Testing parents' patience, while treating kids' problem behavior
2014-10-14
Humans have a focus on the short term. We are more interested in a potential benefit if we can get it now.
The ability to delay gratification has been studied in children with the "marshmallow test": a child can have one treat now, or two if he or she can wait a few minutes without gobbling the first treat.
Psychologists and economists have shown that similar trends can be observed and measured in many spheres of life. They call the tendency for the perceived value of a delayed benefit to diminish "delay discounting."
Now researchers at Marcus Autism Center are studying ...
NASA satellite spots Hudhud's remnants
2014-10-14
Cyclone Hudhud made landfall in east-central India on Oct. 12 and caused a lot of damage and several fatalities as it moved inland and weakened to a remnant low pressure area. NASA saw those remnants on Oct. 14.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Indochina, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided picture proof that the remnants of Typhoon Hudhud were still over India, Nepal, and China. Aqua passed over the region on Oct. 14 at 08:05 UTC (4:05 a.m. EDT).
Infrared satellite imagery and multispectral satellite imagery indicated ...
EMA open to discuss use of complementary methodologies for rare cancers
2014-10-14
On 3 October 2014, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) hosted a meeting with representatives of Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) to discuss RCE's recent publication of a consensus paper on the methodology of clinical trials in rare cancers (1).
Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) is a multi stakeholder initiative promoted by ESMO (representing healthcare professionals, patients and industry) dedicated to putting rare cancers on the European political agenda. In their consensus document, RCE argue that a higher degree of uncertainty should be accepted for regulatory as well as clinically ...
New information about how neurons act could lead to brain disorder advancements
2014-10-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Neurons are electrically charged cells, located in the nervous system, that interpret and transmit information using electrical and chemical signals. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that individual neurons can react differently to electrical signals at the molecular level and in different ways—even among neurons of the same type. This variability may be important in discovering underlying problems associated with brain disorders and neural diseases such as epilepsy.
"Genetic mutations found in neurological disorders ...
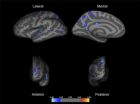
Orphanage care linked to thinner brain tissue in regions related to ADHD
2014-10-14
Under the rule of dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, thousands of Romanian children were placed in overcrowded orphanages with bleak conditions and minimal human contact. Even after the 1989 revolution, the legacy of institutionalization continued. Only recently has research and public concern over early childhood environments caused changes in policies.
University of Washington research on children who began life in these institutions shows that early childhood neglect is associated with changes in brain structure. A paper published this month in Biological Psychiatry shows ...
Corruption of the health care delivery system
2014-10-14
LEBANON, NH – The foundation of evidence-based research has eroded and the trend must be reversed so patients and clinicians can make wise shared decisions about their health, say Dartmouth researchers in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Drs. Glyn Elwyn and Elliott Fisher of The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice are authors of the report in which they highlight five major problems set against a backdrop of "obvious corruption." There is a dearth of transparent research and a low quality of evidence synthesis. ...
Personalised treatment for stress-related diabetes
2014-10-14
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden are testing a treatment for type 2 diabetes which targets the disease mechanism itself - and not just the symptoms. For the first time, knowledge about the individual patient's genetic risk profile is being used. The treatment completely restores the capacity to secrete insulin, which is impaired by the risk gene.
"The concept of treatment personalised to the individual's risk profile has great potential. Our results show that it is possible to block the effects of a common risk gene for type 2 diabetes", says Anders Rosengren, ...
Are there enough fish to go around?
2014-10-14
Scientists from the University of York have released a report highlighting the gap between declining wild fish supplies and healthy eating advice recommending more seafood.
While the health benefits of eating fish have become better appreciated in recent years, many wild fish stocks continue to be overfished.
In a study published in Marine Pollution Bulletin, Dr Ruth Thurstan, now a Research Fellow at the University of Queensland, and Professor Callum Roberts, Professor of Marine Conservation at the University of York, used historical fisheries data and population ...
Immune cells in the liver drive fatty liver disease and liver cancer
2014-10-14
The results of their research have been published as the cover story of the renowned medical journal Cancer Cell.
Fatty liver disease – alongside fatty liver due to massive alcohol consumption – is mainly caused by excessive consumption of fat and sugar combined with a lack of exercise or a sedentary life style. This is referred to as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). If NAFLD becomes chronic – e.g. through the constant uptake of high lipids and high sugar combined with lack of excercise a chronic inflammatory response is triggered in the liver ...
