Researchers discover 'gateway' in nucleus has a second important job no one noticed before
2013-03-08
UAlberta medical researchers and their American colleagues have discovered that the "gateway" known to control the movement of molecules in and out of a cell's nucleus appears to play another critically important role – one no one had noticed until now.
These "gateways" have a second key job in a cell – the ability to control the structure of chromosomes and the DNA linked to those chromosomes. This impacts what genes produce or express. The discovery gives scientists a new way to investigate the triggers for various kinds of disease, says Richard Wozniak, the principal ...
New form of animal communication discovered
2013-03-08
Sniffing, a common behavior in dogs, cats and other animals, has been observed to also serve as a method for rats to communicate—a fundamental discovery that may help scientists identify brain regions critical for interpreting communications cues and what brain malfunctions may cause some complex social disorders.
Researchers have long observed how animals vigorously sniff when they interact, a habit usually passed off as simply smelling each other. But Daniel W. Wesson, PhD, of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, whose research is published in Current ...
Is this peptide a key to happiness?
2013-03-08
What makes us happy? Family? Money? Love? How about a peptide?
The neurochemical changes underlying human emotions and social behavior are largely unknown. Now though, for the first time in humans, scientists at UCLA have measured the release of a specific peptide, a neurotransmitter called hypocretin, that greatly increased when subjects were happy but decreased when they were sad.
The finding suggests that boosting hypocretin could elevate both mood and alertness in humans, thus laying the foundation for possible future treatments of psychiatric disorders like ...
U of T engineering breakthrough promises significantly more efficient solar cells
2013-03-08
TORONTO, ON – March 7, 2013: A new technique developed by U of T Engineering Professor Ted Sargent and his research group could lead to significantly more efficient solar cells, according to a recent paper published in the journal Nano Letters.
The paper, "Jointly-tuned plasmonic-excitonic photovoltaics using nanoshells," describes a new technique to improve efficiency in colloidal quantum dot photovoltaics, a technology which already promises inexpensive, more efficient solar cell technology. Quantum dot photovoltaics offers the potential for low-cost, large-area solar ...
Education's protective effect on marriage differs between white and African-American women
2013-03-08
NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – Married couples who have attained higher levels of education are less likely to divorce than less-educated couples, but a new study conducted at Rutgers School of Social Work points to significant racial differences.
"African-American women don't seem to enjoy the same degree of protection that education confers on marriage," said Jeounghee Kim, assistant professor at the school. "For white Americans, higher education is related to a lower chance of divorce, and this protective effect of education on marriage increased consistently among the recent ...
Prairie dogs disperse when all close kin have disappeared
2013-03-08
FROSTBURG, MD (March 7, 2013)—Prairie dogs pull up stakes and look for a new place to live when all their close kin have disappeared from their home territory--a striking pattern of dispersal that has not been observed for any other species. This is according to a new study published in Science by behavioral ecologist John Hoogland, Professor at the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science's Appalachian Laboratory. He has been studying the ecology and social behavior of prairie dogs in national parks in Arizona, South Dakota, and Utah for the last 40 years.
For ...
Drugs targeting blood vessels may be candidates for treating Alzheimer's
2013-03-08
University of British Columbia researchers have successfully normalized the production of blood vessels in the brain of mice with Alzheimer's disease (AD) by immunizing them with amyloid beta, a protein widely associated with the disease.
While AD is typically characterized by a build-up of plaques in the brain, recent research by the UBC team showed a near doubling of blood vessels in the brain of mice and humans with AD.
The new study, published online last week in Scientific Reports, a Nature journal, shows a reduction of brain capillaries in mice immunized with ...
Engineers develop techniques to boost efficiency of cloud computing infrastructure
2013-03-08
Computer scientists at the University of California, San Diego, and Google have developed a novel approach that allows the massive infrastructure powering cloud computing as much as 15 to 20 percent more efficiently. This novel model has already been applied at Google. Researchers presented their findings at the IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture conference Feb. 23 to 27 in China.
Computer scientists looked at a range of Google web services, including Gmail and search. They used a unique approach to develop their model. Their first ...
The future of ion traps
2013-03-08
Recently Science Magazine invited JQI fellow Chris Monroe and Duke Professor Jungsang Kim to speculate on ion trap technology as a scalable option for quantum information processing. The article is highlighted on the cover of this week's issue, which is dedicated to quantum information. The cover portrays a photograph of a surface trap that was fabricated by Sandia National Labs and used to trap ions at JQI and Duke, among other laboratories.
