Around the world in 400,000 years: The journey of the red fox
2014-10-07
Imagine attempting to trace your genetic history using only information from your mother's side. That's what scientists studying the evolution of the red fox had been doing for decades.
Now, University of California, Davis, researchers have for the first time investigated ancestry across the red fox genome, including the Y chromosome, or paternal line. The data, compiled for over 1,000 individuals from all over the world, expose some surprises about the origins, journey and evolution of the red fox, the world's most widely distributed land carnivore.
"The genome and ...
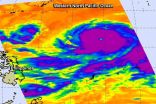
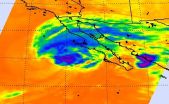
NASA eyes Super typhoon Vongfong
2014-10-07
Typhoon Vongfong strengthened into a Super typhoon on Tuesday, October 7 as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.
On Oct. 7 at 0429 UTC (12:29 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Super typhoon Vongfong. AIRS data very strong thunderstorms circling Vongfong's clear 27 nautical-mile wide eye. Those cloud top temperatures were colder than -62F/-53C indicating that they were high in the troposphere and capable of generating heavy rainfall. The bands of thunderstorms circling ...
Very low concentrations of heavy metals and antibiotics contribute to resistance
2014-10-07
New Swedish research shows that plasmids containing genes that confer resistance to antibiotics can be enriched by very low concentrations of antibiotics and heavy metals. These results strengthen the suspicion that the antibiotic residues and heavy metals (such as arsenic, silver and copper) that are spread in the environment are contributing to the problems of resistance. These findings have now been published in the highly regarded journal mBio.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing medical problem that threatens human health worldwide. Why and how these resistant bacteria ...
Efficacy of potential therapy for autoimmune disorder of muscle weakness
2014-10-07
PHILADELPHIA — Nearly 60,000 Americans suffer from myasthenia gravis (MG), a non-inherited autoimmune form of muscle weakness. The disease has no cure, and the primary treatments are nonspecific immunosuppressants and inhibitors of the enzyme cholinesterase.
Now, a pair of researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have developed a fast-acting "vaccine" that can reverse the course of the disease in rats, and, they hope, in humans. Jon Lindstrom, PhD, a Trustee Professor in the department of Neuroscience led the study, published ...
Advocating weight diversity
2014-10-07
A new review of the way health care professionals emphasise weight to define health and wellbeing suggests the approach could be harmful to patients.
Author of the review article, Dr Rachel Calogero of the School of Psychology at the University of Kent, together with experts from other institutions and organisations, recommends that this approach, known as 'weight-normative', is replaced by health care professionals, public health officials and policy-makers with a 'weight-inclusive' approach.
Weight-inclusive approaches, such as the Health At Every Size initiative, ...
Hospitalized patients don't wash their hands enough, study finds
2014-10-07
Hamilton, ON (October 7, 2014) – Hospital visitors and staff are greeted with hand sanitizer dispensers in the lobby, by the elevators and outside rooms as reminders to wash their hands to stop infections, but just how clean are patients' hands?
A study led by McMaster University researcher Dr. Jocelyn Srigley has found that hospitalized patients wash their hands infrequently. They wash about 30 per cent of the time while in the washroom, 40 per cent during meal times, and only three per cent of the time when using the kitchens on their units. Hand hygiene rates ...
Probiotic yogurt could help protect against heavy metal poisoning
2014-10-07
LONDON, ON – New research shows probiotic yogurt can reduce the uptake of certain heavy metals and environmental toxins by up to 78% in pregnant women. Led by Scientists at Lawson Health Research Institute's Canadian Centre for Human Microbiome and Probiotic Research, this study provides the first clinical evidence that a probiotic yogurt can be used to reduce the deadly health risks associated with mercury and arsenic.
Environmental toxins like mercury and arsenic are commonly found in drinking water and food products, especially fish. These contaminants are particularly ...
The 'cyberwar' against cancer gets a boost from intelligent nanocarriers
2014-10-07
Two years ago, Prof. Eshel Ben-Jacob of Tel Aviv University's School of Physics and Astronomy and Rice University's Center for Theoretical Biological Physics made the startling discovery that cancer, like an enemy hacker in cyberspace, targets the body's communication network to inflict widespread damage on the entire system. Cancer, he found, possessed special traits for cooperative behavior and used intricate communication to distribute tasks, share resources, and make decisions.
In research published in the Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of ...
Satellite sees Tropical Storm Simon over Baja California
2014-10-07
NOAA's GOES-West satellite took a picture of Tropical Storm Simon weakening over Mexico's Baja California.
