Georgia Health Insurance Company Offers Tips to Remedy Your Winter Cold
2013-01-23
Getting sick is just not an option these days. In this economy, staying healthy can mean the difference between financial breathing room vs. woes. Many companies offer sick time to employees, but depending on your current work status, this may or may not be sufficient. In addition, workers who drop below full-time status run the risk of losing their benefits altogether. Luckily there are individual health plans in Georgia that can keep you covered.
Every day you are sick may cost you a day's worth of wages. For the vast majority of Americans, making ends meet is a blessing. ...
HealthyLife Sciences Introduces Healthe Trim Powered by Raspberry Ketone
2013-01-23
HealthyLife Sciences, LLC, the maker of natural weight loss supplement Healthe Trim, is pleased to introduce its newest product: Healthe Trim Powered by Raspberry Ketone. Naturally found in raspberries, Raspberry Ketone is a revolutionary compound that has been shown to aid in the breakdown of fat molecules and significantly aid in weight loss.
Raspberry Ketone is the compound in raspberries that gives them their sweet and fruity smell. Over the years, it has been extensively studied, and scientists have linked it to preventing weight gain in mice who were fed high-fat ...
Eyewear Retailer, Eyeglass World, Celebrates Hot Seasonal Glasses Colors
2013-01-23
With the changing of the seasons, the desire to spice up your look with some new fashions can be hard to resist. Eyeglass World has a way to change your look without breaking the bank: picking up new glasses.
Switching to a new style designer eyeglasses frame or simply switching your old eyeglasses for frames in one of the colors of the season provides an immediate change in your look. Adding new eyewear in shades of red, blue, gold, silver, or other colors can help you connect to the latest and most-spirited fashions in a way that is uniquely yours.
One of the least ...
Products That Make a Difference: Discover MaxiAids 2013/14 Catalog
2013-01-23
MaxiAids Products for Independent Living (www.MaxiAids.com) has released their 2013/14 Catalog. Commonly accepted as the 'Reference Guide of the Industry,' the MaxiAids Catalog contains the largest available assortment of items that support active, healthy and independent lives.
The most viewed catalog in the industry, it has thousands of budget-friendly assistive items for all age groups, no matter what their special need is. See more clearly with magnified, talking or large print daily living items such as talking watches and large numbered clocks! Never oversleep ...
etc.venues Recognised at the VenueVerdict Awards for 2012
2013-01-23
As recognition of their fantastic customer service, etc.venues has swept the board at the 2012 VenueVerdict Service award. The specialist venue group has always prided itself on its fantastic levels of service, and believe that this impressive performance in the leading independent, customer research based survey confirms etc.venues as leaders for service in the venue industry.
etc.venues managed to out-perform all other venue groups in the Gold Award categories, and even secured the Gold Standard Brand Award, earning 6 Gold accreditations this year in the process. ...
Zero Robotics Challenge Kicks Off the New Year for Space Station Student Activities
2013-01-23
On Friday, Jan. 11th, high school students from around the world joined in fierce competition to claim the championship spot in the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, Zero Robotics High School Tournament 2012. The young competitors operated robotic satellites aboard the International Space Station, or ISS, using programs they wrote in preparation for the event. The finalists watched the action via live downlink from the space station with anticipation, as astronauts supervised the satellites during the ISS Finals.
The ...
Severe abuse at home linked to dating violence
2013-01-22
Young urban black women who are exposed to severe abuse within their families are much more likely to be victims of dating violence, according to a study led by a Michigan State University researcher.
Angie Kennedy said efforts to prevent dating violence should include discussion of what might be going on in the victim's home.
"There is a lot of focus on trying to prevent dating violence for high school students, which is an important goal," said Kennedy, MSU associate professor of social work. "But if you're sitting in a group talking about conflict with your dating ...
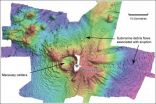
A new type of volcanic eruption
2013-01-22
Scientists based in the UK and New Zealand have described a "new" type of volcanic eruption.
Volcanic eruptions are commonly categorised as either explosive or effusive. But now, in research published this month in Nature Geoscience, researchers at Victoria University, Wellington and the National Oceanography Centre in Southampton have uncovered a previously undocumented type of eruption in underwater volcanoes – by looking at tiny original bubble spaces trapped in volcanic rock.
Inside volcanoes, gases are dissolved in the molten magma as a function of the very high ...