Trapped atomic ions are a promising architecture that satisfies many of the critical requirements for constructing a quantum computer. ...
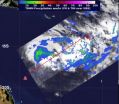
NASA's TRMM satellite sees Tropical Cyclone 19P form
2013-03-08
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite noticed areas of heavy rainfall in low pressure System 92P hours before it became the nineteenth tropical cyclone of the Southern Pacific Ocean.
NASA's TRMM satellite captured a look at the rainfall rates within low pressure System 92P on March 7 at 0023 UTC (March 6 at 7:23 p.m. EST), just hours before it became Tropical Cyclone 19P (TC 19P). TRMM data indicated that heavy rain was falling at a rate of 2 inches/50 mm per hour around the center of circulation, and that some of the thunderstorms were powerful as they ...
Trauma simulation technique makes better journalists
2013-03-08
This press release is available in French.
Montreal, March 7, 2013 – Just hours after the tragic shooting of 27 victims at Sandy Hook Elementary School, Twitter was overloaded with messages slamming reporters for interviewing children involved in the tragedy. While some of the journalists probably knew better but wanted the story at all costs, others were rookie reporters facing ethical decisions for the first time and unaware of the impact these interviews might have on the young survivors.
Past studies have documented that new journalists can cause a number of ...
Hubble finds birth certificate of oldest known star
2013-03-08
A team of astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has taken an important step closer to finding the birth certificate of a star that's been around for a very long time.
"We have found that this is the oldest known star with a well-determined age," said Howard Bond of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, Pa., and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md.
The star could be as old as 14.5 billion years (plus or minus 0.8 billion years), which at first glance would make it older than the universe's calculated age of about 13.8 billion ...
Small physician practices that care for children unprepared to become medical homes
2013-03-08
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Primary care practices around the country are being encouraged and even paid to become "medical homes," but small practices might be at a significant disadvantage in this race to improve health care for children, according to a new study by child health experts at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
Efforts around the country to improve health care for children have increasingly focused on the medical home as a model to make primary care practices more accessible, comprehensive, and focused on quality improvement. Since 2008, practices could become officially ...
Biologists produce rainbow-colored algae
2013-03-08
What can green algae do for science if they weren't, well, green?
That's the question biologists at UC San Diego sought to answer when they engineered a green alga used commonly in laboratories, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, into a rainbow of different colors by producing six different colored fluorescent proteins in the algae cells.
While fluorescent green, red, blue and yellow may be all the rage this year for running shoes and other kinds of sporting gear, fluorescent algae hasn't been a style trend yet in scientific laboratories. But in announcing their achievement in ...
Stocking Florida bass in Texas reservoirs may alter stream systems connected to stocked reservoirs
2013-03-08
WACO, Texas (March 7, 2013) - A genetic analysis by Baylor University biologists suggests that the stocking of Florida bass in Texas reservoirs impacts bass populations far beyond the actual stocking location.
The native largemouth bass has a long and nearly continuous stocking history in Texas. However, the Florida bass is widely considered a better sport fish because it grows to a greater size. Subsequently, stocking efforts in Texas reservoirs have transitioned from largemouth bass to Florida bass.
The Baylor researchers analyzed the genetic composition of 69 largemouth ...
Net advantage
2013-03-08
Malaria, the leading cause of death among children in Africa, could be eliminated if three-fourths of the population used insecticide-treated bed nets, according to a new study from the National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis (NIMBioS).
The study, which uses a mathematical model, found that use of insecticide-treated bed nets or ITNs positively affected the infection's reproduction number, or R, which is the primary epidemiological number used to determine the degree which a disease can spread through a population. The model concludes that if 75 percent ...
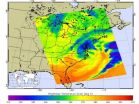
NASA provides satellite views of Nor'easter on March 7, 2013
2013-03-08
VIDEO:
This animation of NOAA GOES-13 satellite imagery from March 5-7, 2013, shows the progression of a cold front from the west associated with a low pressure system that brought snow...
Click here for more information.
The merging of two low pressure areas into a large Nor'easter on March 6 brought winter weather advisories and warnings to the Mid-Atlantic. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared and near infrared image of the storm's power, and NASA created an animation ...