On Oct. 7, a Tropical Storm Watch was in effect for Punta Abreojos to Punta Eugenia, Mexico. The National Hurricane Center expects Simon to produce storm total rainfall amounts of 3 to 5 inches with isolated amounts around 8 inches through Wednesday, Oct. 8, across northern portions of the Baja California Peninsula and the state of Sonora in northwestern Mexico. Over the next few days, storm total rainfall amounts of 1 to 2 inches with isolated amounts of around ...
Anorexia/bulimia: A bacterial protein implicated
2014-10-07
Eating disorders (ED) such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and binge eating disorder affect approximately 5-10% of the general population, but the biological mechanisms involved are unknown. Researchers at Inserm Unit 1073, "Nutrition, inflammation and dysfunction of the gut-brain axis" (Inserm/University of Rouen) have demonstrated the involvement of a protein produced by some intestinal bacteria that may be the source of these disorders. Antibodies produced by the body against this protein also react with the main satiety hormone, which is similar in structure. According ...
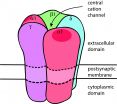
Gothenburg researchers identify molecule that protects women's eggs
2014-10-07
A new study led by Professor Kui Liu at the University of Gothenburg has identified the key molecule 'Greatwall kinase' which protects women's eggs against problems that can arise during the maturation process.
In order to be able to have a child, a woman needs eggs that can grow and mature. One of these eggs is then fertilised by a sperm, forming an embryo. During the maturation process, the egg needs to go through a number of stages of reductional division, called meiosis. If problems occur during any of these stages, the woman can become infertile. Around 10-15% of ...
Closing the gap: Extreme desert gecko spotted on salt-flats in central Oman
2014-10-07
The Gulf Sand gecko is a remarkable desert reptile in that it is the only lizard found habitually on sabkha substrate across large parts of the eastern Arabian Peninsula. These arid salt flats constitute one of the harshest habitats on earth, due to their extraordinary salinity.
The Gulf gecko, Pseudoceramodactylus khobarensis, belongs to a genus with a single species, and it is well adapted to this substrate featuring spiny scales beneath the fingers, long extremities and swollen nostrils.
Data on its distribution range showed a conspicuous gap between eastern United ...
Equation helps assess blood flow to flaps for breast reconstruction
2014-10-07
October 7, 2014 – For women undergoing breast reconstruction using the advanced "DIEP" technique, a simple formula can reliably tell whether there will be sufficient blood flow to nourish the DIEP flap, reports a paper in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open®, the official open-access medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Drs Joseph Richard Dusseldorp and David G. Pennington of Macquarie University Hospital, Sydney, performed an ultrasound study to see how well the flap viability index (FVI) equation predicted blood ...
Study: Stroke-fighting drug offers potential treatment for traumatic brain injury
2014-10-07
DETROIT – The only drug currently approved for treatment of stroke's crippling effects shows promise, when administered as a nasal spray, to help heal similar damage in less severe forms of traumatic brain injury.
In the first examination of its kind, researchers Ye Xiong, Ph.D, Zhongwu Liu, Ph.D., and Michael Chopp, Ph.D., Scientific Director of the Henry Ford Neuroscience Institute, found in animal studies that the brain's limited ability to repair itself after trauma can be enhanced when treated with the drug tPA, or tissue plasminogen activator.
"Using this ...
Sharing makes both good and bad experiences more intense
2014-10-07
Undergoing an experience with another person — even if we do it in silence, with someone we met just moments ago — seems to intensify that experience, according to new research published in Psychological Science. The research shows that people who share experiences with another person rate those experiences as more pleasant or unpleasant than those who undergo the experience on their own.
"We often think that what matters in social life is being together with others, but we've found it also really matters what those people are doing," says psychological scientist ...
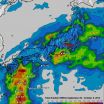
NASA adds up Japan's soaking rains from Typhoon Phanfone
2014-10-07
Typhoon Phanfone packed heavy rainfall as it brushed over Japan and NASA's TRMM satellite identified where the rain fell. That data was used to make a map of rainfall totals.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite has the ability to calculate rainfall rates within storms as it orbits around the Earth's tropics from space. TRMM data can also be used to create rainfall maps that show how much rain has fallen over given areas.
Phanfone was a powerful super typhoon with sustained wind speed estimated at 130 knots (150 mph) as it approached Japan but ...
