Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease yields promise in transgenic mouse model
2021-02-18
Inhibitors based on approved drugs and designed to disrupt the SARS-CoV-2 viral protein Mpro display strong antiviral activity both in vitro and in a transgenic mouse model, a new study reports. While vaccines are an important tool in the fight against COVID-19, it remains a high priority to develop antiviral drugs, especially with the rise of variants that may partially evade vaccines. The viral protein Mpro is a protease that is required for cleaving precursor polyproteins into functional viral proteins. This essential function makes it a key drug target. Jingxin Qiao et al. designed 32 ...
New report calls for universal coverage of long-term care for older adults in U.S.
2021-02-18
The COVID-19 pandemic's heavy toll on older Americans highlights the need to strengthen the nation's safety net for people in need of long-term services and supports, an Oregon Health & Science University researcher and co-authors argue in a new report published by Milbank Quarterly.
The report proposes a system of universal coverage to support the long-term care of all older Americans.
"This approach would protect against financial catastrophe and end the current system that is based on the need to be financially destitute in order to access coverage via Medicaid," ...
Antibody response may drive COVID-19 outcomes
2021-02-18
BOSTON -- COVID-19, the source of the current pandemic, may be caused by a single virus, but it has a variety of presentations that make treatment difficult. Children, for example, almost exclusively experience mild or asymptomatic COVID-19, while adults can develop severe or even fatal COVID-19. But children who contract COVID-19 are at risk for a rare but serious syndrome called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Severe cases of MIS-C can lead to cardiac disease and ventricular failure, and require hospitalization and intense medical support.
Researchers Galit Alter, PhD, core member of the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, and Lael Yonker, MD, ...
Researchers uncover new information on the effects of antidepressants
2021-02-18
The effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and other conventional antidepressants are believed to be based on their increasing the levels of serotonin and noradrenalin in synapses, while ketamine, a new rapid-acting antidepressant, is thought to function by inhibiting receptors for the neurotransmitter glutamate.
Neurotrophic factors regulate the development and plasticity of the nervous system. While all antidepressants increase the quantity and signalling of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the brain, the drugs have so far been thought to act on BDNF indirectly, through serotonin or glutamate receptors.
A new study published this week in Cell demonstrates, however, that antidepressants bind directly to a BDNF receptor known as TrkB. This finding challenges ...
Which suicide prevention strategies work?
2021-02-18
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 18, 2021)--A new study from Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons has found that suicide mortality can be reduced by a Federally coordinated approach employing scientifically proven options.
Columbia researchers J. John Mann, MD, Christina A. Michel, MA, and Randy P. Auerbach, PhD, conducted a systematic review, determining which suicide prevention strategies work and are scalable to national levels.
The study, "Improving Suicide Prevention Through Evidence-Based
Strategies: A Systematic Review," was published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
The researchers found that screening school children or the general population for those at risk for suicide--the ...
Light and genetic probes untangle dynamics of brain blood flow
2021-02-18
While the human brain has over 400 miles of total vasculature, little is known about the tiny capillaries that make up much of this intricate labyrinth of blood vessels critical for delivering oxygenated blood and nutrients to billions of brain cells.
According to Dr. Andy Shih, a principal investigator in the Center for Developmental Biology and Regenerative Medicine at Seattle Children's Research Institute, understanding how this vast network regulates blood flow in the brain could hold the key to new treatments for neonatal and childhood neurologic conditions, such as stroke and hypoxia, and issues of aging like dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
"Insufficient blood flow contributes to many of the common neurologic problems seen in children and adults," he said. "Yet, ...
Poor swelter as urban areas of U.S. Southwest get hotter
2021-02-18
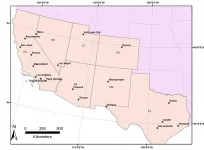
Acres of asphalt parking lots, unshaded roads, dense apartment complexes and neighborhoods with few parks have taken their toll on the poor. As climate change accelerates, low-income districts in the Southwestern United States are 4 to 7 degrees hotter in Fahrenheit -- on average -- than wealthy neighborhoods in the same metro regions, University of California, Davis, researchers have found in a new analysis.
This study provides the most detailed mapping yet of how summer temperatures in 20 urban centers in California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico and Texas affected different neighborhoods between 2018 and 2020. The researchers found even greater heat disparities in California than in other states. The largest disparities showed ...
Promoting and protecting human milk and breastfeeding during COVID-19
2021-02-18
PHILADELPHIA (February 18, 2021) - With stressors mounting daily on the health care system due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a de-prioritization of the childbearing family has been noted. Their care has changed, resulting in mothers forced to go through labor and birth without their partners, parents barred from NICU visitation, and discharge of mothers and newborns early without enough expert lactation care. There is great concern that these changes in childbearing families' care may become permanent - to the detriment of the health of both mother and ...
Internet trends suggest COVID-19 spurred a return to earlier values and activities
2021-02-18
American values, attitudes and activities have changed dramatically during COVID-19, according to a new study of online behavior.