Parkinson: How toxic proteins stress nerve cells
2014-10-14
This news release is available in German. FRANKFURT Parkinson's Disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder. In Germany alone, almost half a million people are affected. The focus of the disease is the progressive degeneration of dopamine-producing nerve cells in a certain region of the midbrain, the substantia nigra. Misfolded proteins are the cause. Until recently, it was unclear why damage is confined to specific nerve cells. A team or researchers led by Frankfurt neurophysiologists has now defined how this selective disease process begins using ...
Researchers identify potential drug that could help treat cystic fibrosis
2014-10-14
From an early age, the lungs of individuals with cystic fibrosis (CF) are colonised and infected by bacteria, a common example being S. aureus. These bacterial infections cause the lungs to become inflamed, infected, and can eventually lead to permanent lung damage. Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute previously showed that an enzyme called Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase C (SMaseC) produced by the S. aureus bacterium may harm the health of CF patients. Now, they have discovered an inhibitor for this pathogenic bacterial ...
More physical activity improved school performance
2014-10-14
Just two hours of extra physical activity each week can improve school performance. This has been shown by a study of approximately 2,000 twelve-year-olds carried out by scientists at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg.
The scientists Lina Bunketorp Käll, Michael Nilsson and Thomas Linden, at the Centre for Brain Repair and Rehabilitation at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, have tested the hypothesis that increased physical activity stimulates learning and improves school performance.
In the study, published in the scientific periodical ...
The neuroscience of holding it
2014-10-14
Wherever you are right now: squeeze your glutes. Feel that? You just also contracted your pelvic floor too, whether you wanted to or not.
Scientists studying the source of chronic abdominal and pelvic floor pain found an unexpected connection in the brain between the pelvic floor – the muscle responsible for, among other things, keeping you from peeing your pants – and various muscles throughout the body. They've found some evidence for a link as far away as the toes (try tapping a toe and see if you feel the clench), but the strongest link so far is with ...
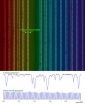
Rediscovering Venus to find faraway earths
2014-10-14
WASHINGTON, Oct. 14, 2014—Astronomers Chih-Hao Li and David Phillips of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics want to rediscover Venus—that familiar, nearby planet stargazers can see with the naked eye much of the year.
Granted, humans first discovered Venus in ancient times. But Li and Phillips have something distinctly modern in mind. They plan to find the second planet again using a powerful new optical device installed on the Italian National Telescope that will measure Venus' precise gravitational pull on the sun. If they succeed, their first-of-its-kind ...
US college students eat their vegetables. Really?!
2014-10-14
U.S. college students do better than their counterparts in the United Kingdom when it comes to physical activity, a healthy diet and less smoking, according to new research published in the latest issue of the journal Education and Health.
"Among U.S. students, we see greater consumption of fruits and vegetables, more participation in organized sports, and less smoking," said American University Prof. Stacey Snelling, a lead study author. "Participation in organized sports and exercise could reflect the more formal focus on physical activity at the college level that ...
Teachable moments about climate change
2014-10-14
First-hand experience of extreme weather often makes people change their minds about the realities of climate change. That's because people are simply more aware of an extreme weather event the closer they are to its core, and the more intense the incidence is. So says Peter Howe of Utah State University in the US, who led a study in Springer's journal Climatic Change Letters about people's ability to accurately recall living through extreme weather events. It also focused on how people's proximity to such events – the so-called "shadow of experience" – aids ...
New 'tree of life' traces evolution of a mysterious cotinga birds
2014-10-14
Ithaca, N.Y.—They are some of the brightest, loudest, oddest-looking, least-understood birds on the planet. Some have bulbous crests, long fleshy wattles, or Elvis-worthy pompadours in addition to electric blue, deep purple, or screaming orange feathers. But thanks to a comprehensive new evolutionary "tree of life" generated for the tropical cotinga family of South America, the door is now open to new discoveries about the more than 60 species in this amazingly diverse group of birds.
"Our study provides comprehensive insight into how nearly all the cotinga species ...
