(Press-News.org) A new study based on real-time audio recordings of parents practicing corporal punishment discovered that spanking was far more common than parents admit, that children were hit for trivial misdeeds and that children then misbehaved within 10 minutes of being punished.
Advocates of corporal punishment have outlined best practices for responsible spanking. But real-time audio from this study revealed that parents fail to follow the guidelines, said psychologist George Holden, who is lead author on the study and a parenting and child development expert at Southern Methodist University, Dallas.
The real-time audio interactions revealed that parents were not always calm, as the guidelines recommend, but instead were often angry when they spanked or hit their child; they didn't spank as a last resort; and they gave spankings for minor infractions, not just serious misbehavior. And while many spanking advocates recommend hitting children no more than twice, parents in the audio recordings were slapping and hitting their children more often.
"From the audio, we heard parents hitting their children for the most extraordinarily mundane offenses, typically violations of social conventions," Holden said. "Also, corporal punishment wasn't being used as a last resort. On average, parents hit or spanked just half a minute after the conflict began."
Parents who used corporal punishment in the audio commonly violated three of the six "use" guidelines the researchers examined: Spank infrequently, use it only for serious misbehavior, and only as a last resort.
"The recordings show that most parents responded either impulsively or emotionally, rather than being intentional with their discipline," Holden said.
The findings are reported in "Eavesdropping on the Family: A Pilot Investigation of Corporal Punishment in the Home," which was published online April 15 at http://bit.ly/1eLnRZs (requires login) by the American Psychological Association before it appears in a final print and online issue of Journal of Family Psychology.
Parents agreed to wear tape recorders to capture home interactions
The unique recordings captured parent and child interactions in 33 families over the course of four to six evenings. Parents volunteered to wear the recorders; most were mothers who were home with their children after a day's work. The recordings captured 41 instances of corporal punishment, mainly during everyday activities such as fixing supper and bathing children.
More than 80 percent of the moms were married and had completed more education than the general population. About 60 percent were white and worked outside the home, and their children averaged just shy of 4 years old.
In 90 percent of the incidents, noncompliance was the immediate cause, such as sucking fingers, eating improperly, getting out of a chair, and going outside without permission. In 49 percent of the incidents, the parent sounded angry prior to spanking or hitting. On average, less than 30 seconds elapsed from the time when parents initiated nonviolent discipline to when they used corporal punishment. In 30 of the 41 incidents, the children misbehaved again within 10 minutes of being hit or spanked. The youngest child hit was 7 months old. One mother hit her child 11 times in a row.
Most remarkably, the researchers noted an unusual finding: The rate of corporal punishment exceeded estimates in other studies, which relied on parents self-reporting. Those studies found that American parents of a 2-year-old typically report they spank or slap about 18 times a year.
"The average rate we observed using the real-time audio equates to an alarming 18 times a week," Holden said.
Holden co-authored the study with Paul A. Williamson and Grant W.O. Holland, also of SMU. Funding for the study was provided by the nonprofit Timberlawn Psychiatric Research Foundation, Dallas.
"Although spanking advocates may acknowledge these incidents as inappropriate use of corporal punishment, evidence indicates that mothers who report their child gets spanked are also more likely to report physical abuse of that child," the authors noted.
INFORMATION:
Follow @SMUResearch on Twitter.
For more information, http://www.smuresearch.com.
SMU is a nationally ranked private university in Dallas founded 100 years ago. Today, SMU enrolls nearly 11,000 students who benefit from the academic opportunities and international reach of seven degree-granting schools. For more information see http://www.smu.edu.
SMU has an uplink facility located on campus for live TV, radio, or online interviews. To speak with an SMU expert or book an SMU guest in the studio, call SMU News & Communications at 214-768-7650.
Real-time audio of corporal punishment shows kids misbehave within 10 minutes of spanking
First-of-its-kind study finds that parents ignored best practices recommended by spanking advocates
2014-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breaking bad mitochondria
2014-04-15
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a mechanism that explains why people with the hepatitis C virus get liver disease and why the virus is able to persist in the body for so long.
The hard-to-kill pathogen, which infects an estimated 200 million people worldwide, attacks the liver cells' energy centers – the mitochondria – dismantling the cell's innate ability to fight infection. It does this by altering cells mitochondrial dynamics.
The study, published in today's issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy ...
