Set of molecules found to link insulin resistance in the brain to diabetes
2014-10-09
A key mechanism behind diabetes may start in the brain, with early signs of the disease detectable through rising levels of molecules not previously linked to insulin signaling, according to a study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai published today in the journal Cell Metabolism.
Past studies had found that levels of a key set of protein building blocks, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), are higher in obese and diabetic patient, and that this rise occurs many years before someone develops diabetes. Why and how BCAA breakdown may be ...
New computational approach finds gene that drives aggressive brain cancer
2014-10-09
NEW YORK, NY (October 9, 2014)—Using an innovative algorithm that analyzes gene regulatory and signaling networks, Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) researchers have found that loss of a gene called KLHL9 is the driving force behind the most aggressive form of glioblastoma, the most common form of brain cancer. The CUMC team demonstrated in mice transplants that these tumors can be suppressed by reintroducing KLHL9 protein, offering a possible strategy for treating this lethal disease. The study was published today in the online issue of Cell.
The team used ...
Scientists discover a 'good' fat that fights diabetes
2014-10-09
VIDEO:
Salk researchers explain how a new class of lipids may be tied to diabetes.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston have discovered a new class of molecules—produced in human and mouse fat—that protects against diabetes.
The researchers found that giving this new fat, or lipid, to mice with the equivalent of type 2 diabetes lowered their elevated blood sugar, ...
Long-term treatment success using gene therapy to correct a lethal metabolic disorder
2014-10-09
New Rochelle, NY, October 9, 2014—Excessive and often lethal blood levels of bilirubin can result from mutations in a single gene that are the cause of the metabolic disease known as Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1 (CNS1). A new gene therapy approach to correcting this metabolic error achieved significant, long-lasting reductions in bilirubin levels in a mouse model of CNS1 and is described in an Open Access article in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the Human Gene Therapy website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/hum.2013.233. ...
Clove oil tested for weed control in organic Vidalia sweet onion
2014-10-09
TIFTON, GA – Weed control is one of the most challenging aspects of organic crop production. Most growers of certified organic crops rely heavily on proven cultural and mechanical weed control methods while limiting the use of approved herbicides. A new study of herbicides derived from clove oil tested the natural products' effectiveness in controlling weeds in Vidalia® sweet onion crops.
"Cultivation with a tine weeder and hand weeding are the primary tools currently used for weed control in organic sweet onion (Allium ceps)," explained scientist W. Carroll ...
Wild tomato species focus of antioxidant study
2014-10-09
IZMIR, TURKEY – Tomatoes are known to be rich in antioxidants such as vitamin C, lycopene, β-carotene, and phenolics. Antioxidants, substances capable of delaying or inhibiting oxidation processes caused by free radicals, are of interest to consumers for their health-related contributions, and to plant breeders for their ability to provide plants with natural resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. While tomato domestication and breeding programs have typically focused on traits such as fruit weight, color, shape, and disease resistance, scientists are now ...
Study examines effect of antibiotic susceptibility for patients with bloodstream infection
2014-10-09
In an analysis of more than 8,000 episodes of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections, there were no significant differences in the risk of death when comparing patients exhibiting less susceptibility to the antibiotic vancomycin to patients with more vancomycin susceptible strains of S. aureus, according to a study published in JAMA. The study is being released early online to coincide with the IDWeek 2014 meeting.
Staphylococcus aureus is among the most common causes of health care-associated infection throughout the world. It causes a wide range of infections, ...
Hospitalized children benefit from antibiotic stewardship programs
2014-10-09
PHILADELPHIA – Hospitalized children go home sooner and are less likely to be readmitted when the hospital has an antibiotic stewardship program that's dedicated to controlling antibiotic prescriptions and treatment, according to a study being presented at IDWeek 2014™. The study is the first to show the benefits of such programs on children's health.
Antibiotic stewardship programs are increasingly being used to manage how and when antibiotics are being prescribed in hospitals and other health care facilities across the country. Often led by epidemiologists or ...
Chemists uncover new role of a key base in organic synthesis
2014-10-09
An international team of chemists has discovered a new piece to the puzzle of how a powerful base used in organic synthesis, cesium carbonate, plays a pivotal role during a catalytic reaction.
The research, published by the Journal of the American Chemical Society, was led by Jamal Musaev, a theoretical chemist at Emory University, and Ken Itami, an experimental chemist from Nagoya University in Japan. Sun Yat-Sen University in Guangzhou, China, also contributed to the findings.
