Proton therapy induces biologic response to attack treatment-resistant cancers
2021-02-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a novel proton therapy technique to more specifically target cancer cells that resist other forms of treatment. The technique is called LEAP, an acronym for "biologically enhanced particle therapy." The findings are published today in Cancer Research, the journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"The human body receives tens of thousands of DNA lesions per day from a variety of internal and external sources," says Robert Mutter, M.D., a radiation oncologist at Mayo Clinic and co-principal investigator of the study." Therefore, cells have evolved complex repair pathways to efficiently repair damaged DNA. Defects in these repair pathways ...
Do sweat it! Wearable microfluidic sensor to measure lactate concentration in real time
2021-02-17
With the seemingly unstoppable advancement in the fields of miniaturization and materials science, all sorts of electronic devices have emerged to help us lead easier and healthier lives. Wearable sensors fall in this category, and they have received much attention lately as useful tools to monitor a person's health in real time. Many such sensors operate by quantifying biomarkers, that is, measurable indicators that reflect one's health condition. Widely used biomarkers are heartrate and body temperature, which can be monitored continuously with relative ease. On the contrary, ...
Edible holograms could someday decorate foods
2021-02-17
Holograms are everywhere, from driver's licenses to credit cards to product packaging. And now, edible holograms could someday enhance foods. Researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a laser-based method to print nanostructured holograms on dried corn syrup films. The edible holograms could also be used to ensure food safety, label a product or indicate sugar content, the researchers say.
Most holograms are imprinted with lasers onto metal surfaces, such as aluminum, but the materials aren't edible. For foods, holograms made with nanoparticles have been proposed, but the tiny particles can generate reactive oxygen species, which might be harmful for people to eat. In a different approach, food scientists have ...
Researchers identify gene implicated in neuroblastoma, a childhood cancer
2021-02-17
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A new study by Mayo Clinic researchers has identified that a chromosome instability gene, USP24, is frequently missing in pediatric patients with neuroblastoma, an aggressive form of childhood cancer. The finding provides important insight into the development of this disease. The study is published in Cancer Research, the journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Neuroblastoma is a highly aggressive cancer that nearly exclusively affects young children," says Paul Galardy, M.D., a pediatric hematologist and oncologist at Mayo Clinic. Despite the use of multiple treatment approaches, Dr. Galardy says many children die of this disease every year.
To identify new ...
Mutation in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein renders virus up to eight times more infectious
2021-02-17
A mutation in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2--one of several genetic mutations in the concerning variants that have emerged in the United Kingdom, South Africa, and Brazil--makes the virus up to eight times more infectious in human cells than the initial virus that originated in China, according to research published in the journal END ...
Fish diet heats up marine biodiversity hotspot
2021-02-17
Scientists have discovered a never-before-seen biodiversity pattern of coral reef fishes that suggests some fishes might be exceptionally vulnerable to environmental change.
A new study shows plankton-eating coral reef fishes (planktivores) are far more diverse than others in the Indo-Australian Archipelago, a global marine biodiversity hotspot.
The findings highlight, for the first time, a unique link between the diet and distribution of species across the marine realm.
"The archipelago is one of the most complex and dynamic geological regions in the tropics," said lead author Dr Ale Siqueira from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University (Coral CoE at JCU). "And its ...
Most teen bullying occurs among peers climbing the social ladder
2021-02-17
Teens who bully, harass, or otherwise victimize their peers are not always lashing out in reaction to psychological problems or unhealthy home environments, but are often using aggression strategically to climb their school's social hierarchy, a University of California, Davis, study suggests. These findings point to the reasons why most anti-bullying programs don't work and suggest possible strategies for the future.
"To the extent that this is true, we should expect them to target not vulnerable wallflowers, but their own friends, and friends-of-friends, who are more ...
Silencing the alarm
2021-02-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Like a scene from a horror movie, tomato fruitworm caterpillars silence their food plants' cries for help as they devour their leaves. That is the finding of a multidisciplinary team of researchers, who said the results may yield insights into the abilities of crop plants -- such as tomato and soybean -- to withstand additional stressors, like climate change.
"We have discovered a new strategy whereby an insect uses saliva to inhibit the release of airborne plant defenses through direct manipulation of plant stomata," said Gary Felton, professor and head of the Department of Entomology at Penn State, noting that stomata are tiny pores on plant leaves that regulate gas exchange, including plant defensive emissions ...
Termite gut microbes could aid biofuel production
2021-02-17
Wheat straw, the dried stalks left over from grain production, is a potential source of biofuels and commodity chemicals. But before straw can be converted to useful products by biorefineries, the polymers that make it up must be broken down into their building blocks. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering have found that microbes from the guts of certain termite species can help break down lignin, a particularly tough polymer in straw.
In straw and other dried plant material, the three main polymers -- cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin -- are interwoven into a complex 3D structure. The first two polymers are polysaccharides, which can be broken down into sugars and then converted to fuel in bioreactors. ...
How and when do children recognize power and social hierarchies?
