Seniors run for the suburbs in their golden years
2014-10-14
Montreal, October 14, 2014 — By 2040, there will be more than three times the number of Americans aged 80+ than there were in 2000. Condo towers crowding city skylines seem to reflect builders' hopes that the grey set will head to urban centres for increased services and better transit options. But new research from Concordia University suggests that the opposite is more likely to occur.
In a study recently published in the Journal of Transport Geography, researcher Zachary Patterson uses census data to map seniors' moving habits. What emerges is a clear pattern: ...
NASA's Aqua satellite sees Extra-Tropical Storm Vongfong pulling away from Hokkaido, Japan
2014-10-14
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Extra-Tropical Storm Vongfong on Oct. 4 as it was moving away from Hokkaido, Japan, the northernmost of the big islands. Vongfong transitioned into an extra-tropical storm early on Oct. 4 as its core changed from warm to cold.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Vongfong over Japan on Oct. 14 at 03:15 UTC as it was southeast of the island of Hokkaido, Japan. The image showed that south of the center of circulation was almost devoid ...
Future computers could be built from magnetic 'tornadoes'
2014-10-14
Magnetic materials form the basis of most hard disc drives as they are able to store data. A team from the University of Sheffield's Faculty of Engineering have been investigating whether they could also be used to perform calculations, and so take on the role of a computer's central processing unit (CPU).
Lead researcher, Dr Tom Hayward, explains: "Magnetic materials are useful for data storage because they can retain information without consuming energy. A computer built around a CPU made of magnetic materials should be much more power efficient than existing technologies, ...
Institutional rearing may increase risk attention-deficit disorder
2014-10-14
Philadelphia, PA, October 14, 2014 – Over the past decades, we have seen numerous tragic examples where the failure of institutions to meet the needs of infants for social contact and stimulation has led to the failure of these infants to thrive.
Infancy and childhood are critical life periods that shape the development of the cortex. A generation of research suggests that enriched environments, full of interesting stimuli to explore, promote cortical development and cognitive function. In contrast, deprivation and stress may compromise cortical development and ...
New discovery will enhance yield and quality of cereal and bioenergy crops
2014-10-14
ST. LOUIS, MO – October 13, 2014 –A team of scientists led by Thomas Brutnell, Ph.D., director of the Enterprise Rent-A-Car Institute for Renewable Fuels at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center have developed a new way of identifying genes that are important for photosynthesis in maize, and in rice. Their research helps to prioritize candidate genes that can be used for crop improvement and revealed new pathways and information about how plants fix carbon. The findings, published in "Comparative analyses of C4 and C3 photosynthesis in developing leaves of ...
Scientists link ALS progression to increased protein instability
2014-10-14
LA JOLLA, CA—October 13, 2014—A new study by scientists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI), Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and other institutions suggests a cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease.
"Our work supports a common theme whereby loss of protein stability leads to disease," said John A. Tainer, professor of structural biology at TSRI and senior scientist at Berkeley Lab, who shared senior authorship of the new research with TSRI Professor Elizabeth Getzoff.
Getzoff, Tainer and ...
Taking infestation with a grain of salt
2014-10-14
Twenty years ago, biologists Kathy Boyer and Joy Zedler, then researchers at San Diego State University, speculated that too many insects feeding on cordgrass in the marshes of San Diego Bay could endanger the grass, and in turn endanger the bay wildlife that relies on it.
Picking up where Boyer and Zedler left off, SDSU biologist Jeremy Long is currently further exploring the dimensions of this relationship. What he's found so far suggests that it's not a simple as saying too many insects spell death for a host plant. Instead, his research suggests a complex interplay ...
Fermented milk made by Lactococcus lactis H61 improves skin of healthy young women
2014-10-14
Philadelphia, PA, October 13, 2014 – There has been much interest in the potential for using probiotic bacteria for treating skin diseases and other disorders. Japanese researchers have now found that milk that has been fermented using a probiotic dairy starter can also benefit the skin of young healthy women, reports the Journal of Dairy Science®.
Probiotics have been defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization-World Health Organization as "live microorganisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host."
"Although ...
Study reveals how deadly MERS virus enters human cells
2014-10-14
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have uncovered details of how the deadly Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) enters host cells, and offer possible new avenues for treatment.
The study, appearing online this month in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, discovered that a common protease enzyme known as furin activates the MERS-CoV to fuse with cell membranes and enter host cells.