Back off: Female chimps stressed out by competing suitors
2014-10-07
Being the center of attention can have its drawbacks. For female chimpanzees, being around too many rowdy males is disadvantageous when foraging for food, an effect that can ultimately interfere with her reproductive ability. These are some of the findings of an 11-year-long study of wild East African chimpanzees in Uganda, led by Melissa Emery Thompson of the University of New Mexico in the US. It is published in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
Female chimpanzees have an exceedingly slow reproductive schedule, and only give birth every five to ...
Why do women struggling with low sexual desire not seek treatment?
2014-10-07
New Rochelle, NY, October 7, 2014—Low sexual desire is common among both pre- and post-menopausal women. It can cause personal distress, harm relationships, and have a negative impact on body image and self confidence. Yet few women seek medical care for this condition, and the reasons are explored in a timely article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jwh.2014.4743 until November 7, ...
Potty training before age 2 linked to increased risk of later wetting problems
2014-10-07
Winston-Salem, N.C. – Sept. Oct. 7, 2014 – Children who start toilet training before age 2 have a three times higher risk of developing daytime wetting problems later, according to new research at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
"Parents who train their children early to meet preschool deadlines, to save landfills from diapers or because they think toddlers are easier to train should know there can be serious repercussions," says lead author Steve Hodges, M.D., an associate professor of pediatric urology at Wake Forest Baptist.
The study, reported ...
Can physical therapy before hip or knee replacement surgery improve outcomes?
2014-10-07
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Physical therapy after total hip (THR) or total knee replacement (TKR) surgery is standard care for all patients. A new study, appearing in the October 1 issue of the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS), also found that physical therapy before joint replacement surgery, or "prehabilitation," can diminish the need for postoperative care by nearly 30 percent, saving an average of $1,215 per patient in skilled nursing facility, home health agency or other postoperative care.
Approximately 50 million U.S. adults have physician-diagnosed arthritis. ...
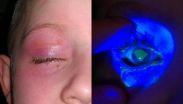
Liquid detergent pods pose risk to children's eye health
2014-10-07
San Francisco, CA, October 7, 2014 – Liquid laundry and dishwasher detergent pods are an emerging source of chemical exposure in children. When squeezed or bitten into, these pods can burst and send detergent into the mouth, nose, and eyes. A new report published in the current issue of the Journal of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) cautions that these products should be kept away from children because the bursting detergent pods can cause significant corneal injury.
Detergent pods may offer a simpler way to do laundry, ...
Sugar linked to memory problems in adolescent rats
2014-10-07
Studying rats as model subjects, scientists found that adolescents were at an increased risk of suffering negative health effects from sugar-sweetened beverage consumption.
Adolescent rats that freely consumed large quantities of liquid solutions containing sugar or high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in concentrations comparable to popular sugar-sweetened beverages experienced memory problems and brain inflammation, and became pre-diabetic, according to a new study from USC. Neither adult rats fed the sugary drinks nor adolescent rats who did not consume sugar had the same ...
The unexamined diversity in the 'Coral Triangle'
2014-10-07
Research on zoantharians, a group of animals related to corals and anemones, by researchers James Reimer of the University of the Ryukyus in Okinawa, Japan, Angelo Poliseno of Universita Politecnica delle Marche in Italy, and Bert Hoeksema from Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Netherlands, has demonstrated how little we know about marine diversity in the so-called "center of marine biodiversity" located in the central Indo-Pacific Ocean. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The researchers utilized previously collected specimens from Indonesia, ...
Sandwiches are a major contributor to dietary sodium intake
2014-10-07
Philadelphia, PA, October 6, 2014 – Sandwiches make up a substantial part of the American diet and are a significant contributor to daily energy and sodium intake. By closely analyzing data from the federal nationwide dietary intake survey known as "What We Eat in America NHANES 2009-2010," a team of Department of Agriculture (USDA) researchers found that on any given day 49 percent of U.S. adults eat at least one sandwich, and sandwiches account for one-fifth of total daily sodium intake. The study was conducted by USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) investigators ...
Tropical Storm Simon says, 'US Southwest is an 'arm's reach'
2014-10-07
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows what looks like an arm from Tropical Storm Simon's northern quadrant, reaching over Baja California to mainland Mexico. Forecasters at the National Hurricane Center noted that Simon is just an "arm's reach" to the southern U.S. and expect rainfall and rough surf to affect that area of the country.
On Oct. 6 at 0347 UTC (Oct. 5 at 11:47 p.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder called AIRS that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data on Simon. On band of thunderstorms wrapping into ...
[1] ... [3286]
[3287]
[3288]
[3289]
[3290]
[3291]
[3292]
[3293]
3294
[3295]
[3296]
[3297]
[3298]
[3299]
[3300]
[3301]
[3302]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.