Scent detection dogs can identify individuals infected with COVID-19
2021-02-11
In a recent article in the Journal of Osteopathic Medicine, authors gathered previously published research to summarize current thinking on the feasibility and efficacy of using scent detection dogs to screen for the COVID-19 virus. The researchers report that sensitivity, specificity, and overall success rates reported by the canine scent detection studies are comparable or better than the standard RT-PCR and antigen testing procedures.
These findings indicate scent detection dogs can likely be used to effectively screen and identify individuals infected with the COVID-19 virus in hospitals, senior care facilities, schools, universities, ...
New insights to past ecosystems are now available based on pollen and plant traits
2021-02-11
EUGENE, Ore. -- Feb. 11, 2021 -- Researchers have mined and combined information from two databases to link pollen and key plant traits to generate confidence in the ability to reconstruct past ecosystem services.
The approach provides a new tool to that can be used to understand how plants performed different benefits useful for humans over the past 21,000 years, and how these services responded to human and climate disturbances, including droughts and fires, said Thomas Brussel, a postdoctoral researcher in the University of Oregon's Department of Geography.
The approach is detailed in a paper published online ...
A plant's nutrient-sensing abilities can modulate its response to environmental stress
2021-02-11
Palo Alto, CA-- Understanding how plants respond to stressful environmental conditions is crucial to developing effective strategies for protecting important agricultural crops from a changing climate. New research led by Carnegie's Zhiyong Wang, Shouling, Xu, and Yang Bi reveals an important process by which plants switch between amplified and dampened stress responses. Their work is published by Nature Communications.
To survive in a changing environment, plants must choose between different response strategies, which are based on both external environmental factors and internal nutritional and energy demands. For example, a plant might either delay or accelerate its lifecycle, depending on the availability of the stored ...
Once bitten, twice shy: the neurology of why one bad curry could put us off for life
2021-02-11
A negative experience with food usually leaves us unable to stomach the thought of eating that particular dish again. Using sugar-loving snails as models, researchers at the University of Sussex believe these bad experiences could be causing a switch in our brains, which impacts our future eating habits.
Like many other animals, snails like sugar and usually start feeding on it as soon as it is presented to them. But through aversive training which involved tapping the snails gently on the head when sugar appeared, the snails' behaviour was altered and they refused to feed on the sugar, even when hungry.
When the team ...
Climate research: rapid formation of iodic particles over the Arctic
2021-02-11
FRANKFURT. More than two thirds of the earth is covered by clouds. Depending on whether they float high or low, how large their water and ice content is, how thick they are or over which region of the Earth they form, it gets warmer or cooler underneath them. Due to human influence, there are most likely more cooling effects from clouds today than in pre-industrial times, but how clouds contribute to climate change is not yet well understood. Researchers currently believe that low clouds over the Arctic and Antarctic, for example, contribute to the warming of these regions by blocking the direct radiation of long-wave heat from the Earth's surface.
All ...
Low-income middle-aged African-American women with hypertension are likely to suffer from depression
2021-02-11
Low-income middle-aged African-American women with high blood pressure very commonly suffer from depression and should be better screened for this serious mental health condition, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers found that in a sample of over 300 low-income, African-American women, aged 40-75, with uncontrolled hypertension, nearly 60 percent screened positively for a diagnosis of depression based on a standard clinical questionnaire about depressive symptoms.
The results appeared February 10 in JAMA Psychiatry.
"Our findings suggest that low-income, middle-aged African-American women with hypertension really should be screened for depression symptoms," ...
Patient education program with mental health component reduces cardiovascular disease risks
2021-02-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- People who participated in a health education program that included both mental health and physical health information significantly reduced their risks of cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases by the end of the 12-month intervention - and sustained most of those improvements six months later, researchers found.
People who participated in the integrated mental and physical health program maintained significant improvements on seven of nine health measures six months after the program's conclusion. These included, on average, a 21% ...
New study reveals biodiversity important at regional scales
2021-02-11
New research shows that biodiversity is important not just at the traditional scale of short-term plot experiments--in which ecologists monitor the health of a single meadow, forest grove, or pond after manipulating its species counts--but when measured over decades and across regional landscapes as well. The findings can help guide conservation planning and enhance efforts to make human communities more sustainable.
Published in a recent issue of Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, the multi-institutional study was led by Dr. Christopher Patrick ...
Use of mobile stroke units improves clinical outcomes
2021-02-11
STEMOs (Stroke-Einsatz-Mobile) have been serving Berlin for ten years. The specialized stroke emergency response vehicles allow physicians to start treating stroke patients before they reach hospital. For the first time, a team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin has been able to show that the dispatch of mobile stroke units is linked to improved clinical outcomes. The researchers' findings, which show that patients for whom STEMOs were dispatched were more likely to survive without long-term disability, have been published in JAMA*.