The researchers, Gary Whittaker, Cornell professor of virology, and Jean Millet, a postdoctoral associate in Whittaker's lab, suggest ...
Turtle tumors linked to excessive nitrogen from land-based pollution
2014-10-14
Hawai'i's sea turtles are afflicted with chronic and often lethal tumors caused by consuming non-native algae "superweeds" along coastlines where nutrient pollution is unchecked. The disease that causes these tumors is considered the leading cause of death in endangered green sea turtles. The new research was just published in the scientific journal PeerJ.
Turtles that graze on blooms of invasive seaweeds end up with a diet that is rich in a particular amino acid, arginine, which promotes the virus that creates the tumors. Scientists at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa ...
QUT study helps outdoor workers reduce their skin cancer risk
2014-10-14
Skin cancer is one of the biggest fears for one in two outdoor workers and when the boss and staff work together the sun safe message gets through, a QUT study has found.
The study, which found more than 50 per cent of outdoor workers rated UV radiation exposure at work as one of their biggest concerns, also identified how a workplace intervention could improve workers' behaviours and attitudes towards sun protection to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
QUT in collaboration with Cancer Council Queensland and Curtin University worked with 14 Queensland outdoor workplaces ...
Mediterranean diet, olive oil and nuts can help reverse metabolic syndrome
2014-10-14
For people with metabolic syndrome, a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil or nuts may help reverse the condition, indicate findings from a clinical trial published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
About 25% of adults around the world have metabolic syndrome. The syndrome exists in the presence of three or more factors such as large waist circumference, high blood pressure, low HDL-cholesterol, high levels of triglycerides and high blood sugar concentrations that can increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease and death.
Spanish ...
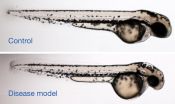
For one family, zebrafish help provide genetic answers
2014-10-14
Research in zebrafish has helped identify the cause of an unknown genetic disorder affecting a boy and two of his uncles, scientists report in an article published October 14 in the journal Genetics.
The findings demonstrate the growing importance of zebrafish as laboratory models of rare diseases. Such models allow geneticists to make sense of the deluge of candidate disease genes being uncovered by advances in sequencing technologies. Although rare diseases are uncommon individually, together they affect as many as 25 million people in the United States.
The project ...
Side effects of cancer prevention surgery can be helped with education program
2014-10-14
BOSTON –– More women are having ovary-removing surgery as a cancer prevention measure, but many are often unaware of sexual or psychological side effects of the procedure. A new study by researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute shows a half-day educational program can help successfully deal with these issues by educating women on how to address them.
The program taught women how to manage some of the physical and emotional difficulties that can follow ovary-removing surgery and helped many participants resume satisfying sexual activity and reduce feelings ...
Scientists create new protein-based material with some nerve
2014-10-14
Berkeley — Scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, have taken proteins from nerve cells and used them to create a "smart" material that is extremely sensitive to its environment. This marriage of materials science and biology could give birth to a flexible, sensitive coating that is easy and cheap to manufacture in large quantities.
The work, to be published Tuesday, Oct. 14, in the journal Nature Communications, could lead to new types of biological sensors, flow valves and controlled drug release systems, the researchers said. Biomedical applications ...
Feeling guilty or ashamed? Think about your emotions before you shop
2014-10-14
Suppose you grabbed a few cookies before heading out to the grocery store and start to feel guilty or ashamed about breaking your diet. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, feeling guilty might find you comparing calories in different cartons of ice cream. Feeling ashamed might keep you from buying any ice cream in the first place.
"We examined the emotions of guilt and shame and found that when consumers feel guilty, they tend to focus on concrete details at the expense of the bigger picture. On the other hand, when consumers feel ashamed, they ...
Marketing an innovative new product? An exciting product launch could hurt sales
2014-10-14
Should every successful product launch involve some sort of dazzling spectacle? A new study in the Journal of Consumer Research tells us that this might be a great way to market an upgrade, but a flashy launch could backfire if a new product is truly innovative.
"The accepted wisdom is that consumers get excited about new and unique products they cannot immediately understand. However, these feelings of excitement can quickly change to tension and anxiety if we can't ultimately make sense of what a product does, especially if we are in a stimulating retail environment," ...
