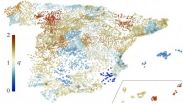
The dynamic of Spain's population follows the maximum entropy principle
2013-03-11
A team of Spanish and Argentinean researchers have verified that the distribution of the inhabitants in each Spanish province evolves in accordance with the maximum entropy principle in the field of physics. Therefore, this evolution is predictable. The results have allowed authors to put forward a 'socio-thermodynamic' theory that applies the laws of thermodynamics to collective human behaviour.
Spanish and Argentinean scientists have researched the way in which we as people group together on a large scale as a way of seeing whether there is any law or pattern that explains ...
Ground-level ozone falling faster than model predicted
2013-03-11
There is good news and better news about ground-level ozone in American cities. While dangerous ozone levels have fallen in places that clamp down on emissions from vehicles and industry, a new study from Rice University suggests that a model widely used to predict the impact of remediation efforts has been too conservative.
Particularly in Northeastern cities, ozone levels dropped even beyond what was anticipated by cutting emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from 2002 to 2006. The study published online by the journal Atmospheric Environment suggests the Community Multiscale ...
Can energy drinks improve the physical and mental performance of cyclists?
2013-03-11
New Rochelle, NY, March 11, 2013–Consumption of energy drinks containing caffeine may have beneficial effects on exercise but probably not for mental function. The effects of pre-exercise caffeine consumption by trained cyclists on racing times and cognitive performance were measured and are reported in Journal of Caffeine Research, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Caffeine Research website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jcr.
Race performance improved for all study participants after consuming ...
Common MS drugs taken together do not reduce relapse risk
2013-03-11
A recent clinical trial found that interferonβ-1a (INF) and glatiramer acetate (GA), two of the most commonly prescribed drugs for multiple sclerosis (MS), provide no additional clinical benefit when taken together. While findings published today in Annals of Neurology, a journal of the American Neurological Association and Child Neurology Society, suggest that taking both INF and GA together was not superior to GA monotherapy in reducing relapse risk; the combination therapy does appear to reduce new lesion activity and total lesion volume.
The National Institute ...
The closest star system found in a century
2013-03-11
A pair of newly discovered stars is the third-closest star system to the Sun, according to a paper that will be published in Astrophysical Journal Letters. The duo is the closest star system discovered since 1916. The discovery was made by Kevin Luhman, an associate professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State University and a researcher in Penn State's Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds.
Both stars in the new binary system are "brown dwarfs," which are stars that are too small in mass to ever become hot enough to ignite hydrogen fusion. As a result, ...
Stroke risk in elderly treated with antipsychotics is newly linked to specific drug actions
2013-03-11
Philadelphia, PA, March 11, 2013 – Antipsychotic administration in the elderly is associated with an increased risk for cerebrovascular accident, more commonly known as stroke; a new study published in Biological Psychiatry provides additional insight into this important relationship.
Antipsychotics are prescribed to elderly patients to treat symptoms such as agitation, psychosis, anxiety, insomnia, and depression. The increased risk of stroke associated with these medications was identified approximately a decade ago and has since been replicated by subsequent studies. ...
Biodiesel algae: Starvation diets damage health
2013-03-11
It may be better to tolerate lower oil content in algae grown for biodiesel to boost growth and overall productivity, says research from the University of Sheffield.
The research shows that the commonly accepted method of depriving algae of key nutrients such as nitrogen in order to boost its oil content may be detrimental to overall oil yield in the long term.
"Total oil production depends not just on the oil content of the algal cells but how quickly the cells grow and multiply," says Dr Stephen Wilkinson of the University's Department of Chemical and Biological ...
Need for culturally sensitive treatment for deaf patients with psychiatric disorders
2013-03-11
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 11, 2013) – Members of the Deaf community who suffer from mental health problems need culturally sensitive treatment to avoid misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment, according to a report in the March Journal of Psychiatric Practice. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Deaf individuals comprise a cultural and linguistic minority group within the United States, and culturally and linguistically appropriate psychiatric treatment must reflect these differences," according to Sarah A. Landsberger, ...
Study finds fat and bone mass are genetically linked
2013-03-11
When it comes to body shape, diet and exercise can only take us so far. Our body shape and geometry are largely determined by genetic factors. Genetics also have an impact on our body composition – including soft fat tissue and hard bone tissue – and can lead to excess fat or osteoporosis.
