University of Calgary research leads to brain cancer clinical trial
2014-10-14
Researchers at the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain Institute (HBI) and Southern Alberta Cancer Research Institute (SACRI) have made a discovery that could prolong the life of people living with glioblastoma – the most aggressive type of brain cancer. Samuel Weiss, PhD, Professor and Director of the HBI, and Research Assistant Professor Artee Luchman, PhD, and colleagues, published their work today in Clinical Cancer Research, which is leading researchers to start a human phase I/II clinical trial as early as Spring 2015.
Researchers used tumour cells derived ...
Thyroid carcinoma: Biomarker reveals cancer cause
2014-10-14
CLIP2 serves as a radiation marker: After exposure to radiation from radioiodine, both the genetic activity and the protein expression are increased, as the scientists' studies were able to substantiate.
CLIP2 appears to be particularly significant in the development of tumours in the thyroid gland after radiation exposure. The team around Martin Selmansberger, Dr. Julia Heß, Dr. Kristian Unger and Prof. Dr. Horst Zitzelsberger from the Radiation Cytogenetics Research Unit at the Helmholtz Zentrum München discovered a connection between high CLIP2 levels and ...
CWRU studies how women in recovery manage personal networks with family and friend users
2014-10-14
Substance abuse counselors and social workers often recommend recovering addicts establish new networks of non-using friends and supporters.
But researchers at Case Western Reserve University's social work school found, for many women in poverty, it's not so easy to drop the users in their lives. Many are people that women depend on for childcare, transportation and other necessities to live.
"People in the women's networks might be family members, parents or children, who also use drugs. It's hard to cut these people out of their lives," said Elizabeth M. Tracy, ...
A neurotic personality increases the risk of Alzheimer's disease
2014-10-14
Women who worry, cope poorly with stress and/or experience mood swings in middle age run a higher risk of developing Alzheimer disease later in life. This is the conclusion of a study carried out at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, that followed 800 women for nearly 40 years.
The study, which will be published in the scientific journal Neurology, started in 1968 when 800 women in Gothenburg took a personality test that measured, among other things, their levels of neuroticism and extroversion.
High Stress
The women in the study stated whether they ...
CWRU dental survey finds dental anxiety leads cause for moderate sedation
2014-10-14
Dental anxiety can be so extreme for some patients that a simple cotton swab on the gums makes them flinch. And others, fearful of pain, simply avoid seeing the dentist, according to a new study by Case Western Reserve University dental researchers on when and how to use sedatives during dental procedures.
As a result, dentistry is responding with sedation techniques to make fearful and anxious patients more comfortable.
For a master's thesis in endodontics, Madhavi Setty, DDS, MSD, set out to understand how dental specialties like endodontics for root canals, periodontics ...
NASA sees a weaker Typhoon Vongfong near Amami Oshima
2014-10-14
The once-powerful Category 5 Typhoon Vongfong has fortunately weakened to a barely Category 1 typhoon as it approaches the big islands of Japan. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite and NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Vongfong on Oct. 11 and noticed the heaviest precipitation was north of the center.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Vongfong on Oct. 11 at 17:23 UTC (1:23 p.m. EDT) and captured an infrared image of the storm from the VIIRS instrument. The VIIRS instrument showed that the strongest thunderstorms that stretched highest in the atmosphere were in the ...
NASA sees Cyclone Hudhud approaching India's coast
2014-10-14
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cyclone Hudhud as it was nearing east-central India's coastline on Oct. 11.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua captured infrared data on the storm on Oct. 11 at 07:23 UTC (3:23 a.m. EDT) that showed cloud top temperatures had dropped, indicating stronger uplift and stronger thunderstorms. That's an indication that the storm has strengthened in the last day.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that animated infrared satellite imagery shows the eye feature has become cloud filled while the overall structure ...
Satellite sees cold front headed to absorb Bermuda's Tropical Storm Fay
2014-10-14
VIDEO:
This animation of imagery from NOAA GOES-East satellite from Oct. 10-12 shows the movement of Tropical Storm Fay in the Atlantic an approaching cold front over the eastern US....
Click here for more information.
Tropical Storm Fay is affecting Bermuda on Sunday, Oct. 12, but a cold front over the eastern U.S. is expected to absorb the storm over the next day or two. Both were seen in an image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite.
On Saturday, Oct. 11, Tropical Depression 7 ...
NASA sees newborn Tropical Storm Gonzalo form and threaten Caribbean islands
2014-10-14
Tropical Storm Gonzalo formed quickly on Oct. 12 just east of the Leeward Islands, triggering tropical storm warnings for many islands. NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured an image of the newborn storm on Sunday, Oct. 12, and Tropical Storm Fay northeast of Bermuda.
