Photographic cholesterol test
2012-08-17
Researchers in India have developed a total cholesterol test that uses a digital camera to take a snapshot of the back of the patient's hand rather than a blood sample. The image obtained is cropped and compared with images in a database for known cholesterol levels.
Writing in the International Journal of Medical Engineering and Informatics, N.R. Shanker of the Sree Sastha Institute of Engineering and Technology and colleagues describe how they have developed a non-invasive way to test cholesterol levels in patients at increased risk of heart disease. Their approach ...
Regions vary in paying prisoners to participate in research
2012-08-17
TORONTO, Aug. 17, 2012--When members of the public participate in research studies, they are often given incentives – such as cash or gift cards for food – as compensation or reimbursement for their time and effort. Not so for Canada's prison population. A new analysis shows that there is inconsistency in how and when incentives are used for research participants under criminal justice supervision.
Of the provinces, territories and federal government, only two jurisdictions have written policy around the use of research incentives, according to a national study led by ...
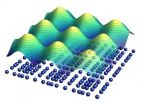
Constructive conflict in the superconductor
2012-08-17
Whether a material conducts electricity without losses is not least a question of the right temperature. In future it may be possible to make a more reliable prediction for high-temperature superconductors. These materials lose their resistance if they are cooled with liquid nitrogen, which is relatively easy to handle. An international team, in which physicists of the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research in Stuttgart played a crucial role, has now discovered that this form of superconductivity competes with charge density waves, i.e. with a periodically fluctuating ...
A urine based 'potion' can act as a CO2 absorbent
2012-08-17
VIDEO:
A Spanish researcher has proposed human, agricultural and livestock waste, such as urine, as a way to absorb CO2.
Click here for more information.
The ocean, the ground, rocks and trees act as carbon drains but are far from places where greenhouses gases are concentrated, especially CO2. A Spanish researcher has proposed human, agricultural and livestock waste, such as urine, as a way to absorb this gas.
Absorbing the large quantities of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse ...
2 new owls discovered in the Philippines
2012-08-17
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Two new species of owls have been discovered in the Philippines, and a Michigan State University researcher played a key role in confirming their existence.
The discovery, which is featured in the current issue of Forktail, the Journal of Asian Ornithology, took years to confirm, but it was well worth the effort, said the paper's lead author Pam Rasmussen, MSU assistant professor of zoology and assistant curator of mammalogy and ornithology at the MSU Museum.
"More than 15 years ago, we realized that new subspecies of Ninox hawk-owls existed ...
MIT-developed 'microthrusters' could propel small satellites
2012-08-17
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A penny-sized rocket thruster may soon power the smallest satellites in space.
The device, designed by Paulo Lozano, an associate professor of aeronautics and astronautics at MIT, bears little resemblance to today's bulky satellite engines, which are laden with valves, pipes and heavy propellant tanks. Instead, Lozano's design is a flat, compact square — much like a computer chip — covered with 500 microscopic tips that, when stimulated with voltage, emit tiny beams of ions. Together, the array of spiky tips creates a small puff of charged particles that ...
Writing the book in DNA
2012-08-17
Although George Church's next book doesn't hit the shelves until Oct. 2, it has already passed an enviable benchmark: 70 billion copies—roughly triple the sum of the top 100 books of all time.
And they fit on your thumbnail.
That's because Church, the Robert Winthrop Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School and a founding core faculty member of the Wyss Institute for Biomedical Engineering at Harvard University, and his team encoded the book, Regenesis: How Synthetic Biology Will Reinvent Nature and Ourselves, in DNA, which they then read and copied.
Biology's ...
NASA sees wind shear affecting Tropical Storm Gordon
2012-08-17
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Gordon as it continues to spin up in the North central Atlantic Ocean, and revealed the storm has become less symmetric, indicating it is being battered by wind shear.
When Terra passed over Gordon on August 16, 2012 at 10:25 a.m. EDT (1425 UTC) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible image of the storm. The image showed that the bulk of Gordon's clouds were pushed to the north and northeast as a result of southwesterly wind shear. The MODIS image showed what appeared to ...
Studies shed light on why species stay or go in response to climate change
2012-08-17
Berkeley — Two new studies by scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, provide a clearer picture of why some species move in response to climate change, and where they go.
One study, published online Monday, Aug. 6, in the journal Global Change Biology, finds that changes in precipitation have been underappreciated as a factor in driving bird species out of their normal range. In the other study, published today (Wednesday, Aug. 15) in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, researchers found a sharp decrease in range for the Belding's ground squirrel, ...
Less commonly prescribed antibiotic may be better
2012-08-17
Highlights
Vancomycin was the most commonly prescribed antibiotic in dialysis patients for treating certain bloodstream infections, but cefazolin was 38% better than vancomycin at preventing hospitalizations and deaths from these infections.
Cefazolin was also 48% better at preventing sepsis.
Hundreds of thousands of Americans develop bloodstream infections every year.
Washington, DC (August 16, 2012) — The antibiotic most commonly prescribed to treat bloodstream infections in dialysis patients may not always be the best choice, according to a study appearing ...
Blood markers reveal severity of common kidney disease
2012-08-17
Highlights
The blood levels of certain abnormal proteins and the antibodies that attack them rise according to the severity of one of the most common diseases of the kidney.
The findings may help in the diagnosis and management of the disease, called IgA nephropathy.
IgA nephropathy can lead to high blood pressure, swelling and, in some cases, kidney failure.
Washington, DC (August 16, 2012) — Increasing blood levels of particular proteins may act as warning signs for patients with one of the most common diseases of the kidney, according to a study appearing ...
What's your lifetime risk of developing kidney failure?