Many organic chemistry reactions are acid/base reactions, involving the exchange of positively ...
NASA eyes Tropical Cyclone Hudhud as Warnings posted for East-Central India
2014-10-09
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Hudhud on Oct. 9 and took a picture of the storm that showed it was still somewhat elongated, but more organized than the previous day. Another NASA satellite provided the hint of a developing eye. Warnings for winds, rain and surf are already in effect for the northern Andhra Pradesh coast and south Odisha coastline of eastern India as Hudhud approaches.
Tropical Cyclone Hudhud formed on Oct. 8 and began moving from east to west across the Bay of Bengal, Northern Indian Ocean.
On Oct. 9 at 07:45 UTC (3:45 a.m. EDT), ...
Discovery of new subatomic particle sheds light on fundamental force of nature
2014-10-09
The discovery of a new particle will "transform our understanding" of the fundamental force of nature that binds the nuclei of atoms, researchers argue.
Led by scientists from the University of Warwick, the discovery of the new particle will help provide greater understanding of the strong interaction, the fundamental force of nature found within the protons of an atom's nucleus.
Named Ds3*(2860)ˉ, the particle, a new type of meson, was discovered by analysing data collected with the LHCb detector at CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC) .
The new particle ...
Satellite movie shows Hurricane Simon's remnants moving through US
2014-10-09
VIDEO:
This animation from NOAA's GOES-East satellite over Oct. 6 through Oct. 9 shows Hurricane Simon's landfall and movement into the US Southwest.
Click here for more information.
NOAA's GOES-East satellite has captured visible and infrared images of Hurricane Simon since birth, and a new animation of the data created by NASA shows Simon's landfall in Mexico and movement into the U.S. Southwest. The remnants are expected to move into the U.S. central Plains and Midwest ...
Eleanor Roosevelt, a radio pioneer, perceived as both 'ordinary' and 'expert'
2014-10-09
Following her husband Franklin D. Roosevelt's death in April 1945, Eleanor Roosevelt was freed from the constraints of the White House and eagerly expanded her career. She used radio to communicate on a wide variety of issues and became a radio pioneer, broadcasting from the 1920s, starting with her own radio show in 1932. She spoke on US domestic radio, the BBC, Voice of America, on French radio (in French) and Italian radio (in Italian). She was also interviewed in Spanish and German. In 1948 she hosted a twice weekly radio program with her daughter Anna on ABC.
This ...
'Data smashing' could unshackle automated discovery
2014-10-09
ITHACA, N.Y. – A little known secret in data mining is that simply feeding raw data into a data analysis algorithm is unlikely to produce meaningful results, say the authors of a new Cornell University study.
From recognizing speech to identifying unusual stars, new discoveries often begin with comparison of data streams to find connections and spot outliers. But most data comparison algorithms today have one major weakness – somewhere, they rely on a human expert to specify what aspects of the data are relevant for comparison, and what aspects aren't. But ...
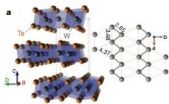
Unstoppable magnetoresistance
2014-10-09
Mazhar Ali, a fifth-year graduate student in the laboratory of Bob Cava, the Russell Wellman Moore Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, has spent his academic career discovering new superconductors, materials coveted for their ability to let electrons flow without resistance. While testing his latest candidate, the semimetal tungsten ditelluride (WTe2), he noticed a peculiar result.
Ali applied a magnetic field to a sample of WTe2, one way to kill superconductivity if present, and saw that its resistance doubled. Intrigued, Ali worked with Jun Xiong, a student ...
College athletes in contact sports more likely to carry MRSA, study finds
2014-10-09
PHILADELPHIA – Even if they don't show signs of infection, college athletes who play football, soccer and other contact sports are more likely to carry the superbug methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), suggests a study on MRSA and athletes, which is being presented at IDWeek 2014™. This puts them at higher risk for infection and increases the likelihood of spreading the bug, which can cause serious and even fatal infections. The study is the first to observe college athletes who are not part of a larger MRSA outbreak.
Contact sport athletes were more ...
When judging art, men and women stand apart
2014-10-09
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- The sexes show stark differences in how they evaluate art, finds a new study co-authored by a Michigan State University marketing scholar.