Now Prof. Gregory Livshits of Tel Aviv University's Department of Anatomy and Anthropology at the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, working alongside Dr. Michael Korostishevsky, has uncovered a clear genetic link between fat and bone mass. These factors, which contribute to bone metabolism, ...
Does winning an Emmy or an election mean you will live longer than those you beat?
2013-03-11
WASHINGTON, DC, March 11, 2013 — Research has long linked high socioeconomic status with better health and lower mortality. But what's remained unclear is whether this association has more to do with access to resources (education, wealth, career opportunity, etc.) or the glow of high social status relative to others. Scholars call the latter "relative deprivation."
To tease apart these factors, a team of investigators at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health led by Dr. Bruce Link, studied Baseball Hall of Fame inductees, Emmy Award winners, and former ...
Researchers find alternative cholesterol-lowering drug for patients who can't tolerate statins
2013-03-11
SAN FRANCISCO — Heart patients who can't tolerate the side effects of cholesterol-lowering drugs may have a new option, according to a new study by researchers from the Intermountain Heart Institute at Intermountain Medical Center in Salt Lake City.
Researchers found that pitavastatin, a newer cholesterol-lowering drug, may reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke and even death in up to 68 percent of patients with high cholesterol who can't tolerate other cholesterol-lowering medications due to side effects.
Researchers are presenting the results of this study today ...
Glaciers contribute significant iron to North Atlantic Ocean
2013-03-11
All living organisms rely on iron as an essential nutrient. In the ocean, iron's abundance or scarcity means all the difference as it fuels the growth of plankton, the base of the ocean's food web.
A new study by biogeochemists and glaciologists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) identifies a unexpectedly large source of iron to the North Atlantic – meltwater from glaciers and ice sheets, which may stimulate plankton growth during spring and summer. This source is likely to increase as melting of the Greenland ice sheet escalates under a warming climate.
The ...
Antibiotic resistance 'has the potential to undermine modern health systems'
2013-03-11
Their warning comes as the Chief Medical Officer launches the UK's Antimicrobial Resistance Strategy and Action Plan, reflecting the need for a clear change in our understanding of and response to antimicrobial resistance by the public, NHS and government.
Current estimates suggest that antibiotic resistance is a relatively cheap problem, they write, but such estimates do not take account of the fact that antimicrobial medicines are integral to modern healthcare. For example, antibiotics are given as standard to patients undergoing surgery, to women delivering by caesarean ...
New study explores link between status and health
2013-03-11
March 11, 2013 -- Research has long linked high socioeconomic status with better health and lower mortality. But what's remained unclear is whether this association has more to do with access to resources (education, wealth, career opportunity, etc.) or the glow of high social status relative to others. Scholars call the latter "relative deprivation."
To tease apart these factors, a team of investigators at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health led by Dr. Bruce Link, studied Baseball Hall of Fame inductees, Emmy Award winners, and former Presidents and ...
New genetic study confirms Indian origins of pumpkins and cucumbers
2013-03-11
It had been suggested that the origin of pumpkins and cucumbers can be traced back to India. This has now been confirmed on the basis of genetic analyses performed by German and Indian botanists. The study was published in the open access journal PhytoKeys.
Vegetables are essential components of a healthy daily diet, not just in India but around the globe. Compared to grains and pulses, however, vegetables are under-investigated taxonomically, and information on their genome is scarce. The cucumber family, Cucurbitaceae, includes many of our favorite foods: pumpkins, ...
Frustration may increase attraction to violent video games
2013-03-11
The temptation to steal or cheat is sometimes great — especially when the risk of being caught is low. A new study suggests that denying people the opportunity to engage in these taboo behaviors may lead them to seek out violent video games as a way of managing their frustration.
The study, led by researcher Brad Bushman of Ohio State University, is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Bushman and his colleagues want to understand what attracts people to violent media. In a previous study, they found that people ...
New WPI report shows how earthquake damage can impact building fire safety performance
2013-03-11
Worcester, Mass. – Damage to building structural elements, elevators, stairs, and fire protection systems caused by the shaking from a major earthquake can play a critical role in the spread of fire, hamper the ability of occupants to evacuate, and impede fire departments in their emergency response operations. These are among the conclusions of a groundbreaking study of post-earthquake building fire performance conducted in 2012 by researchers in the Department of Fire Protection Engineering at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI).
"When the ground stops shaking after ...