Computerized counseling reduces HIV-1 viral load, sexual transmission risk
2014-04-15
Antiretroviral therapy (ART), the primary type of treatment for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), can reduce sexual transmission, prevent illness, and increase longevity and quality of life for patients. However, according to current data, only an estimated 77-percent of U.S patients on ART therapy have suppressed viral loads. This suggests patients' adherence to the current ART treatment regiments is in need of improvement to reduce the viral load and also to lower sexual transmission risk behaviors.
Now, new research from faculty affiliated with New York University's ...
Rethink education to fuel bioeconomy, says report
2014-04-15
Microbes can be highly efficient, versatile and sophisticated manufacturing tools, and have the potential to form the basis of a vibrant economic sector. In order to take full advantage of the opportunity microbial-based industry can offer, though, educators need to rethink how future microbiologists are trained, according to a report by the American Academy of Microbiology.
"Industrial microbiology is experiencing a Renaissance; microorganisms make products ranging from the tightly regulated pharmaceuticals industry to large-scale production of commodity chemicals and ...
UC research illuminates 'touchy' subject
2014-04-15
By solving a long standing scientific mystery, the common saying "you just hit a nerve" might need to be updated to "you just hit a Merkel cell," jokes Jianguo Gu, PhD, a pain researcher at the University of Cincinnati (UC).
That's because Gu and his research colleagues have proved that Merkel cells— which contact many sensory nerve endings in the skin—are the initial sites for sensing touch.
"Scientists have spent over a century trying to understand the function of this specialized skin cell and now we are the first to know … we've proved the Merkel cell to be a primary ...
Predicting bioavailable cadmium levels in soils
2014-04-15
New Zealand's pastoral landscapes are some of the loveliest in the world, but they also contain a hidden threat. Many of the country's pasture soils have become enriched in cadmium. Grasses take up this toxic heavy metal, which is then eaten by the cattle and sheep that graze them. The problem is not unique to New Zealand; cadmium-enriched soils being reported worldwide.
The concern is that if cadmium concentrations rise to unsafe levels in meat and dairy products, human health and New Zealand's agricultural economy could be jeopardized. That so far hasn't happened.
But, ...
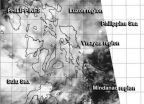
Remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah still raining on Philippines
2014-04-15
Several regions in the south and central Philippines have flood advisories as the remnants of now dissipated Tropical Depression Peipah continue to linger over the country. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite got a look at the remnant clouds from its orbit in space on April 15.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a look at Peipah's remnant clouds on April 15 at 5:44 a.m. EDT. VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. The VIIRS ...
Study examines Vitamin D deficiency and cognition relationship
2014-04-15
WINSTON-SALEM – April 15, 2014 – Vitamin D deficiency and cognitive impairment are common in older adults, but there isn't a lot of conclusive research into whether there's a relationship between the two.
A new study from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center published online ahead of print this month in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society enhances the existing literature on the subject.
"This study provides increasing evidence that suggests there is an association between low vitamin D levels and cognitive decline over time," said lead author Valerie Wilson, ...
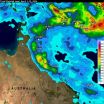
NASA's TRMM Satellite adds up Tropical Cyclone Ita's Australian soaking
2014-04-15
After coming ashore on April 11, Tropical Cyclone Ita dropped heavy rainfall over the weekend that caused flooding in many areas of northeastern Australia's state of Queensland. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM gathered data on rainfall that was used to create a rainfall map at NASA.
TRMM is a satellite managed by both NASA and JAXA, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Hal Pierce created a TRMM-based near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). The TMPA precipitation ...
The key to easy asthma diagnosis is in the blood
2014-04-15
MADISON, Wis. — Using just a single drop of blood, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers has developed a faster, cheaper and more accurate tool for diagnosing even mild cases of asthma.
This handheld technology — which takes advantage of a previously unknown correlation between asthmatic patients and the most abundant type of white blood cells in the body — means doctors could diagnose asthma even if their patients are not experiencing symptoms during their visit to the clinic.
The team described its findings in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
Girls' mental health suffers when romances unfold differently than they imagined
2014-04-15
WASHINGTON, DC, April 15, 2014 — A new study reveals that for adolescent girls, having a romantic relationship play out differently than they imagined it would has negative implications for their mental health.
"I found that girls' risk of severe depression, thoughts of suicide, and suicide attempt increase the more their relationships diverge from what they imagined," said the study's author Brian Soller, an assistant professor of sociology and a senior fellow of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico.
"Conversely, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
[Press-News.org] Real-time audio of corporal punishment shows kids misbehave within 10 minutes of spankingFirst-of-its-kind study finds that parents ignored best practices recommended by spanking advocates