Factors associated with racial differences in deaths among nursing home residents with COVID-19 in US
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This observational study describes differences in the number of COVID-19 deaths by nursing home racial composition and examines the factors associated with these differences.
Authors: Rebecca J. Gorges, Ph.D., of the University of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37431)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37431?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=021021
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
What The Study Did: This article revisits the role of dermatologists in the early HIV/AIDS epidemic for the 40th anniversary of the epidemic.
Authors: Heather Milbar, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5545)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
2021-02-10
What The Study Did: Researchers examined changes in how organ donation from deceased donors differed by race and ethnicity in the United States over time.
Authors: Dorry L. Segev, M.D., Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2020.7083)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news ...
2021-02-10
Researchers in Southampton and San Francisco have developed the first compact 3D LiDAR imaging system that can match and exceed the performance and accuracy of most advanced, mechanical systems currently used.
3D LiDAR can provide accurate imaging and mapping for many applications; it is the "eyes" for autonomous cars and is used in facial recognition software and by autonomous robots and drones. Accurate imaging is essential for machines to map and interact with the physical world but the size and costs of the technology currently needed has limited LIDAR's use in ...
2021-02-10
CINCINNATI--Imagine a day when clinicians treating people with blood diseases such as leukemia or multiple myeloma can send in requests for laboratories to custom-produce specific types of blood cells to replace those affected by the disease.
That day became one step closer to reality with a new study led by experts at Cincinnati Children's that provides powerful new insights into how bone marrow tissue works.
The study, published Feb. 10, 2021 in Nature, was led by senior author Daniel Lucas, PhD, and first authors Jizhou Zhang, MD, and Qingqing Wu, PhD, from the Division of Experimental Hematology and Cancer Biology. Co-authors include a team of scientists from Cincinnati Children's and the University of Cincinnati, plus collaborators in Colorado, Texas and Michigan.
The ...
2021-02-10
Imaging planets orbiting around nearby stars, which could potentially harbour life, has become a possibility thanks to the progress made in observational methods by an international team of astronomers. First candidate: Alpha Centauri, a system similar to ours, "only" 4.3 light years away. This study is the subject of a publication in the journal Nature Communications.
Efforts to obtain direct images of exoplanets - planets outside our solar system - have so far been hampered by technological limitations, which have led to a bias towards detecting planets much larger than Jupiter, around very young stars and far from the habitable zone, the area in which a planet may have liquid water on its surface, and thus ...
2021-02-10
Researchers from the University of Seville's Nursing Department, with the collaboration of professionals from the ICU at Virgen Macarena University Hospital in Seville, have analysed the key factors in caring for critical COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic. Their study concludes that nursing care was impacted by fear and isolation, which made it difficult to maintain the human experience of health care.
The break down in the humanising trend of ICU care during this period was mainly the result of the isolation of COVID-19 patients. This, along with the personal protection equipment worn by staff to prevent becoming infected ...
2021-02-10
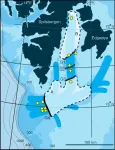
10,000 km2 of ice disappeared in a blink of an eye from an ice sheet in the Storfjorden Through offshore Svalbard, a new study shows. This dramatic break off was preceded by quite a rapid melt of 2.5 kilometres of ice a year. This parallels the current melt rates in Antarctica and Greenland and worries the scientists behind the study.
"Our measurements of the ice retreat in Storfjorden Through show that the prevailing conditions to the great break off, match what we see in Antarctica and Greenland today. It is uncanny. There are new studies published almost weekly, that show that the retreat of current ice sheets is two to four km a year and that it's speeding up." Says CAGE-professor and first author Tine Lander Rasmussen.
Climatically unstable period
The last deglaciation, ...
2021-02-10
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have a huge potential for providing devices with much smaller size and extended functionalities with respect to what can be achieved with today's silicon technologies. But to exploit this potential we must be able to integrate 2D materials into semiconductor manufacturing lines - a notoriously difficult step. A team of Graphene Flagship researchers in Sweden and Germany now reports a new method to make this work.
The technique, just published in Nature Communications by researchers from Graphene Flagship partners RWTH Aachen University, Universität der Bundeswehr ...
2021-02-10
New research from Trinity College Dublin suggests that older adults can be more focused, less impeded by anxiety and less mentally restless than younger adults. The team at the Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience (TCIN) (today, Wednesday, 10th February, 2021) show that older adults appear to mitigate the negative aspects of cognitive decline by increasing motivation and adopting more efficient strategies to suspend the wandering mind when focus is required.
The study, published in the journal Psychology and Aging (American Psychological Association) is the first to adjudicate between competing theories of age-related ...
2021-02-10
In recent years, three meta-analyses of clinical studies have come to the conclusion that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a reduction in the mortality rate from cancer of around 13 percent. Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have now transferred these results to the situation in Germany and calculated: If all Germans over the age of 50 were to take vitamin D supplements, up to 30,000 cancer deaths per year could possibly be avoided and more than 300,000 years of life could be gained - in addition, health care costs could be saved.
For several years now, scientists have been investigating the influence of an adequate supply of vitamin D on the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Factors associated with racial differences in deaths among nursing home residents with COVID-19 in US