. Simulations based on this show that the strong reduction of the magnetic field had considerable effects in the Earth's atmosphere. This is shown by an international team led by Chris Turney from the Australian University of New South Wales, with the participation of Norbert Nowaczyk from the German Research Centre for ...
Artificial intelligence predicts nonlinear ultrafast dynamics in optics
2021-02-19
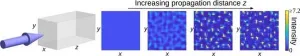
Researchers at Tampere University have successfully used artificial intelligence to predict nonlinear dynamics that take place when ultrashort light pulses interact with matter. This novel solution can be used for efficient and fast numerical modelling, for example, in imaging, manufacturing and surgery. The findings were published in the prestigious Nature Machine Intelligence journal.
Artificial intelligence can distinguish different types of laser pulse propagation, just as it recognizes subtle differences of expression in facial recognition. The newly found solution can make it simpler to design experiments in fundamental research and will allow algorithms ...
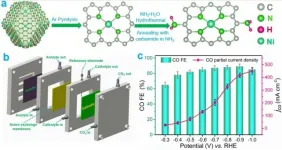
Amination strategy improves efficiency of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction
2021-02-19
Carbon dioxide (CO2) electrocatalytic reduction driven by renewable electricity can solve the problem of excessive CO2 emissions. Since CO2 is thermodynamically stable, efficient catalysts are needed to reduce the energy consumption in the process.
The single-atom catalysts immobilized on nitrogen-doped carbon supports (M-N/C) have been widely used for CO2 electrocatalytic reduction reaction due to their high atom utilization efficiency.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. LIU Licheng from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a two-step amination strategy to regulate the electronic structure of M-N/C catalysts (M=Ni, Fe, Zn) and enhance the intrinsic activity of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction.
In ...
Oregon experiments find that electrical sparks are possible on Mars
2021-02-19
EUGENE, Ore. -- Feb. 19, 2021 -- Friction caused by dry Martian dust particles making contact with each other may produce electrical discharge at the surface and in the planet's atmosphere, according University of Oregon researchers.
However, such sparks are likely to be small and pose little danger to future robotic or human missions to the red planet, they report in a paper published online and scheduled to appear in the March 15 print issue of the journal Icarus.
Viking landers in the 1970s and orbiters since then detected silts, clays, wind-blown bedforms and dust devils on Mars, raising questions about potential electrical activity.
Scientists ...
Northern Hemisphere cold surges result of Arctic and tropical Pacific synergistic effects
2021-02-19
China is just one of many countries in the Northern Hemisphere having what researchers are calling an "extremely cold winter," due in part to both the tropical Pacific and the Arctic, according to an analysis of temperatures from Dec. 1, 2020, to mid-January of 2021. A country-specific case study, the investigation potentially has far-reaching implications for predictions and early warnings to protect against harmful impacts, researchers said.
The results were published online, ahead of print, on Feb. 12 in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
"We are trying to explain why the countries in the Northern Hemisphere ...
Dynamics of nanoparticles using a new isolated lymphatic vessel lumen perfusion system
2021-02-19
Nanoparticles used in drug delivery systems, bioimaging, and regenerative medicine migrate from tissues to lymphatic vessels after entering the body, so it is necessary to clarify the interaction between nanoparticles and lymphatic vessels. Although technology to observe the flow of nanoparticles through lymphatic vessels in vivo has been developed, there has been no method to evaluate the flow of nanoparticles in a more detailed and quantitative manner ex vivo. Thus, research was conducted to develop an ex vivo lymphatic vessel lumen perfusion system to determine how nanoparticles move in lymphatic vessels and how they affect the physiological movement of lymphatic vessels.
Nanoparticles introduced into the ...
HKUST decodes a deep-sea vent-endemic snail hologenome
2021-02-19
A research team led by Prof. QIAN Peiyuan, Head and Chair Professor from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)'s Department of Ocean Science and David von Hansemann Professor of Science, has published their cutting-edge findings of symbiotic mechanisms of a deep-sea vent snail (Gigantopelta aegis) in the scientific journal Nature Communications. They discovered that Gigantopelta snail houses both sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and methane-oxidizing bacteria inside its esophageal gland cells (part of digestive system) as endosymbionts. By decoding the ...
Asthmatics no higher risk dying from COVID, review of studies on 587,000 people shows
2021-02-19
A new study looking at how COVID-19 affects people with asthma provides reassurance that having the condition doesn't increase the risk of severe illness or death from the virus.
George Institute for Global Health researchers in Australia analysed data from 57 studies with an overall sample size of 587,280. Almost 350,000 people in the pool had been infected with COVID-19 from Asia, Europe, and North and South America and found they had similar proportions of asthma to the general population.
The results, published in the peer-reviewed END ...
New method converts methane in natural gas to methanol at room temperature
2021-02-19
Researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have discovered a way to convert the methane in natural gas into liquid methanol at room temperature.
This discovery, reported in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could potentially provide a cleaner energy source for many of our everyday activities.
