Differences in walking patterns could predict type of cognitive decline in older adults
2021-02-16
Canadian researchers are the first to study how different patterns in the way older adults walk could more accurately diagnose different types of dementia and identify Alzheimer's disease.
A new study by a Canadian research team, led by London researchers from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, evaluated the walking patterns and brain function of 500 participants currently enrolled in clinical trials. Their findings are published today in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
"We have longstanding evidence showing that cognitive problems, such as poor memory and executive dysfunction, can ...
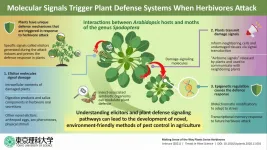
Perceiving predators: Understanding how plants 'sense' herbivore attack
2021-02-16
Nature has its way of maintaining balance. This statement rightly holds true for plants that are eaten by herbivores--insects or even mammals. Interestingly, these plants do not just silently allow themselves to be consumed and destroyed; in fact, they have evolved a defense system to warn them of predator attacks and potentially even ward them off. The defense systems arise as a result of inner and outer cellular signaling in the plants, as well as ecological cues. Plants have developed several ways of sensing damage; a lot of these involve the sensing of various "elicitor" molecules produced by either the predator ...
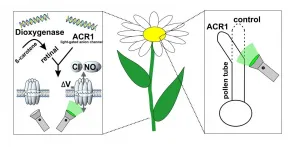
A boost for plant research
2021-02-16
It is almost ten years since the scientific journal Science called optogenetics the "breakthrough of the decade". Put simply, the technique makes it possible to control the electrical activity of cells with pulses of light. With its help, scientists can gain new insights into the functioning of nerve cells, for example, and thus better understand neurological and psychiatric diseases such as depression and schizophrenia.
Established procedure on animal cells
In research on animal cells, optogenetics is now an established technique used in many fields. The picture is different in plant research: transferring the principle to plant cells and applying it widely has not been possible until now.
However, this has now changed: Scientists ...
Individual differences in Achilles tendon shape can affect susceptibility to injury
2021-02-16
Individual variation in the shape and structure of the Achilles tendon may influence our susceptibility to injury later in life, says a study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that studying individual Achilles tendon shape (or 'morphology') could help with identifying patients at risk of injury and designing new, potentially personalised approaches for treating and preventing Achilles tendinopathy and similar conditions.
The Achilles tendon is the tissue that links the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is fundamental to our movement and athletic ability. Its unique structure, which combines three smaller sub-tendons, increases the efficiency of our movement by allowing individual control from connected muscles. For this control to occur, the ...
The body produces new satiety factor during prolonged exercise
2021-02-16
A drug that helps us to eat less could help the more than 650 million people around the world who live with obesity. One of the emerging drug candidates that interest researchers is the hormone GDF15 that, when given to rodents, lowers their appetite and body weight. New research from the University of Copenhagen finds that the body produces large amounts GDF15 during extended bouts of vigorous exercise, presumably as a physiological stress signal.
This finding highlights central differences between GDF15 given as a drug (pharmacology), and GDF15 released naturally in response to vigorous exercise (physiology). This is an important distinction ...
Internet access spending in public schools increases test scores, but also disciplinary problems
2021-02-16
From 2015 to 2019, public school districts in the United States invested nearly $5 billion to upgrade their Wi-Fi networks, according to EducationSuperHighway. However, in the age of COVID-19-mandated virtual learning, millions of K-12 students still lack the minimal connectivity at home for digital learning.
In a new study from the University of Notre Dame, researchers quantify how school district connectivity increases test scores, but underscore the dark side of technology -- increased behavior problems.
A $600,000 increase in annual internet access spending produces a financial gain of approximately $820,000 to $1.8 million, alongside losses from disciplinary problems totaling $25,800 to $53,440, according to new research from Yixing Chen, an ...
Evidence shows how the human brain may tap into visual cues when lacking a sense of touch
2021-02-16
Researchers at the University of Chicago, the University of Birmingham, and Bournemouth University have uncovered evidence that physical embodiment can occur without the sense of touch, thanks to a study involving two participants who lack the ability to feel touch. The research was published on Feb. 12 in END ...
Quantum leaps in understanding how living corals survive
2021-02-16
Coral reefs have thrived for millions of years in their shallow ocean water environments due to their unique partnerships with the algae that live in their tissues. Corals provide a safe haven and carbon dioxide while their algal symbionts provide them with food and oxygen produced from photosynthesis. Using the corals Orbicella annularis and Orbicella faveolate in the southern Caribbean, researchers at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology (IGB) have improved our ability to visualize and track these symbiotic interactions in the face of globally warming sea surface temperatures and ...