Researchers from UCLA and Harvard University analyzed how two types of internet activity changed in the U.S. for 10 weeks before and 10 weeks after March 13, 2020 -- the date then-President Donald Trump declared COVID-19 a national emergency. One was Google searches; the other was the phrasing of more than a half-billion words and phrases posted on Twitter, blogs and internet forums.
The study is the lead research article in a special issue of the journal Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies ...
New UCF study examines leeches for role in major disease of sea turtles in Florida
2021-02-18
ORLANDO, Feb. 18, 2021 - University of Central Florida researchers are homing in on the cause of a major disease of sea turtles, with some of their latest findings implicating saltwater leeches as a possible factor.
The disease, known as fibropapillomatosis, or FP, causes sea turtles to develop tumors on their bodies, which can limit their mobility and also their health by interfering with their ability to catch and eat prey.
While the cause of FP isn't known, saltwater leeches have been suspected to play a role due to their frequent presence on areas of sea turtles where FP tumors often develop, such as on their eyes, mouths and ...
Deep learning may help doctors choose better lung cancer treatments
2021-02-18
MALVERN, Pa. -- Doctors and healthcare workers may one day use a machine learning model, called deep learning, to guide their treatment decisions for lung cancer patients, according to a team of Penn State Great Valley researchers.
In a study, the researchers report that they developed a deep learning model that, in certain conditions, was more than 71 percent accurate in predicting survival expectancy of lung cancer patients, significantly better than traditional machine learning models that the team tested. The other machine learning models the team ...
Neoadjuvant combination immunotherapy improves outcomes for early stage non-small cell lung cancer
2021-02-18
HOUSTON -- The first randomized Phase II clinical trial to report on single and combined neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in stage I-III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) found combination therapy produced a significant clinical benefit, as assessed by major pathologic response (MPR) rate, as well as enhanced tumor immune cell infiltration and immunological memory. Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center published the study results today in Nature Medicine.
The NEOSTAR trial tested combined neoadjuvant therapy of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, as well as neoadjuvant nivolumab monotherapy in patients with operable NSCLC. The trial met its prespecified primary endpoint efficacy threshold in ...
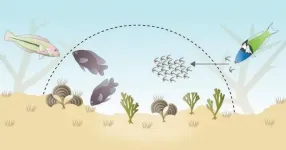
A natural protection racket among damselfish and mysid shrimp
2021-02-18
Throughout nature, there are instances of animals aiding one another and living together in mutually beneficial relationships that have helped shape the world's landscapes and biodiversity.
These domesticator-domesticate relationships form when one species provides multigenerational support to another species in exchange for a resource or service that benefits both species. An example of this type of relationship is how early humans domesticated gray wolves. The wolves were attracted to the human encampments, which provided them with protection and resources, and the wolves, in turn, helped the humans increase their hunting proficiency.
One area ...
Rich nations see virus rates fall quicker -- study
2021-02-18
Richer countries were more likely to see rates of COVID-19 fall faster during the first wave of the pandemic, according to new research published in the journal Frontiers in Public Health.
The study by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) professors Shahina Pardhan and Nick Drydakis examined economic indicators in 38 European countries, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, life expectancy, and public spending, and the number of new coronavirus cases per million of the population between 1 April and 31 May 2020, using data from Our World in Data based on the seven-day rolling average of new cases for each country.
A significant negative correlation ...
UCLA study finds combination therapy suppresses pancreatic tumor growth in mice
2021-02-18
UCLA RESEARCH ALERT
FINDINGS
UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have uncovered a potential new way to target pancreatic tumors that express high intratumoral interferon signaling (IFN). The team found that high type I IFN signaling is present in a subset of pancreatic tumors and it triggers a decrease in the level of NAD and NADH in pancreatic cancer cells, which are vital cofactors in critical metabolic processes.
After the researchers delineated the mechanism by which the NAD depletion occurs, they demonstrated that cells with high IFN signaling were more sensitive to NAMPT inhibitors, which inhibit a major pathway ...
First report on mass shootings from Columbia University database
2021-02-18
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 18, 2021)--A research team at the Center of Prevention and Evaluation (COPE) at Columbia University Irving Medical Center and the New York State Psychiatric Institute, led by Drs. Gary Brucato and Ragy R. Girgis, found that, contrary to popular belief, serious mental illness was present in only 11% of all mass murderers and in only 8% of mass shooters.
The study--the first published report on mass shootings from the Columbia Mass Murder Database--appeared online Feb. 17th in Psychological Medicine.
The investigators sought to gain much-needed insight into the relationship between serious mental ...
Migratory birds track climate across the year
2021-02-18
As climate change takes hold across the Americas, some areas will get wetter, and others will get hotter and drier. A new study of the yellow warbler, a widespread migratory songbird, shows that individuals have the same climatic preferences across their migratory range. The work is published Feb. 17 in Ecology Letters.
"What's amazing is that the birds track similar climates despite the fact that they have migrated thousands of miles," said Rachael Bay, assistant professor in the Department of Evolution and Ecology, College of Biological Sciences at the University of California, Davis. "It seems that individual birds may be adapted to particular ...