When burned, natural gas -- the fuel used to heat homes, cook food and generate electricity -- produces carbon dioxide, a powerful greenhouse gas.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the U.S. consumed approximately 31 trillion cubic feet of natural gas in 2019, contributing roughly 1.6 gigatons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
A better way to use natural gas would be to convert it to methanol, a liquid fuel that burns more ...
Ultraviolet 'television' for animals helps us better understand them
2021-02-19
University of Queensland scientists have developed an ultraviolet 'television' display designed to help researchers better understand how animals see the world.
Until now, standard monitors on devices like televisions or computer screens have been used to display visual stimuli in animal vision studies, but none have been able to test ultraviolet vision - the ability to see wavelengths of light shorter than 400 nanometres.
Dr Samuel Powell, from the Queensland Brain Institute's Marshall lab, said this new technology will help unveil the secrets of sight in all sorts of animals, such as fish, birds and insects.
"Human TVs generally use three colours - red, green and blue - to create images, but our newly-developed ...
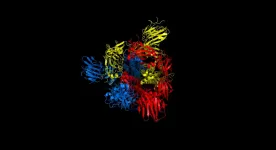
Electron cryo-microscopy sheds light on how bioenergy makers are made in our body
2021-02-19
Mitochondria are organelles that act as the powerhouses in our body. They use oxygen which we inhale and food we eat to produce energy that supports our life. This molecular activity is performed by bioenergetic nano-factories incorporated in specialized mitochondrial membranes. The nano-factories consist of proteins cooperatively transporting ions and electrons to generate chemical energy. Those have to be constantly maintained, replaced and duplicated during cell division. To address this, mitochondria have their own bioenergy protein-making machine called the mitoribosome. Given its key role, a deregulation of the mitoribosome can lead to medical disorders such as deafness and diseases including cancer development. The first fundamental understanding of how mitoribosomes ...
Spin hall effect of light with near 100% efficiency
2021-02-19
A POSTECH-KAIST joint research team has successfully developed a technique to reach near-unity efficiency of SHEL by using an artificially-designed metasurface.
Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, and Ph.D. candidate Minkyung Kim and Dr. Dasol Lee of Department of Mechanical Engineering in collaboration with Professor Bumki Min and Hyukjoon Cho of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have together proposed a technique to enhance the SHEL with near 100% efficiency using an anisotropic metasurface. For this, the joint research team designed a metasurface that transmits most ...
Release of nutrients from lake-bottom sediments worsens Lake Erie's annual 'dead zone,'
2021-02-19
Photo and map
Robotic laboratories on the bottom of Lake Erie have revealed that the muddy sediments there release nearly as much of the nutrient phosphorus into the surrounding waters as enters the lake's central basin each year from rivers and their tributaries.
Excessive phosphorus, largely from agricultural sources, contributes to the annual summer cyanobacteria bloom that plagues Lake Erie's western basin and the central basin's annual "dead zone," an oxygen-starved region that blankets several thousand square miles of lake bottom and that reduces habitat for fish and other organisms.
The release of phosphorus from Lake Erie sediments during periods of low oxygen--a phenomenon known as self-fertilization or internal loading--has been acknowledged since the 1970s. ...
Seeing stable topology using instabilities
2021-02-19
We are most familiar with the four conventional phases of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Changes between two phases, known as phase transitions, are marked by abrupt changes in material properties such as density. In recent decades a wide body of physics research has been devoted to discovering new unconventional phases of matter, which typically emerge at ultra-low temperatures or in specially-structured materials. Exotic "topological" phases exhibit properties that can only change in a quantized (step-wise) manner, making them intrinsically robust against impurities and defects.
In addition to topological ...
A better tool for the job: Laser-based technique to elucidate the mysteries of exosomes
2021-02-19
Despite our great progress in understanding various cellular mechanisms over the last decades, many of them remain unclear. Such is the case for exosomes, small vesicles released by cells that contain genetic materials called "RNA" and various proteins. The roles of exosomes are believed to be very varied and important, both for normal bodily functions and also in the spreading of diseases like cancer. However, exosomes are so small that studying them is challenging and calls for costly and time-consuming techniques, such as electron microscopy (EM).
To tackle this issue, a team of undergraduate students from ...
Making sense of the mass data generated from firing neurons
2021-02-19
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in predicting the behaviour of neurons in large networks operating at the mysterious edge of chaos.
New research from the University of Sussex and Kyoto University outlines a new method capable of analysing the masses of data generated by thousands of individual neurons.
The new framework outperforms previous models in predicting and assessing network properties by more accurately estimating a system's fluctuations with greater sensitivity to parameter changes.
As new technologies allow recording of thousands of neurons from living animals, there is a pressing demand for mathematical tools to study the non-equilibrium, complex dynamics of the high-dimensional ...
Good cop, bad cop
2021-02-19
Cancer researcher Rita Fior uses zebrafish to study human cancer. Though this may seem like an unlikely match, her work shows great promise with forthcoming applications in personalised medicine.
The basic principle of Fior's approach relies on transplanting human cancer cells into dozens of zebrafish larvae. The fish then serve as "living test tubes" where various treatments, such as different chemotherapy drugs, can be tested to reveal which works best. The assay is rapid, producing an answer within four short days.