The GOES East satellite is a geostationary satellite managed by NOAA. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland the NASA/NOAA GOES Project creates images and animations and today's visible image, taken at 2:45 p.m. EDT showed a smaller Gonzalvo east of the Leeward Islands while Fay was ...
One gene links susceptibility to rare infections with predisposition to autoimmune disease
2014-10-14
The mutations were familiar, but the patients' conditions seemed baffling at first. A team lead by Rockefeller University researchers had linked variations in an immune gene to rare bacterial infections. Shortly afterward, Chinese scientists told them of three children in that country with mutated versions of the same gene. However, the Chinese children had no history of the severe bacterial infections. Instead, they had seizures and unusual calcium deposits deep in their brains.
This discrepancy led to the discovery of an immune protein with paradoxical roles: It both ...
Antibiotic resistance: Bacterial defense policies
2014-10-14
High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy has now revealed in unprecedented detail the structural changes in the bacterial ribosome which results in resistance to the antibiotic erythromycin.
Multiresistant bacterial pathogens that are insensitive to virtually all available antibiotics are one of the major public-health challenges of our time. The question of how resistance to various antibiotics develops is the focus of research being carried out by Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich biochemist Daniel Wilson and his colleagues. As they report in the journal ...
Scientists identify potential cause for 40 percent of pre-term births
2014-10-14
Scientists from Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) and UCL (University College London) have identified what they believe could be a cause of pre-term premature rupture of the fetal membrane (PPROM), which accounts for 40 per cent of pre-term births, and is the main reason for infant death world-wide.
The researchers, whose work was funded by the charity Wellbeing of Women, used bioengineering techniques to test the effect of repetitive stretch on tissues of the amniotic membrane which surrounds and protects the baby prior to birth.
They found that stretching of the ...
Balancing renewable energy costs
2014-10-14
New York | Heidelberg, 13 October 2014 Increasing reliance on renewable energies is the way to achieve greater CO2 emission sustainability and energy independence. As such energies are yet only available intermittently and energy cannot be stored easily, most countries aim to combine several energy sources. In a new study in EPJ Plus, French scientists have come up with an open source simulation method to calculate the actual cost of relying on a combination of electricity sources. Bernard Bonin from the Atomic Energy Research Centre CEA Saclay, France, and colleagues demonstrate ...
Ultra-fast charging batteries that can be 70 percent recharged in just 2 minutes
2014-10-14
Scientists from Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) have developed a new battery that can be recharged up to 70 per cent in only 2 minutes. The battery will also have a longer lifespan of over 20 years.
Expected to be the next big thing in battery technology, this breakthrough has a wide-ranging impact on many industries, especially for electric vehicles which are currently inhibited by long recharge times of over 4 hours and the limited lifespan of batteries.
This next generation of lithium-ion batteries will enable electric vehicles to charge 20 times ...
Older women more likely to have multiple health conditions
2014-10-14
In the context of an aging population, the number of cases of people with multimorbidity, or multiple health conditions, is increasing, creating significant healthcare challenges. Now, the first comprehensive systematic review in this field has found higher levels of multimorbidity in women. Equally as importantly, it has revealed the poor quality of evidence on this increasingly critical area of healthcare.
The review's main author, Professor Jose M Valderas, NIHR Clinician Scientist of the University of Exeter Medical School, is calling for better quality research to ...
Bio-inspired 'nano-cocoons' offer targeted drug delivery against cancer cells
2014-10-14
Biomedical engineering researchers have developed a drug delivery system consisting of nanoscale "cocoons" made of DNA that target cancer cells and trick the cells into absorbing the cocoon before unleashing anticancer drugs. The work was done by researchers at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
"This drug delivery system is DNA-based, which means it is biocompatible and less toxic to patients than systems that use synthetic materials," says Dr. Zhen Gu, senior author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor in ...
Cushing's syndrome: LCSB researchers characterize a new tumor syndrome
2014-10-14
Scientists at the Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine (LCSB) of the University of Luxembourg have published their findings that mutations in a gene known as "ARMC5" promote the growth of benign tumours in the adrenal glands and on the meninges: ARMC5 appears to belong to the group of so-called tumour suppressor genes. It is the first time in years that scientists have characterized such a gene.
The ARMC5 gene was discovered by independent workgroups studying benign tumours – so-called adrenal adenomas – in connection with Cushing's syndrome. In this ...