Giant predatory worms roamed the seafloor until 5.3 million years ago
2021-02-18
An international study in which the University of Granada participated--recently published in the journal Scientific Reports--has identified a new fossil record of these mysterious animals in the northeast of Taiwan (China), in marine sediments from the Miocene Age (between 23 and 5.3 million years ago)
These organisms, similar to today's Bobbit worm (Eunice aphroditois), were approximately 2 m long and 3 cm in diameter and lived in burrows
An international study in which the University of Granada (UGR) participated (recently published in the prestigious journal Scientific Reports) has revealed that the seafloor was inhabited by giant predatory worms during the Miocene Age (23-5.3 million years ...
A study with 1,600 dogs: More than 20 gene loci associated with canine hip dysplasia
2021-02-18
Hip dysplasia is a developmental disorder common in most dog breeds, and its onset is affected by both hereditary and environmental factors.
Prior studies have identified dozens of genetic loci associated with hip dysplasia in various breeds. The relevance of the loci to disease susceptibility remains an open question. The previously identified loci were reinvestigated at the University of Helsinki, Finland, using a large independent cohort of 1,600 dogs representing ten breeds.
The individual genetic variants at the target loci were determined from blood samples. The standardized ...
Older adults and antibiotics: Study shows healthy attitudes but unhealthy practices
2021-02-18
While most adults over 50 understand that overuse of antibiotics is a problem, and say they're cautious about taking the drugs, a sizable minority have used antibiotics for something other than their original purpose, and appear to think the drugs could help treat colds, which are caused by viruses not bacteria.
These findings, contained in a new paper in Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, come from a national poll of people between the ages of 50 and 80 carried out as part of the National Poll on Healthy Aging.
The authors, from the University of ...
LHC/ATLAS: A unique observation of particle pair creation in photon-photon collisions
2021-02-18
Cracow, 18 February 2021
Creation of matter in an interaction of two photons belongs to a class of very rare phenomena. From the data of the ATLAS experiment at the LHC, collected with the new AFP proton detectors at the highest energies available to-date, a more accurate - and more interesting - picture of the phenomena occurring during photon collisions is emerging.
If you point a glowing flashlight towards another one, you do not expect any spectacular phenomena. The photons emitted by both flashlights simply pass by each other. However, in certain collisions involving high-energy protons the situation is different. The ...
Shale gas development in PA increases exposure of some to air pollutants
2021-02-18
Air pollution levels may have exceeded air quality standards during the development of some Marcellus Shale natural gas wells in Pennsylvania, potentially impacting more than 36,000 people in one year alone during the drilling boom, according to Penn State scientists.
"The construction and drilling of these wells are a relatively short-term thing, and assessment of the impact on air quality is something that often falls through the cracks," said Jeremy Gernand, associate professor of industrial health and safety at Penn State. "But there are thousands and thousands of wells drilled depending on the year, and we wanted to see what the impact would be if we added it all up."
More than 20,000 unconventional Marcellus Shale gas wells have been drilled ...
The distribution of vertebrate animals redefines temperate and cold climate regions
2021-02-18
The distribution of vegetation is routinely used to classify climate regions worldwide, yet whether these regions are relevant to other organisms is unknown. Umeå researchers have established climate regions based on vertebrate species' distributions in a new study published in eLife. They found that while high-energy climate regions are similar across vertebrate and plant groups, there are large differences in temperate and cold climates.
Climate determines how life organises across the world. Understanding which climatic conditions drive important changes in ecosystems is crucial to understanding and predicting how life functions and evolves.
Human well-being critically ...
Pandemic got you down? A little nature could help
2021-02-18
Having trouble coping with COVID?
Go take a hike. Literally.
Researchers have long been aware of the positive impact of a connection with nature on psychological health and, according to a new study published in the journal Personality and Individual Differences, the pandemic hasn't decreased the power of nature to improve mental well-being.
"Thinking about the natural world in an interconnected and harmonious way corresponds to improved psychological health, no matter where you are," says Brian W. Haas, the lead author of the new study and an associate professor in the Behavioral and Brain Sciences Program at the University of Georgia.
Haas and his collaborators - Fumiko Hoeft, a professor of psychological sciences at UConn ...
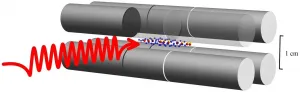
Investigating the wave properties of matter with vibrating molecules
2021-02-18
Almost 100 years ago, a revolutionary discovery was made in the field of physics: microscopic matter exhibits wave properties. Over the decades, more and more precise experiments have been used to measure the wave properties of electrons in particular. These experiments were mostly based on spectroscopic analysis of the hydrogen atom and they enabled verifying the accuracy of the quantum theory of the electron.
For heavy elementary particles - for example protons - and nuclides (atomic nuclei), it is difficult to measure their wave properties accurately. In principle, however, these properties can be seen everywhere. In molecules, the wave properties ...
[1] ... [2617]
[2618]
[2619]
[2620]
[2621]
[2622]
[2623]
[2624]
2625
[2626]
[2627]
[2628]
[2629]
[2630]
[2631]
[2632]
[2633]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.