The phrase 'time is brain' emphasizes a fundamental principle from emergency medicine, namely that after stroke, every minute counts. Without ...
Astronomers confirm solar system's most distant known object is indeed Farfarout
2021-02-11
With the help of the international Gemini Observatory, a Program of NSF's NOIRLab, and other ground-based telescopes, astronomers have confirmed that a faint object discovered in 2018 and nicknamed "Farfarout" is indeed the most distant object yet found in our Solar System. The object has just received its designation from the International Astronomical Union.
Farfarout was first spotted in January 2018 by the Subaru Telescope, located on Maunakea in Hawai'i. Its discoverers could tell it was very far away, but they weren't sure exactly how far. They needed more observations.
"At that time we did not know the object's orbit as we only had the Subaru discovery observations over 24 hours, but it takes years of ...
Experts' top COVID mitigation action: Nat'l stay at home order with financial compensation
2021-02-11
A report summary released today by a team at Lehigh University led by Thomas McAndrew , a computational scientist and assistant professor in Lehigh's College of Health, shares the consensus results of experts in the modeling of infectious disease when asked to rank the top 5 most effective interventions to mitigate the spread and impact of COVID-19 in the U.S.
The report is part of an ongoing meta forecasting project aimed at translating forecasting and real world experience into actions.
McAndrew and his colleagues wanted to answer "Here is where ...
Affordable CRISPR app reveals unintended mutations at site of CRISPR gene repair
2021-02-11
Wilmington, DE, Feb. 11, 2020 -Scientists have developed an affordable, downloadable app that scans for potential unintended mistakes when CRISPR is used to repair mutations that cause disease. The app reveals potentially risky DNA alterations that could impede efforts to safely use CRISPR to correct mutations in conditions like sickle cell disease and cystic fibrosis. The development of the new tool, called DECODR (which stands for Deconvolution of Complex DNA Repair), was reported today in The CRISPR Journal by researchers from ChristianaCare's Gene Editing Institute.
"Our research has shown that when CRISPR is used to repair a gene, it also can introduce a variety of subtle changes to DNA near the site of the repair," said Eric ...
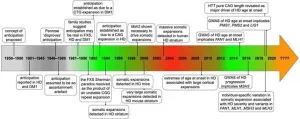
Insights into the role of DNA repair and Huntington's disease gene mutation open new avenues for drug discovery
2021-02-11
Amsterdam, February 11, 2021 - Recent genetic data from patients with Huntington's disease (HD) show that DNA repair is an important factor that determines how early or late the disease occurs in individuals who carry the expanded CAG repeat in the HTT gene that causes HD. The processes of DNA repair further expand the CAG repeats in HTT in the brain implicated in pathogenesis and disease progression. This special issue of the Journal of Huntington's Disease (JHD) is a compendium of new reviews on topics ranging from the discovery of somatic CAG repeat expansion in HD, to our current understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved ...
A new way of forming planets
2021-02-11
In the last 25 years, scientists have discovered over 4000 planets beyond the borders of our solar system. From relatively small rock and water worlds to blisteringly hot gas giants, the planets display a remarkable variety. This variety is not unexpected. The sophisticated computer models, with which scientists study the formation of planets, also spawn very different planets. What the models have more difficulty to explain is the observed mass distribution of the planets discovered around other stars. The majority have fallen into the intermediate mass category - planets with masses of several Earth masses to around that of Neptune. Even in ...
Study: Facing heat illness, dehydration risks, marching bands need access to athletic trainers
2021-02-11
LAWRENCE -- Nearly every fall, as football teams return to the field, tragic stories of players falling ill and even dying of heat trauma make the headlines. What many don't consider is that marching band members -- who don heavy uniforms and perform in the same sweltering temperatures -- may also be at risk.
A study led by the University of Kansas has measured core temperatures, hydration and sweat levels of marching band members and found that they are very much at risk and deserve access to athletic trainers for their safety -- just as players do.
The study used high tech methods to gauge band members' body core ...
SRC-3 is a novel regulator of human immune T regulatory cells
2021-02-11
A study led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine reveals a novel role of the steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3/NCOA3), a protein crucial for steroid hormone function and a prognostic marker for aggressive human breast and other cancers.
The team discovered that SRC-3 also regulates human immune T regulatory cells (Tregs), which contribute to the regulation of the body's immunological activity by suppressing the function of other immune cells, including those involved in fighting cancer. The study, which appears in the journal Scientific Reports, shows that Tregs whose SRC-3 function was eliminated failed to suppress the activity of other immune cells in the lab. The authors anticipate that their findings ...
Small mammals climb higher to flee warming temperatures in the Rockies
2021-02-11
The golden-mantled ground squirrel (Callospermophilus lateralis) is a popular sight among tourists in the Rocky Mountains--the small rodent is a photogenic creature with a striped back and pudgy cheeks that store seeds and other food.