University of Leicester archaeologists discover bronze remains of Iron Age chariot
2014-10-14
University of Leicester archaeologists have made a "once-in-a-career" discovery of the decorated bronze remains of an Iron Age chariot.
A team from the University's School of Archaeology and Ancient History has unearthed a hoard of rare bronze fittings from a 2nd or 3rd century BC chariot which appears to have been buried as a religious offering.
The archaeologists found the remains during their ongoing excavation of the Burrough Hill Iron Age hillfort, near Melton Mowbray, Leicestershire.
The School has led a 5-year project there since 2010, giving archaeology students ...
Disputed theory on Parkinson's origin strengthened
2014-10-14
Parkinson's disease is strongly linked to the degeneration of the brain's movement center. In the last decade, the question of where the disease begins has led researchers to a different part of the human anatomy. In 2003, the German neuropathologist Heiko Braak presented a theory suggesting that the disease begins in the gut and spreads to the brain. The idea has since, despite vocal critics, gained a lot of ground. Researchers at Lund University in Sweden now present the first direct evidence that the disease can actually migrate from the gut to the brain.
The so-called ...
Magnetic superconductor: Strange bedfellows
2014-10-14
Chemists at Ludwig-Maximilias-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have synthesized a ferromagnetic superconducting compound that is amenable to chemical modification, opening the route to detailed studies of this rare combination of physical properties.
Superconductivity and ferromagnetism – the "normal" form of magnetism, such as that found in the familiar horseshoe magnet – are like chalk and cheese: They generally don't go together. Ferromagnets are magnetic because the parallel alignment of adjacent electron spins in the iron atoms generates a strong internal ...
Rising sea levels of 1.8 meters in worst-case scenario
2014-10-14
The climate is getting warmer, the ice sheets are melting and sea levels are rising – but how much? The report of the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2013 was based on the best available estimates of future sea levels, but the panel was not able to come up with an upper limit for sea level rise within this century. Now researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute and their colleagues have calculated the risk for a worst-case scenario. The results indicate that at worst, the sea level would rise a maximum of 1.8 meters. The results are published ...
The chemistry of pizza (video)
2014-10-14
WASHINGTON, Oct. 13, 2014 — Whether it's a plain cheese, a deep-dish stacked with meats or a thin-crust veggie delight, there's just something about pizza that makes it delicious. There's a lot of chemistry that goes into everything from dough to sauce to toppings to, of course, cheese. There's also a very specific chemical reaction at work on every single slice, no matter what toppings you choose. Check out the latest episode here: http://youtu.be/tOkCgAwhh9U.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to ...
Oral drug reduces formation of precancerous polyps in the colon, UB researchers find
2014-10-14
BUFFALO, N.Y. — An oral biologic medication has successfully treated chronic, precancerous inflammation in the intestine, according to results of an animal study authored by an MD/PhD student in the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences.
The study is featured on the cover of the current issue of Cancer Research; it was published online ahead of print in September. The journal's editors characterized the study's findings as "striking."
Inflammatory cells in the colon, or polyps, are very common after the age of 50. The average 60-year-old ...
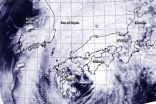
NASA satellite sees wind shear affecting Tropical Storm Vongfong
2014-10-14
Tropical Storm Vongfong continues to weaken as it tracks across the big islands of Japan, and NASA satellite data showed that westerly wind shear is taking its toll on the storm's structure.
On Oct. 12 at 0500 UTC (1 a.m. EDT), the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Vongfong approaching Japan. Despite weakening to a tropical storm, Vongfong still appeared to have an eye as its northeastern quadrant blanketed the large island of Kyushu, Japan. By 11 a.m. EDT, Maximum sustained winds had dropped to 55 knots (63 mph/102 kph). ...
Tropical Storm Gonzalo triggered many warnings in Eastern Caribbean
2014-10-14
The Eastern Caribbean islands were getting the brunt of Tropical Storm Gonzalo as the storm slowly moved through on Oct. 13. NASA's Terra satellite and NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided data on the storm. Gonzalo is the sixth named storm in the Atlantic Ocean Hurricane Season.
On Oct. 12 at 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT), NASA's Terra satellite flew over Tropical Storm Gonzalo while it moved over the Lesser Antilles. The MODIS instrument captured a visible image of the storm that showed a concentration of strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation and in a thick ...
[1] ... [3272]
[3273]
[3274]
[3275]
[3276]
[3277]
[3278]
[3279]
3280
[3281]
[3282]
[3283]
[3284]
[3285]
[3286]
[3287]
[3288]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.