Pan-STARRS finds a 'lost' supernova
2013-03-08
The star Eta Carinae is ready to blow. 170 years ago, this 100-solar-mass object belched out several suns' worth of gas in an eruption that made it the second-brightest star after Sirius. That was just a precursor to the main event, since it will eventually go supernova.
Supernova explosions of massive stars are common in spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, where new stars are forming all the time. They are almost never seen in elliptical galaxies where star formation has nearly ceased. As a result, astronomers were surprised to find a young-looking supernova in an old ...
Earth is warmer today than during 70 to 80 percent of the past 11,300 years
2013-03-08
With data from 73 ice and sediment core monitoring sites around the world, scientists have reconstructed Earth's temperature history back to the end of the last Ice Age.
The analysis reveals that the planet today is warmer than it's been during 70 to 80 percent of the last 11,300 years.
Results of the study, by researchers at Oregon State University (OSU) and Harvard University, are published this week in a paper in the journal Science.
Lead paper author Shaun Marcott of OSU says that previous research on past global temperature change has largely focused on the ...
UTHealth research: Low incidence of venous insufficiency in MS
2013-03-08
HOUSTON – (March 7, 2013) – Results of a study using several imaging methods showed that CCSVI (chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency) occurs at a low rate in both people with multiple sclerosis (MS) and non-MS volunteers, contrary to some previous studies. The research by an interdisciplinary team at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) was published in a recent early online edition of the Annals of Neurology.
"Our results in this phase of the study suggest that findings in the major veins that drain the brain consistent with CCSVI ...
'Climate-smart strategies' proposed for spectacular US-Canadian landscape
2013-03-08
A new report from the Wildlife Conservation Society Canada (WCS Canada) creates a conservation strategy that will promote wildlife resiliency in the Southern Canadian Rockies to the future impacts of climate change and road use. The report's "safe passages and safe havens" were informed in part by an assessment of six iconic species—bull trout, westslope cutthroat trout, grizzly bears, wolverines, mountain goats and bighorn sheep—five of which were ranked as highly vulnerable to projected changes.
Nestled between Glacier National Park in Montana and Banff National ...
How to thrive in battery acid and among toxic metals
2013-03-08
In the movie Alien, the title character is an extraterrestrial creature that can survive brutal heat and resist the effects of toxins.
In real life, organisms with similar traits exist, such as the "extremophile" red alga Galdieria sulphuraria.
In hot springs in Yellowstone National Park, Galdieria uses energy from the sun to produce sugars through photosynthesis.
In the darkness of old mineshafts in drainage as caustic as battery acid, it feeds on bacteria and survives high concentrations of arsenic and heavy metals.
How has a one-celled alga acquired such ...
Disease knowledge may advance faster with CRISPR gene probing tool
2013-03-08
Scientists at UC San Francisco have found a more precise way to turn off genes, a finding that will speed research discoveries and biotech advances and may eventually prove useful in reprogramming cells to regenerate organs and tissues.
The strategy borrows from the molecular toolbox of bacteria, using a protein employed by microbes to fight off viruses, according to the researchers, who describe the technique in the current issue of Cell.
Turning off genes is a major goal of treatments that target cancer and other diseases. In addition, the ability to turn genes off ...
Sing a new song: Computer scientists use music to lure students to STEM majors
2013-03-08
To students in Jennifer Burg's computer science classes, making music is the main objective. But her goal is to get them to understand how the underlying technology works – and to love it so much they decide on a science-based career path.
And that, Burg's study has shown, has helped Wake Forest University fulfill the national imperative to increase the number of majors in the STEM disciplines of science, technology, engineering and math.
The results of Burg's research, "Computer Science 'Big Ideas' Play Well in Digital Sound and Music," will be published during the ...
Outdoor heat increases risk of emergency respiratory hospitalization in elderly
2013-03-08
Outdoor heat is associated with a significantly increased risk of emergency hospitalization for respiratory disorders in the elderly, according to a large epidemiological study of more than 12.5 million Medicare beneficiaries.
"While outdoor heat has been shown to increase respiratory mortality, evidence on the relationship between heat and respiratory hospitalizations has been less consistent," said lead author G. Brooke Anderson, PhD, postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Biostatistics at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. "In the largest population ...
[1] ... [5081]
[5082]
[5083]
[5084]
[5085]
[5086]
[5087]
[5088]
5089
[5090]
[5091]
[5092]
[5093]
[5094]
[5095]
[5096]
[5097]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.