Despite sea-level rise risks, migration to some threatened coastal areas may increase
2021-02-16
In coming decades as coastal communities around the world are expected to encounter sea-level rise, the general expectation has been that people's migration toward the coast will slow or reverse in many places.
However, new research co-authored by Princeton University shows that migration to the coast could actually accelerate in some places despite sea-level change, contradicting current assumptions.
The research, published in Environmental Research Letters, uses a more complex behavioral decision-making model to look at Bangladesh, whose coastal zone is at high risk. They found job opportunities are most abundant in coastal cities across Bangladesh, attracting more ...
The impact of COVID-19 on motherhood
2021-02-16
It's no secret that the risk related to the coronavirus (COVID-19) increases with age, making older adults more vulnerable than younger people.
Less examined has been effects on pregnancy and birthing. According to a new study led by Sarah DeYoung, assistant professor in the Department of Sociology and Criminal Justice, and Michaela Mangum, a master's student in disaster science and management, the pandemic causes additional stress for people who were pregnant or gave birth during the pandemic. The stress was especially prevalent if the person ...
Women have a lower range of 'normal' blood pressure than men
2021-02-16
A new study from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai shows that women have a lower “normal” blood pressure range compared to men. The findings were published today in the peer-reviewed journal Circulation.Currently, established blood pressure guidelines state that women and men have the same normal healthy range of blood pressure. But the new research shows there are differences in normal blood pressure between the sexes.“Our latest findings suggest that this one-size-fits-all approach to considering blood pressure may be detrimental to a woman’s health,” ...
Study finds alligator hearts keep beating no matter what
2021-02-16
Mammals and cold-blooded alligators share a common four-chamber heart structure - unique among reptiles - but that's where the similarities end. Unlike humans and other mammals, whose hearts can fibrillate under stress, alligators have built-in antiarrhythmic protection. The findings from new research were reported Jan. 27 in the journal Integrative Organismal Biology.
"Alligator hearts don't fibrillate - no matter what we do. They're very resilient," said Flavio Fenton, a professor in the School of Physics at the Georgia Institute of Technology, researcher ...
Improving discharge process key to reducing avoidable rehospitalizations, MU study finds
2021-02-16
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Throughout her career, Lori Popejoy provided hands-on clinical care in a variety of health care settings, from hospitals and nursing homes to community centers and home health care agencies. She became interested in the area of care coordination, as patients who are not properly cared for after being discharged from the hospital often end up being readmitted in a sicker, more vulnerable state of health.
Now an associate professor in the University of Missouri Sinclair School of Nursing, Popejoy and her research team conducted a study to determine the most effective way patients ...
Researchers identify muscle factor that controls fat metabolism
2021-02-16
Metabolic diseases, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, have risen to epidemic proportions in the U.S. and occur in about 30 percent of the population. Skeletal muscle plays a prominent role in controlling the body's glucose levels, which is important for the development of metabolic diseases like diabetes.
In a recent study, published in END ...
Study finds gender disparities on National Institutes of Health study sections
2021-02-16
Investigators at the University of Chicago Medicine have found that women are less likely to be represented as chairs and reviewers on study sections for the National Institutes of Health (NIH), based on data from one review cycle in 2019. The results, published on Feb. 15 in JAMA Network Open, have implications for the distribution of federal scientific funding.
The NIH is the top source of federal funding for biomedical research in the U.S., providing critical support and guidance on the nation's research programs. The study sought to understand the gender distribution ...
Campylobacter strains exchange genes, can become more virulent and antibiotic resistant
2021-02-16
New research from North Carolina State University has found that Campylobacter bacteria persist throughout poultry production - from farm to grocery shelves - and that two of the most common strains are exchanging genetic material, which could result in more antibiotic-resistant and infectious Campylobacter strains.
Campylobacter is a well-known group of foodborne bacteria, spread primarily through consumption of contaminated food products. In humans it causes symptoms commonly associated with food poisoning, such as diarrhea, fever and cramps. However, Campylobacter infections also constitute one of the leading precursors ...
A groundbreaking solution? Polymers can protect buildings from large fault ruptures
2021-02-16
Surface rupturing during earthquakes is a significant risk to any structure that is built across a fault zone that may be active, in addition to any risk from ground shaking. Surface rupture can affect large areas of land, and it can damage all structures in the vicinity of the fracture. Although current seismic codes restrict the construction in the vicinity of active tectonic faults, finding the exact location of fault outcrop is often difficult.