Some years ago, when Fior was developing this assay, she noticed something curious. "The majority of human ...
Covid-19: Future targets for treatments rapidly identified with new computer simulations
2021-02-19
University of Warwick scientists model movements of nearly 300 protein structures in Covid-19
Scientists can use the simulations to identify potential targets to test with existing drugs, and even check effectiveness with future Covid variants
Simulation of virus spike protein, part of the virus's 'corona', shows promising mechanism that could potentially be blocked
Researchers have publicly released data on all protein structures to aid efforts to find potential drug targets: https://warwick.ac.uk/flex-covid19-data
Researchers have detailed a mechanism in the ...
Spina bifida can be caused by uninherited genetic mutations
2021-02-19
Genetic mutations which occur naturally during the earliest stages of an embryo's development can cause the severe birth defect spina bifida, finds a new experimental study in mice led by UCL scientists.
The research, published in Nature Communications, explains for the first time how a 'mosaic mutation' - a mutation which is not inherited from either parent (either via sperm or egg cell) but occurs randomly during cell divisions in the developing embryo - causes spina bifida.
Specifically the scientists, based at UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, found that when a mutation in the gene Vangl2 (which contains information needed to create spinal cord tissue) was present in 16% of developing spinal cord cells of mouse embryos, this ...
How to calculate the social cost of carbon? Researchers offer roadmap in new analysis
2021-02-19
The Biden administration is revising the social cost of carbon (SCC), a decade-old cost-benefit metric used to inform climate policy by placing a monetary value on the impact of climate change. In a newly published analysis in the journal Nature, a team of researchers lists a series of measures the administration should consider in recalculating the SCC.
"President Biden signed a Day One executive order to create an interim SCC within a month and setting up a process to produce a final, updated SCC within a year," explains Gernot Wagner, a climate economist at New York University's Department of Environmental Studies and NYU's Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service and the paper's lead author. "Our work outlines how the ...
To end HIV epidemic, we must address health disparities
2021-02-19
Scientific strides in HIV treatment and prevention have reduced transmissions and HIV-related deaths significantly in the United States in the past two decades. However, despite coordinated national efforts to implement HIV services, the epidemic persists, especially in the South. It also disproportionately impacts marginalized groups, such as Black/African-American and Latinx communities, women, people who use drugs, men who have sex with men, and other sexual and gender minorities. Following the release of the HIV National Strategic Plan and marking two years since the launch of the Ending the HIV Epidemic: ...
The Lancet: USA failing to reach populations most in need of HIV prevention and treatment services as epidemic grows in the South and rural areas
2021-02-19
People who are racial, sexual, and gender minorities continue to be affected by HIV at significantly higher rates than white people, a disparity also reflected in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The US HIV epidemic has shifted from coastal, urban settings to the South and rural areas.
Despite its role as the largest funder for HIV research and global AIDS programs worldwide, the USA has higher rates of new HIV infections and a more severe HIV epidemic than any other G-7 nation.
Series authors call for a unified effort to curb the HIV epidemic in the USA, including universal health ...
What happens when consumers pick their own prices?
2021-02-19
Researchers from California Polytechnic State University and University of Oregon published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines the potential benefits for firms and consumers of pick-your-price (PYP) over pay-what-you-want (PWYW) and fixed pricing strategies.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "The Control-Effort Trade-Off in Participative Pricing: How Easing Pricing Decisions Enhances Purchase Outcomes" and is authored by Cindy Wang, Joshua Beck, and Hong Yuan.
Over the past few decades, marketers have experimented with pricing strategies ...
Local and national restrictions in England reduced contacts in small and varied ways
2021-02-19
The imposition of various local and national restrictions in England during the summer and autumn of 2020 gradually reduced contacts between people, but these changes were smaller and more varied than during the lockdown in March, according to a study published in the open access journal BMC Medicine.
A team of researchers at London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), UK combined data from the English participants of the UK CoMix survey and information on local and national restrictions from Gov.uk collected between August 31st and December 7th 2020. CoMix is an online survey asking individuals to record details of their direct contacts in the day prior to the survey.
The authors used the data to compare the number of contacts in different settings, such ...
Boys who play video games have lower depression risk
2021-02-19
Boys who regularly play video games at age 11 are less likely to develop depressive symptoms three years later, finds a new study led by a UCL researcher.
The study, published in Psychological Medicine, also found that girls who spend more time on social media appear to develop more depressive symptoms.
Taken together, the findings demonstrate how different types of screen time can positively or negatively influence young people's mental health, and may also impact boys and girls differently.
Lead author, PhD student Aaron Kandola (UCL Psychiatry) said: "Screens allow us to engage in a wide range of activities. Guidelines and recommendations about screen time should be based on our understanding of how these different ...
[1] ... [2615]
[2616]
[2617]
[2618]
[2619]
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
2623
[2624]
[2625]
[2626]
[2627]
[2628]
[2629]
[2630]
[2631]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.