Protein abundant in cancerous cells causes DNA 'supercoiling'
2013-03-11
A team of USC scientists has identified a protein that can change DNA topology, making DNA twist up into a so-called "supercoil."
The finding provides new insight about the role of the protein—known as mini-chromosome maintenance (MCM)—in cancer cells, which have high levels of MCM.
Think about twisting one end of a rubber band while holding the other end still. After a few turns, it forms a neatly twisted rope. But if you keep on turning, the twisted band will twist back upon itself into an increasingly coiled-up knot. Similarly, a DNA molecule can be twisted and ...
No increase in risk of death for patients with well-controlled HIV, reports AIDS journal
2013-03-11
Philadelphia, Pa. (March 11, 2013) – For HIV-infected patients whose disease is well-controlled by modern treatment, the risk of death is not significantly higher than in the general population, according to a study published in AIDS, official journal of the International AIDS Society. AIDS is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The study suggests that patients with undetectable viral loads and near-normal levels of immune cells on state-of-the art antiretroviral therapy (ART) can expect to have about the same risk of death as ...
Combination therapy provides similar clinical benefit as single drug treatment in MS
2013-03-11
People with multiple sclerosis (MS) who were treated with combination therapy did not see significant clinical benefit over those treated with single drug therapy, but combination therapy did reduce the development of new lesions, according to an international research team led by The Mount Sinai Medical Center. The findings, part of the largest-ever MS trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, are published in the March 11 issue of Annals of Neurology.
In the Phase III CombiRx trial, researchers led by Fred Lublin, MD, of The Mount Sinai Medical Center, sought ...
Older adults benefit from home-based DVD exercise program
2013-03-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Fitness DVDs are a multimillion-dollar business, and those targeting adults over the age of 55 are a major part of the market. With names like "Boomers on the Move," "Stronger Seniors" and "Ageless Yoga," the programs promise much, but few have ever been rigorously tested.
"There are tons of DVDs out there, 20 percent of them are purchased by older adults, and with few exceptions there is no evidence that they work," said University of Illinois kinesiology and community health professor Edward McAuley, who led a new study testing the efficacy of a home-based ...
Tiny piece of RNA keeps 'clock' running in earliest stages of life
2013-03-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research shows that a tiny piece of RNA has an essential role in ensuring that embryonic tissue segments form properly.
The study, conducted in chicken embryos, determined that this piece of RNA regulates cyclical gene activity that defines the timing of the formation of tissue segments that later become muscle and vertebrae.
Genes involved in this activity are turned on and off in an oscillating pattern that matches the formation of each tissue segment. If the timing of these genes' activity doesn't remain tightly regulated, the tissue either won't ...
International conference to tackle climate-change threats to agriculture
2013-03-11
Scientists and policymakers from around the world will gather March 20-22 at the University of California, Davis, to grapple with the threats of climate change for global agriculture and recommend science-based actions to slow its effects while meeting the world's need for food, livelihood and sustainability.
The Climate-Smart Agriculture Global Science Conference, planned in coordination with the World Bank, builds on a 2011 international meeting on this theme in the Netherlands.
"Climate change, which brings severe weather events and more subtle but equally menacing ...
Fluoride in drinking water cuts tooth decay in adults
2013-03-11
A new study conducted by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the University of Adelaide, Australia, has produced the strongest evidence yet that fluoride in drinking water provides dental health benefits to adults, even those who had not received fluoridated drinking water as children.
In the first population-level study of its kind, the study shows that fluoridated drinking water prevents tooth decay for all adults regardless of age, and whether or not they consumed fluoridated water during childhood.
Led by UNC School of Dentistry faculty ...
Nonprofits a major source of employment growth globally
2013-03-11
A new report from the Johns Hopkins Institute for Policy Studies reveals that nonprofit organizations are major employers and major sources of employment growth in countries throughout the world. The report draws on new data generated by statistical offices in 16 countries that have implemented a new United Nations Handbook on Nonprofit Institutions. This Handbook calls on national statistical offices to report on the economic scale and composition of nonprofit organizations in their countries for the first time. Key findings to date from implementation of this Handbook, ...
[1] ... [5083]
[5084]
[5085]
[5086]
[5087]
[5088]
[5089]
[5090]
5091
[5092]
[5093]
[5094]
[5095]
[5096]
[5097]
[5098]
[5099]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.