Blood-based biomarkers may lead to earlier diagnosis of Parkinson's disease
2013-01-22
Amsterdam, NL, 20 January 2013 – Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological condition. At present, it is usually diagnosed only when motor features are present. Hence, there is a need to develop objective and measurable biomarkers to improve PD diagnostics during its earlier stage, prior to its motor onset. In this pilot study, researchers identified and tested the first blood-based circulating microRNA (miRNA) biomarkers for PD. Their results are published in the latest issue of Journal of Parkinson's Disease.
PD is the second most common neurodegenerative ...
New technology shows diabetes
2013-01-22
A new imaging method for the study of insulin-producing cells in diabetes among other uses is now being presented by a group of researchers at Umeå University in Sweden in the form of a video in the biomedical video journal, The Journal of Visualized Experiments.
The developed techniques have contributed to the reasons why the research team recently received a SEK 4.3 million grant from the EU in a Marie Curie program to link together leading research teams in Europe in the field of diabetes imaging.
Professor Ulf Ahlgren and his associates at the Umeå Center for Molecular ...
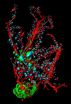
Protein structure: Immune system foiled by a hairpin
2013-01-22
The innate immune system detects invasive pathogens and activates defense mechanisms to eliminate them. Pathogens, however, employ a variety of tricks to block this process. A new study led by Karl-Peter Hopfner of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich shows how the measles virus thwarts the system, by means of a simple hairpin-like structure.
The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense against invasive pathogens and noxious chemicals. Essentially the system consists of an array of receptors that recognize particular molecular conformations ...
Monkeys stressed from longer foraging times
2013-01-22
Endangered Mexican howler monkeys are consuming more leaves and less fruit as a result of habitat disturbance by humans, which is forcing them to invest much more time foraging for sustenance and leading to increased 'stress' levels, as detected through hormone analysis.
The research, published today in the International Journal of Primatology, took place in the tropical rainforests of the Mexican state of Veracruz, which are being deforested and fragmented by human activity - primarily the clearing of forest for cattle raising.
It shows that increases in howler monkey ...
Smoke-free law linked to large fall in child asthma hospital admissions
2013-01-22
The introduction of smoke-free legislation in England was immediately followed by a fall in the number of children admitted to hospital with asthma symptoms, a new study has found.
NHS statistics analysed by researchers at Imperial College London show a 12.3 per cent fall in admissions for childhood asthma in the first year after the law on smoking in enclosed public places and workplaces came into effect in July 2007. The researchers found that asthma admissions continued to fall in subsequent years, suggesting that the benefits of the legislation were sustained over ...
Cleaning jobs linked to asthma risk
2013-01-22
A new study has found strong evidence for a link between cleaning jobs and risk of developing asthma.
Researchers at Imperial College London tracked the occurrence of asthma in a group of 9,488 people born in Britain in 1958. Not including those who had asthma as children, nine per cent developed asthma by age 42. Risks in the workplace were responsible for one in six cases of adult onset asthma – even more than the one in nine cases attributed to smoking, according to the analysis.
There are many occupations that are thought to cause asthma. In this study, 18 occupations ...
Cotton with special coating collects water from fogs in desert
2013-01-22
Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) together with researchers at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU), have developed a special treatment for cotton fabric that allows the cotton to absorb exceptional amounts of water from misty air: 340 % of its own weight. What makes this 'coated cotton' so interesting is that the cotton releases the collected water by itself, as it gets warmer. This property makes of the coated cotton materials a potential solution to provide water to the desert regions, for example for agricultural purposes. The results ...
New findings on mortality of individuals with schizophrenia
2013-01-22
A new study from Lund University in Sweden shows that the average life expectancy of men and women with schizophrenia is 15 years and 12 years shorter respectively than for those who do not suffer from the disease. The study has been carried out in collaboration with Stanford University in the US.
The reasons why people with schizophrenia have a shorter life expectancy have previously been unknown, but have been much discussed in recent years. The research report that has now been published shows that individuals with schizophrenia are more likely to die of two major ...
Immune function in critically ill kids with influenza reveals immune suppression in non-survivors
2013-01-22
Investigators from 15 children's medical centers, including Nationwide Children's Hospital, observed and evaluated critically ill children with influenza to evaluate the relationships between levels of systemic inflammation, immune function and likelihood to die from the illness. The study appears in the January issue of Critical Care Medicine.
The innate immune system is the cellular arm of the immune system that serves as a first-responder to new threats, and is thought to drive the inflammatory response in many forms of critical illness. Recent evidence indicates that ...