2021-02-17
Humans, like most social animals, tend to be organized hierarchically. In any group or social relationship there are always individuals who, for various reasons, significantly influence the behaviour of others. These individuals are attributed the highest status within the social group they belong to. As everyday examples of hierarchical relationships we find those of parents and children, teachers and students, bosses and workers, etc.
Given the pervasiveness of such social organization, in recent years studies have begun to ascertain how and when children begin to recognize which people have higher and which have lower social status. Specifically, ...
Columbia researchers uncover altered brain connectivity after prolonged anesthesia
2021-02-17
Prolonged anesthesia, also known as medically induced coma, is a life-saving procedure carried out across the globe on millions of patients in intensive medical care units every year.
But following prolonged anesthesia--which takes the brain to a state of deep unconsciousness beyond short-term anesthesia for surgical procedures--it is common for family members to report that after hospital discharge their loved ones were not quite the same.
"It is long known that ICU survivors suffer lasting cognitive impairment, such as confusion and memory loss, that can languish for months and, in some cases, years," said Michael Wenzel, MD, lead author of a study published in PNAS this month that documents changes associated with prolonged anesthesia in the brains of mice.
Wenzel, a former ...
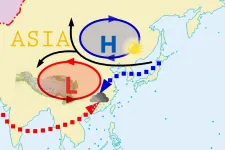
Challenge of the summer rainfall forecast skill in China: A possible solution
2021-02-17
The Mongolian Cyclone is a major meteorological driving force across southeast Asia. This cyclone is known for transporting aerosols, affecting where precipitation develops. Meteorologists are seeking ways to improve seasonal prediction of the relationship between the Mongolian cyclone and South Asia high. These features are major components of the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) and the corresponding heavy rain events. New research suggests that analyzing these phenomena in the upper-level atmosphere will enhance the summer rainfall forecast skill in China.
"The lower seasonal predictability of EASM may happen when the coupling wheel of Mongolian cyclone and South Asia high prevails over East Asia." said Prof. ...
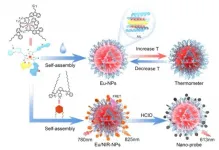
Self-assembly induced luminescence of Eu3+-complexes for bioimaging application
2021-02-17
The unique properties of rare earth (RE) complexes including ligand-sensitized energy transfer, fingerprint-like emissions and long-lived emissions, make them promising materials for many applications, such as optical encoding, luminescence imaging/sensing and time-resolved luminescence detection. In particularly, the use of RE luminescent materials for in vitro and in vivo imaging can easily eliminate the autofluorescence of organisms and any interference from background fluorescence. However, most RE complexes have poor solubility and stability in aqueous solution and their luminescence can be easily quenched by nearby X-H (X ...
Innovation predicts higher profits and stock returns
2021-02-17
A large-scale study of the link between innovation and financial performance in Australian companies has found more innovative companies post higher future profits and stock returns.
The findings highlight the significant financial benefits of innovation for companies, which in turn supports job creation and economic growth.
The study, conducted by Dr Anna Bedford, Dr Le Ma, Dr Nelson Ma and Kristina Vojvoda from the University of Technology Sydney, examined patent registrations from 1296 ASX-listed companies between 1997 and 2018.
They matched patent data with ...
High patient uptake for text message system monitoring opioid use in real-time
2021-02-17
After more than 1,000 orthopaedic procedures at a city health system, roughly 61 percent of the opioids prescribed to patients went unused, according to new research. This was discovered within a study at the Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania that showed most patients responded to text messages designed to gauge patients' usage of their prescriptions. Knowing that so many patients are comfortable texting this information to their care teams is extremely useful as medical professionals look to right-size painkiller prescriptions and reduce the amount of opioids that might be misused when they're left over. This study was published in NEJM Catalyst.
"This approach is a step toward building a dynamic learning health system that evolves ...
Timing of physical activity linked to fitness levels, CV risk for men with type 2 diabetes
2021-02-17
BOSTON -- Numerous studies have demonstrated the role of physical activity in improving heart health for patients with type 2 diabetes. But whether exercising at a certain time of the day promises an added health bonus for this population is still largely unknown. Now, research published in Diabetes Care by Brigham and Women's Hospital and Joslin Diabetes Center investigators, along with collaborators, reports a correlation between the timing of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and cardiovascular fitness and health risks for individuals who have type 2 diabetes and obesity or overweight.
The research team found that, in its study of ...
Could a nasal spray prevent coronavirus transmission?
2021-02-17
A nasal antiviral created by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons blocked transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets, suggesting the nasal spray also may prevent infection in people exposed to the new coronavirus, including recent variants
The compound in the spray--a lipopeptide developed by Matteo Porotto, PhD, and Anne Moscona, MD, professors in the Department of Pediatrics and directors of the Center for Host-Pathogen Interaction--is designed to prevent the new coronavirus from entering host cells.
The antiviral lipopeptide is inexpensive to produce, has a long shelf ...