Men seem to focus more on the artist's background and authenticity, while women pay more attention to the art itself.
The study, which appears in the journal Psychology & Marketing, is the first to investigate how important an artist's "brand" is to average consumers when they appraise art. Turns out, that personal brand is very important, a finding that has implications for the $64 billion art market and ...
'Superglue' for the atmosphere
2014-10-09
This news release is available in German.
It has been known for several years that sulfuric acid contributes to the formation of tiny aerosol particles, which play an important role in the formation of clouds. The new study by Kürten et al. shows that dimethylamine can tremendously enhance new particle formation. The formation of neutral (i.e. uncharged) nucleating clusters of sulfuric acid and dimethylamine was observed for the first time.
Previously, it was only possible to detect neutral clusters containing up to two sulfuric acid molecules. However, ...
New advances in additive manufacturing using laser solid forming to produce metallic parts
2014-10-09
New Rochelle, NY, October 9, 2014—Laser Solid Forming (LSF) is an innovative method for direct fabrication of metallic components in additive manufacturing. Renowned researchers Weidong Huang and Lin Xin, from China's Northwestern Polytechnical University, Shaanxi, describe their progress and applications with LSF technology and the excellent mechanical properties of the metallic parts produced in a Review article in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the 3D Printing ...
All that glitters is... slimy? Gold nanoparticles measure the stickiness of snot
2014-10-09
WASHINGTON, Oct. 9, 2014—Some people might consider mucus an icky bodily secretion best left wrapped in a tissue, but to a group of researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, snot is an endlessly fascinating subject. The team has developed a way to use gold nanoparticles and light to measure the stickiness of the slimy substance that lines our airways. The new method could help doctors better monitor and treat lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
The research team will present their work at The ...
Drinking decaf coffee maybe good for the liver
2014-10-09
Researchers from the National Cancer Institute report that decaffeinated coffee drinking may benefit liver health. Results of the study published in Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, show that higher coffee consumption, regardless of caffeine content, was linked to lower levels of abnormal liver enzymes. This suggests that chemical compounds in coffee other than caffeine may help protect the liver.
Coffee consumption is highly prevalent with more than half of all Americans over 18 drinking on average three cups each day ...
Cellular 'power grid' failure triggers abnormal heart rhythms after a heart attack
2014-10-09
VIDEO:
The 'heart attack in a dish' experiment reveals that the mitochondria--or cellular powerhouses--of heart muscle cells flicker and oscillate following heart attack and disrupt the heart's entire electrical system...
Click here for more information.
Heart attack survivors often experience dangerous heart rhythm disturbances during treatment designed to restore blood flow to the injured heart muscle, a common and confounding complication of an otherwise lifesaving intervention. ...
The mathematics behind the Ebola epidemic
2014-10-09
This news release is available in German. The Ebola epidemic in West Africa appears to be spiralling out of control. More than ever, local and global health authorities want to know how the epidemic will develop and, above all, how to prevent it from spreading further. Certain parameters help them to determine this, such as the reproductive number, which is the average number of infections caused by a single infected individual. The incubation and infectious periods are also highly relevant; i.e. the time from infection to the onset of symptoms and the time from onset ...
New increase in antimicrobial use in animals in Denmark
2014-10-09
Antimicrobial usage in animals in Denmark continued to increase in 2013 – mainly due to an increased use in pigs. However, antimicrobial use in pigs is still 12% lower than in 2009. In general, livestock received very little of the critically important antimicrobials, which are used to treat humans. These findings appear in the annual DANMAP report from Statens Serum Institut and the National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark. DANMAP is the Danish integrated antimicrobial resistance monitoring and research programme.
In 2013, the total use of antimicrobials ...
Climate change alters the ecological impacts of seasons
2014-10-09
This news release is available in German. Only recently, the UN Climate Summit came together in New York to further address the necessary measures to protect the Earth from a dramatic climate change. It has long been recognised that an increase of the average temperature will cause rising oceans and thus flooded landscapes. Particularly, regions close to the coasts are endangered. While it is well known that climate change has increased average temperatures, it is less clear how temperature variability has altered with climate change.
Postdoctoral fellow George Wang, ...
[1] ... [3279]
[3280]
[3281]
[3282]
[3283]
[3284]
[3285]
[3286]
3287
[3288]
[3289]
[3290]
[3291]
[3292]
[3293]
[3294]
[3295]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.