Jobs plentiful for college grads
2014-10-14
EAST LANSING, Mich. — The job market for new college graduates is red hot.
After several years of modest growth, hiring is expected to jump a whopping 16 percent for newly minted degree-holders in 2014-15, according to key findings from Recruiting Trends. The annual survey, by Michigan State University economist Phil Gardner, is the nation's largest with nearly 5,700 companies responding.
"Employers are recruiting new college graduates at levels not seen since the dot-com frenzy of 1999-2000," said Gardner, director of MSU's Collegiate Employment Research Institute. ...
New light on the 'split peak' of alcohols
2014-10-14
WASHINGTON D.C., October 14, 2014 -- For scientists probing the electronic structure of materials using a relatively new technique called resonant inelastic soft X-ray scattering (RIXS) in the last few years, a persistent question has been how to account for "split peak" spectra seen in some hydrogen-bonded materials.
In RIXS, low-energy X-rays from synchrotron or X-ray free-electron laser light sources scatter off molecules within the studied material. If those molecules include light elements, such as the -OH group in alcohols, the complex spectra RIXS produces are ...
Protein found in insect blood that helps power pests' immune responses
2014-10-14
MANHATTAN, Kansas — Pest insects may be sickened to learn to that researchers at Kansas State University have discovered a genetic mechanism that helps compromise their immune system.
Michael Kanost, university distinguished professor of biochemistry and molecular biophysics, led a study by Kansas State University researchers that looked at how protein molecules in the blood of insects function in insects' immune system. Insects use proteins that bind to the surface of pathogens to detect infections in their body.
"For example, when a mosquito transmits a pathogen ...
The Costco effect: Do consumers buy less variety at bigger stores?
2014-10-14
Do consumers make the same choices when products such as beer, soft drinks, or candy bars are sold individually or in bundles? According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, consumers purchase a greater variety of products when they are packaged individually rather than bundled together.
"When consumers choose multiple products, they are influenced by the mere mechanics of choosing, regardless of their product preference. Consumers are more likely to seek variety when choosing from single rather than bundled products," write authors Mauricio Mittelman (Universidad ...
Study exposes bias in transportation system design
2014-10-14
DENVER (Oct. 14, 2014) – America's streets are designed and evaluated with a an inherent bias toward the needs of motor vehicles, ignoring those of bicyclists, pedestrians, and public transit users, according to a new study co-authored by Wesley Marshall of the University of Colorado Denver.
"The most common way to measure transportation performance is with the level-of-service standard," said Marshall, PhD, PE, assistant professor of civil engineering at the CU Denver College of Engineering and Applied Science, the top public research university in Denver. "But ...
Defective gene renders diarrhoea vaccine ineffective
2014-10-14
Every year rotavirus causes half a million diarrhoea-related deaths amongst children in developing countries. Existing vaccines provide poor protection. The reason could be a widespread genetic resistance amongst children, according to virologists at Linköping University.
Acute diarrhoeal illnesses cause nearly one-fifth of all child deaths in developing countries. The most common cause is rotavirus. Improved sanitation and hygiene have had a limited effect on the spread of the illness. Today, vaccination is considered the most important method for reducing mortality. ...
Common gene variants linked to delayed healing of bone fractures
2014-10-14
Slow-healing or non-healing bone fractures in otherwise healthy people may be caused by gene variants that are common in the population, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers.
"We found associations between certain gene polymorphisms and delayed fracture healing in a sample of patients," said J. Spence Reid, professor of orthopaedics and rehabilitation. "Our study was preliminary but it demonstrated the feasibility of a larger one, which we're now working to set up."
The identification of gene variants that delay fracture healing could lead to screening ...
Precise control over genes results from game-changing research
2014-10-14
The application of a new, precise way to turn genes on and off within cells, described online October 9, 2014 in two articles in the journal Cell, is likely to lead to a better understanding of diseases and possibly to new therapies, according to UC San Francisco scientists.
The key to the advance is a new invention, called the SunTag, a series of molecular hooks for hanging multiple copies of biologically active molecules onto a single protein scaffold used to target genes or other molecules. Compared to molecules assembled without these hooks, those incorporating the ...
[1] ... [3270]
[3271]
[3272]
[3273]
[3274]
[3275]
[3276]
[3277]
3278
[3279]
[3280]
[3281]
[3282]
[3283]
[3284]
[3285]
[3286]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.