But there's a reality that Instagram photos don't capture, said Christy McCain, an ecologist at the University of Colorado Boulder. In a new study spanning nearly 13 years, she and her colleagues discovered that the ground squirrel has joined many other small mammals in Colorado's Rocky Mountains that are making an ominous trek: They're climbing uphill to avoid warming temperatures in the state brought on by climate change.
"It's frightening," ...
Hubble uncovers concentration of small black holes
2021-02-11
Globular clusters are extremely dense stellar systems, in which stars are packed closely together. They are also typically very old -- the globular cluster that is the focus of this study, NGC 6397, is almost as old as the Universe itself. It resides 7800 light-years away, making it one of the closest globular clusters to Earth. Because of its very dense nucleus, it is known as a core-collapsed cluster.
When Eduardo Vitral and Gary A. Mamon of the Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris set out to study the core of NGC 6397, they expected to find evidence for an "intermediate-mass" black hole (IMBH). These are smaller than the supermassive black holes that lie at the cores of large galaxies, but larger than stellar-mass black holes ...
Echocardiographic screening for rheumatic heart disease in Nepal
2021-02-11
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) develops as a long term complication of childhood streptococcal angina. Latent RHD can be detected with echocardiography years before it becomes symptomatic. RHD is curable when treated early with medication.
RHD is responsible for over 300 000 deaths worldwide each year, accounting for just over two-thirds of all deaths from valvular heart diseases. RHD is disproportionally prevalent across sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia and the Pacific Islands and largely a phenomenon of marginalized communities in developing and emerging countries whereas ...
Recommendations for regional action to combat marine plastic pollution
2021-02-11
Millions of tonnes of plastic waste find their way into the ocean every year. A team of researchers from the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) in Potsdam has investigated the role of regional ocean governance in the fight against marine plastic pollution, highlighting why regional marine governance should be further strengthened as negotiations for a new global agreement continue.
In recent years, images of whales and sea turtles starving to death after ingesting plastic waste or becoming entangled in so-called ghost nets have led to a growing ...
To help keep cats from killing wildlife, add more meat and play to their day
2021-02-11
Domestic cats are a major threat to wild species, including birds and small mammals. But researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 11 now have evidence that some simple strategies can help to reduce cats' environmental impact without restricting their freedom. Their studies show that domestic cats hunt less when owners feed them a diet including plenty of meat proteins. Equally, it helps to play with them each day in ways that allow cats to mimic hunting.
"While keeping cats indoors is the only sure-fire way to prevent hunting, some owners ...
Play and meaty food reduce hunting by cats
2021-02-11
Domestic cats hunt wildlife less if owners play with them daily and feed them a meat-rich food, new research shows.
Hunting by cats is a conservation and welfare concern, but methods to reduce this are controversial and often rely on restricting cat behaviour in ways many owners find unacceptable.
The new study - by the University of Exeter - found that introducing a premium commercial food where proteins came from meat reduced the number of prey animals cats brought home by 36%, and also that five to ten minutes of daily play with an owner resulted ...
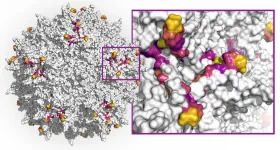
Artificial intelligence generates new diversity of AAV capsids for broader gene therapy
2021-02-11
Cambridge, MA - February 11, 2020 - Dyno Therapeutics, a biotech company applying artificial intelligence (AI) to gene therapy, today announced a publication in Nature Biotechnology that demonstrates the use of artificial intelligence to generate an unprecedented diversity of adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsids towards identifying functional variants capable of evading the immune system, a factor that is critical to enabling all patients to benefit from gene therapies. The research was conducted in collaboration with Google Research, Harvard's Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and the Harvard Medical School laboratory of George M. Church, Ph.D., a Dyno scientific co-founder. The publication is entitled "Deep diversification ...
Compounds from apples may boost brain function
2021-02-11
Natural compounds found in apples and other fruits may help stimulate the production of new brain cells, which may have implications for learning and memory, according to a END ...
Machine-learning how to create better AAV gene delivery vehicles
2021-02-11
(Boston) -- Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have become promising vehicles for delivering gene therapies to defective tissues in the human body because they are non-pathogenic and can transfer therapeutic DNA into target cells. However, while the first gene therapy products approved by the Federal Drug Administration (FDA) use AAV vectors and others are likely to follow, AAV vectors still have not reached their full potential to meet gene therapeutic challenges.
First, currently used AAV capsids - the spherical protein structures enveloping the virus' single-stranded DNA genome which can be modified to encode therapeutic genes - are limited in their ability to specifically hone in on the tissue affected by a disease and their wider distribution throughout ...
[1] ... [2640]
[2641]
[2642]
[2643]
[2644]
[2645]
[2646]
[2647]
2648
[2649]
[2650]
[2651]
[2652]
[2653]
[2654]
[2655]
[2656]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.