In many regions around the world, engineering structures such as earth dams, buildings, pipelines, landfills, bridges, roads and railroads have been built in areas very close to active fault segments. Strike-slip fault rupture occurs when the rock masses slip past each other ...
To improve immunotherapy, researchers look to shift immune cells' access to sugar
2021-02-16
Cancer cells and immune cells share something in common: They both love sugar.
Sugar is an important nutrient. All cells use sugar as a vital source of energy and building blocks. For immune cells, gobbling up sugar is a good thing, since it means getting enough nutrients to grow and divide for stronger immune responses. But cancer cells use sugar for more nefarious ends.
So, what happens when tumor cells and immune cells battle for access to the same supply of sugar? That's the central question that Memorial Sloan Kettering researchers Taha Merghoub, Jedd Wolchok, and Roberta Zappasodi explore in a new study published February 15 in the journal Nature.
Using mouse models and data ...
Regional variation in the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on data collection
2021-02-16
Ithaca, NY--The COVID-19 pandemic has changed life as we know it all around the world. It's changed human behavior, and that has major consequences for data-gathering citizen-science projects such as eBird, run by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. This worldwide database now contains more than a billion observations and is a mainstay of many scientific studies of bird populations. Newly published research in the journal Biological Conservation finds that when human behaviors change, so do the data.
"We examined eBird data submitted during April 2020 and compared them to data from April of prior years," explains lead ...
Unlocking the mystery behind skeletal aging
2021-02-16
Researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry have identified the role a critical enzyme plays in skeletal aging and bone loss, putting them one step closer to understanding the complex biological mechanisms that lead to osteoporosis, the bone disease that afflicts some 200 million people worldwide.
The findings from their study in mice, END ...
Exercise now proven to have mental health benefits for prostate cancer
2021-02-16
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research has found that exercise not only has physical benefits for men with prostate cancer, it also helps reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Up to one in four men experience anxiety either before or after prostate cancer treatment and up to one in five report depression, although few men access the support they need.
The study, published in the Nature journal Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases, is the first randomised controlled trial to examine the long-term effects of different exercise on psychological distress in men with prostate cancer undergoing androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
Researchers randomly selected 135 prostate cancer patients aged ...
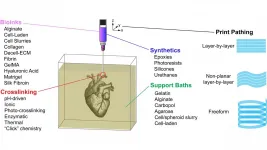
FRESH 3D-printing platform paves way for tissues, organs
2021-02-16
WASHINGTON, February 16, 2021 -- Research into 3D bioprinting has grown rapidly in recent years as scientists seek to re-create the structure and function of complex biological systems from human tissues to entire organs.
The most popular 3D printing approach uses a solution of biological material or bioink that is loaded into a syringe pump extruder and deposited in a layer-by-layer fashion to build the 3D object. Gravity, however, can distort the soft and liquid bioinks used in this method.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University provide perspective on the Freefrom Reversible Embedding of Suspended Hydrogels ...
Association of maternal cardiovascular health during pregnancy with later health of offspring in adolescence
2021-02-16
What The Study Did: The observational study examined associations between maternal cardiovascular health during pregnancy (as measured by body mass index, blood pressure, total cholesterol level, glucose level and smoking) with the later cardiovascular health of their offspring at ages 10 to 14 years old (as measured by body mass index, blood pressure, total cholesterol level and glucose level).
Authors: Amanda M. Perak, M.D., M.S., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0247)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support ...
Low-value health care drops only marginally despite effort to curb practices
2021-02-16
Spending on low-value health care among fee-for-service Medicare recipients dropped only marginally from 2014 to 2018, despite both a national campaign to better educate clinicians and increasing use of payment revisions that discourage wasteful care, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Three items accounted for two-thirds of the low-value care. Among these, prescribing opioids for acute back pain increased despite a growing national awareness of the harms caused by the drugs and the role of such prescribing in fueling the nation's opioid ...
Association of armed guards, severity of school shootings
2021-02-16
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the association between the presence of an armed guard on scene and the severity of shootings at schools kindergarten through high school.
Authors: Jillian Peterson, Ph.D., of Hamline University in St. Paul, Minnesota, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37394)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this ...
[1] ... [2629]
[2630]
[2631]
[2632]
[2633]
[2634]
[2635]
[2636]
2637
[2638]
[2639]
[2640]
[2641]
[2642]
[2643]
[2644]
[2645]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.