A peptide that inhibits virus transmission among ferrets may point to a promising treatment
2021-02-17
An engineered peptide given to ferrets two days before they were co-housed with SARS-CoV-2-infected animals prevented virus transmission to the treated ferrets, a new study shows. The peptides used are highly stable and thus have the potential to translate into effective intranasal prophylaxis to reduce infection and severe SARS-CoV-2 disease in humans, the study's authors say. The SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein binds to host cells to initiate infection. This stage in the virus life history is a target for drug inhibition. Here, researchers with past success designing lipopeptide fusion inhibitors that block this critical first step of infection for SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses sought to design ...
Mimicking a chronic immune response changes the brain
2021-02-17
Tsukuba, Japan -- As March comes around, many people experience hay fever. As excessive immune responses go, most would admit that hay fever really isn't that bad. At the other end of the spectrum are severely debilitating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. A common thread in all these conditions are cytokines, molecules that cause inflammation. Recent research by the University of Tsukuba sheds light on the effect of excessive cytokines on neuronal and glial cells in the brain.
Researchers led by Professor Yosuke Takei and Assistant Professor Tetsuya Sasaki at the University of Tsukuba in ...
Exaggerated radar data above the freezing level induced by terrain
2021-02-17
Meteorologists frequently study precipitation events using radar imagery generated at both ground level and from satellite data. Radar sends out electromagnetic waves that "bounce" off ice or water droplets suspended in the air. These waves quickly return to the radar site in a process named "backscattering." Scientists have observed that backscattering reaches its peak during the melting process as water falls through the atmosphere. High backscattering typically results in warm color returns on a radar displays, indicating heavy precipitation.
However, recent case studies noted that partially frozen droplets seem ...
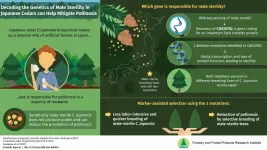
A (pollen-free) sigh of relief for Japan: The genetics of male sterility in cedar trees
2021-02-17
Cryptomeria japonica, or the Japanese cedar, is highly revered as the national tree of Japan. Locally known as "sugi," it covers over 4.5 million hectares of land, accounting for nearly half of Japan's artificial forests. However, it is also notorious for causing hay fever, with a good 26.5% of Japan's population reporting cedar pollen allergies in 2008. Over the past years, pollen allergy caused by this conifer has become a widespread social issue among Japanese residents, with many having to avoid going outdoors during pollen season.
As sterile trees cannot produce and release functional pollen, it is believed that breeding of male-sterile cedar trees could be crucial in reducing the pollen released ...
How inflammatory signalling molecules contribute to carcinogenesis
2021-02-17
A team of MedUni Vienna researchers led by Johannes A. Schmid at the Center for Physiology and Pharmacology, Institute of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research, has managed to identify a previously unknown molecular connection between an inflammatory signalling molecule and one of the main oncogenes. The study has been published in the leading journal "Molecular Cancer".
Johannes A. Schmid's working group at the Center for Physiology and Pharmacology, Institute of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research, already has many years' experience in the molecular ...
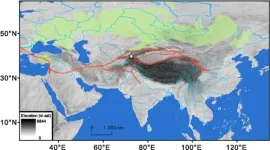
Megadroughts in arid central Asia delayed the cultural exchange along the proto-Silk Road
2021-02-17
The Silk Road was the most elaborate network of trade routes in the ancient world, linking ancient populations in East Asia to those in southwest Asia, via Central Asia. These trade routes fostered the spread of ideas, religions, and technologies over the past 2,000 years. Before the establishment of organized exchange, starting around the time of the Chinese Han Dynasty (2,223 years ago), a process of trans-Eurasian exchange was already underway through the river valleys and oases of Central Asia. The establishment of populations in the oases of the Taklimakan Desert ...
Scientists identifies novel vascular smooth muscle subsets under high hydrostatic pressure
2021-02-17
Cardiovascular system can be regarded as a mechanical system centered on the heart. Blood flow in the vascular system, hemodynamics factors within the vasculature contain wall shear stress, circumferential wall tensile stress and hydrostatic pressure. Mechanical forces play an important role in vasculature and circulation, such as rapid regulation of vascular wall elasticity, administration of vascular remodeling, and the formation of arteriosclerotic lesions. Stress stimulation within the physiological range enables cells in dynamic balance to maintain homeostasis of vascular morphology, structure and function. Inversely, abnormal stresses stimulation, such as low shear stress, disturbed shear stress and high tensile strain, can break this balance ...
Decade of reducing self-inflicted deaths in Japan hindered by COVID-19
2021-02-17
More people than expected ended their own lives in 2020 in Japan, overturning a decadelong slow decline in the nation's annual number of suicides, according to a new analysis by public health experts at the University of Tokyo. The increase in suicides was especially pronounced among women younger than 30, potentially due to the COVID-19 pandemic's disproportionate effect on part-time and travel industry employees.
"This trend of increased suicides among young women and university and high school students is very different from before COVID-19. Before COVID-19, if suicides increased, we would expect more deaths of middle-aged men," said Dr. Haruka Sakamoto, an expert in public health at the University of Tokyo and first author of the research publication in the Journal of the ...
[1] ... [2633]
[2634]
[2635]
[2636]
[2637]
[2638]
[2639]
[2640]
2641
[2642]
[2643]
[2644]
[2645]
[2646]
[2647]
[2648]
[2649]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.