Current models for predicting outcomes after mild traumatic brain injury perform poorly
2014-10-14
New Rochelle, NY, October 14, 2014—For the 5-15% of patients with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) who will have lingering physical, behavioral, or cognitive problems 3 to 6 months after their injury, identification of this at-risk population is essential for early intervention. Existing models used to predict poor outcomes after mTBI are unsatisfactory, according to a new study, and new, more relevant predictive factors are different than those used in cases of moderate or severe TBI, as described in the study published in Journal of Neurotrauma, a peer-reviewed ...
New treatment designed to save more eyes from cancer
2014-10-14
VIDEO:
Some children with advanced retinoblastoma are not good candidates for conventional intraocular ophthalmic infusion therapy -- too often making removal of the eye the only viable treatment for saving their...
Click here for more information.
CINCINNATI – Doctors at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have developed a new technique for treating the eye cancer retinoblastoma to improve the odds for preventing eye loss, blindness or death in children with ...
NASA sees Hurricane Gonzalo head toward Bermuda
2014-10-14
Tropical Storm Gonzalo intensified into a hurricane late on Monday, Oct. 14 and is expected to become a major hurricane as it moves toward Bermuda. NASA's Aqua satellite saw powerful thunderstorms within the center of the storm that were dropping heavy rainfall.
At 5 pm EDT, on Oct. 13 Gonzalo had become a hurricane. At that time, the center of the storm was just 20 miles southeast of St. Martin. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) noted that maximum sustained winds had increased to near 75 mph (120 kph) and additional strengthening was forecast. Gonzalo continued moving ...
Discovery of the Benešov meteorites 20 years after the bolide event
2014-10-14
Astronomy & Astrophysics is publishing the spectacular discovery of meteorite fragments 20 years after the corresponding bolide was seen in the skies of the Czech Republic. This discovery was made possible by reanalyzing the trajectory, which moved the impact line by 330 meters. Interestingly, the meteorites found on the ground are of different types, pointing to a parent asteroid of heterogeneous composition.
Collisions of meter-sized meteoroids with the Earth's atmosphere are relatively rare, occurring about 40 times a year. They cause very spectacular events, known ...
Unique catalysts for hydrogen fuel cells synthesized in ordinary kitchen microwave oven
2014-10-14
Swedish and Chinese researchers show how a unique nano-alloy composed of palladium nano-islands embedded in tungsten nanoparticles creates a new type of catalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction, the most important reaction in hydrogen fuel cells. Their results are published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The world's rapidly growing demand for energy and the requirement of sustainable energy production calls for an urgent change in today's fossil fuel based energy system. Research groups worldwide work intensively to develop novel advanced energy ...
Fires dot the Ukraine countryside
2014-10-14
Numerous fires (marked with red dots) are burning in the Ukraine, likely as a result of regional agricultural practices. The body of water at the lower left of this true-color Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image is the Sea of Azov. The Sea is bordered by Ukraine to the northwest, west and southwest and by Russia to the northeast, east, and southeast. To its left is the Black Sea.
The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the soil ...
Prescribed burns in Western Australia
2014-10-14
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Aqua satellite detected fires burning in Western Australia on October 14, 2014. Matching these hot spots up to the the prescribed fire burns on Western Australia's parks and wildlife site: http://www.dpaw.wa.gov.au/management/fire/prescribed-burning/burns these fires are most likely prescribed burns used to limit bushfire outbreaks. According to the Government of Australia's Department of Parks and Wildlife, "Prescribed burning is the process of planning and applying fire to a predetermined area, under ...
Early detection window when pancreatic cancer is in the family
2014-10-14
Pancreatic cancer likely takes between 10 and 20 years to develop, providing the potential for a very "broad window" of intervention if detected early, which may be possible for people who inherit a predisposition, say Australian clinical researchers.
Dr Jeremy Humphris and Professor Andrew Biankin1, from Sydney's Garvan Institute of Medical Research, analysed medical histories and tumour samples taken from a cohort of 766 pancreatic cancer patients, operated on between 1994 and 20122. Roughly 9% of these patients had a first-degree relative (parent or sibling) with ...
[1] ... [3269]
[3270]
[3271]
[3272]
[3273]
[3274]
[3275]
[3276]
3277
[3278]
[3279]
[3280]
[3281]
[3282]
[3283]
[3284]
[3285]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.