Human-tiger conflict: Are the risks overestimated?
2013-01-22
Wildlife conservationists are well aware of the potential conflicts that exist between the endangered species they seek to protect and the human populations which inhabit areas where the animals live. Carnivores, such as tigers, pose a risk to humans and their livestock and can be killed because of this potential risk. Previous research has found that killing of animals can be motivated as much by social and psychological factors, such as perception of danger, as by any actual real risk posed by a species.
A new study published in the Springer journal Human Ecology ...
Mama bear knows best, University of Alberta study shows
2013-01-22
Mama bear appears to know best when it comes to selecting a place to call home, according to a new University of Alberta study.
The study, published in the latest issue of PLOS ONE, explored whether the rearing of cubs by their mothers shaped which habitats grizzly bears eventually choose.
The findings "suggest that habitat selection is learned by young grizzly bears from their mothers, and would likely be a more adaptive strategy than using instinct," said lead author Scott Nielsen, assistant professor in the U of A Department of Renewable Resources.
The University ...
New evidence indicates auroras occur outside our solar system
2013-01-22
University of Leicester planetary scientists have found new evidence suggesting auroras – similar to Earth's Aurora Borealis - occur on bodies outside our solar system.
Auroras occur on several planets within our solar system, and the brightest - on Jupiter – are 100 times brighter than those on Earth. However, no auroras have yet been observed beyond Neptune.
A new study led by University of Leicester lecturer Dr Jonathan Nichols has shown that processes strikingly similar to those which power Jupiter's auroras could be responsible for radio emissions detected from ...
Penn study sheds light on the complexity of gene therapy for congenital blindness
2013-01-22
PHILADELPHIA - Independent clinical trials, including one conducted at the Scheie Eye Institute at the Perelman School of Medicine, have reported safety and efficacy for Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), a congenital form of blindness caused by mutations in a gene (RPE65) required for recycling vitamin A in the retina. Inherited retinal degenerative diseases were previously considered untreatable and incurable. There were early improvements in vision observed in the trials, but a key question about the long-term efficacy of gene therapy for curing the retinal degeneration ...
Study: Bariatric surgery in extremely obese adolescents
2013-01-22
This time of year many people make resolutions to live a healthier lifestyle, exercise more, lose weight and eat better. For the adolescents who are extremely obese in this country, diet and exercise alone often are not enough to get their weight down. Some of those teens will require weight loss surgery to improve their overall health. According to a recent study published in the January print issue of the Journal of Pediatric Surgery, bariatric surgery in extremely obese adolescents also was shown to be beneficial in helping to reverse previously undiagnosed cardiovascular ...
UBC research: Forget about fair – It's better when bosses pick favorites
2013-01-22
A new study from the University of British Columbia Sauder School of Business shows that bosses should pick favourites if they want top performing teams.
"Conventional wisdom tells us that we should treat everyone the same to create a collegial and productive work atmosphere," says Sauder Professor Karl Aquino, who co-authored the forthcoming study for the Journal of Business Ethics. "But our research shows this can be a disincentive for workers who would otherwise go above and beyond on behalf of the team with a little bit of extra attention."
In a series of experiments, ...
A relative from the Tianyuan Cave
2013-01-22
This press release is available in German.
An international team of researchers including Svante Pääbo and Qiaomei Fu of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, sequenced nuclear and mitochondrial DNA that had been extracted from the leg of an early modern human from Tianyuan Cave near Beijing, China. Analyses of this individual's DNA showed that the Tianyuan human shared a common origin with the ancestors of many present-day Asians and Native Americans. In addition, the researchers found that the proportion of Neanderthal and Denisovan-DNA ...
Enzyme replacement therapy shows promising results in X-linked myotubular myopathy
2013-01-22
A collaborative research team including a Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) pediatric neuropathologist successfully mitigated some of the effects of a muscular disease by using a new targeted enzyme replacement therapy strategy from 4s3 Bioscience.
The findings are published in the January edition of Human and Molecular Genetics http://hmg.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2013/01/09/hmg.ddt003.full.pdf+html.
X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM) is a severe muscle disease caused by an absence of a protein called myotubularin. There is currently no treatment for this ...
[1] ... [5339]
[5340]
[5341]
[5342]
[5343]
[5344]
[5345]
[5346]
5347
[5348]
[5349]
[5350]
[5351]
[5352]
[5353]
[5354]
[5355]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.