2012-08-17
Highlights
Approximately 1 in 40 men and 1 in 60 women of middle age will develop kidney failure if they live into their 90s.
People with reduced kidney function face an even higher risk.
Kidney failure is on the rise and currently afflicts 2 million people worldwide.
Washington, DC (August 16, 2012) — How likely are middle-aged adults to develop kidney failure during their lifetime? A study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN) provides some insights, which may be used to help set priorities related to kidney ...
Psychopaths get a break from biology
2012-08-17
SALT LAKE CITY, Aug. 16, 2012 – A University of Utah survey of judges in 19 states found that if a convicted criminal is a psychopath, judges consider it an aggravating factor in sentencing, but if judges also hear biological explanations for the disorder, they reduce the sentence by about a year on average.
The new study, published in the Aug. 17, 2012, issue of the journal Science, illustrates the "double-edged sword" faced by judges when they are given a "biomechanical" explanation for a criminal's mental disorder:
If a criminal's behavior has a biological basis, ...
Mouse study finds clear linkages between inflammation, bacterial communities and cancer
2012-08-17
What if a key factor ultimately behind a cancer was not a genetic defect but ecological?
Ecologists have long known that when some major change disturbs an environment in some way, ecosystem structure is likely to change dramatically. Further, this shift in interconnected species' diversity, abundances, and relationships can in turn have a transforming effect on health of the whole landscape – causing a rich woodland or grassland to become permanently degraded, for example – as the ecosystem becomes unstable and then breaks down the environment.
For this reason, it ...
Is too much brain activity connected to Alzheimer's disease?
2012-08-17
High baseline levels of neuronal activity in the best connected parts of the brain may play an important role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. This is the main conclusion of a new study appearing in PLoS Computational Biology from a group at VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
In recent times, it has become clear that brain activity patterns change at an early stage in Alzheimer's disease. Moreover, there is reason to believe that, instead of being the consequence of structural damage, they might be the cause: recently, a direct influence ...
Organisms cope with environmental uncertainty by guessing the future
2012-08-17
In uncertain environments, organisms not only react to signals, but also use molecular processes to make guesses about the future, according to a study by Markus Arnoldini et al. from ETH Zurich and Eawag, the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology. The authors report in PLoS Computational Biology that if environmental signals are unreliable, organisms are expected to evolve the ability to take random decisions about adapting to cope with adverse situations.
Most organisms live in ever-changing environments, and are at times exposed to adverse conditions ...
Virus throws a wrench in the immune system
2012-08-17
The cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a member of the herpesvirus family. Although most people carry CMV for life, it hardly ever makes them sick. Researchers from the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research and from the USA have now unveiled long term consequences of the on-going presence of CMV: Later in life, more and more cells of the immune system concentrate on CMV, and as a result, the response against other viruses is weakened. These research results help to explain why the elderly are often more prone to infectious diseases than young people.
The viral immunologist Professor ...
New form of carbon observed
2012-08-17
Washington, D.C. — A team of scientists led by Carnegie's Lin Wang has observed a new form of very hard carbon clusters, which are unusual in their mix of crystalline and disordered structure. The material is capable of indenting diamond. This finding has potential applications for a range of mechanical, electronic, and electrochemical uses. The work is published in Science on Aug. 17.
Carbon is the fourth-most-abundant element in the universe and takes on a wide variety of forms—the honeycomb-like graphene, the pencil "lead" graphite, diamond, cylindrically structured ...
Black stroke survivors face greater risk from high blood pressure
2012-08-17
Black people who survived strokes caused by bleeding in the brain were more likely than whites to have high blood pressure a year later – increasing their risk of another stroke, according to a study in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
The study examined racial and ethnic differences in these strokes, called intracranial hemorrhage or ICH. They account for only 10 percent of all strokes but have a death rate of about 40 percent in the first month, much higher than other types of stroke. High blood pressure is the most important modifiable risk factor associated ...
Secrets of 'SuperAger' brains
2012-08-17
CHICAGO --- Researchers have long chronicled what goes wrong in the brains of older people with dementia. But Northwestern Medicine researcher Emily Rogalski wondered what goes right in the brains of the elderly who still have terrific memories. And, do those people – call them cognitive SuperAgers --- even exist?
Rogalski's new study has for the first time identified an elite group of elderly people age 80 and older whose memories are as sharp as people 20 to 30 years younger than them. And on 3-D MRI scans, the SuperAger participants' brains appear as young -– and ...
World's largest tobacco use study: Tobacco control remains major challenge
2012-08-17
BUFFALO, N.Y. – An international survey of tobacco use in three billion individuals, published in the current issue of The Lancet, demonstrates an urgent need for policy change in low- and middle-income countries, according to the University at Buffalo professor who led the research.
"Governments around the world need to start giving economic and regulatory advantages to agricultural products that promote health instead of to products like tobacco that kill people," says lead author Gary A. Giovino, PhD, chair of the Department of Community Health and Health Behavior ...
Democracy works for Endangered Species Act, study finds
2012-08-17
When it comes to protecting endangered species, the power of the people is key, an analysis of listings under the U.S. Endangered Species Act finds.
The journal Science is publishing the analysis comparing listings of "endangered" and "threatened" species initiated by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, the agency that administers the Endangered Species Act, to those initiated by citizen petition.
"We found that citizens, on average, do a better job of picking species that are threatened than does the Fish and Wildlife Service. That's a really interesting and surprising ...
Genes carried by E. coli bacteria linked to colon cancer
2012-08-17
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have identified a type of E. coli bacteria that may encourage the development of colon cancer.
The Liverpool team had previously shown that people with colon cancer and with the inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, have high numbers of a sticky type of E. coli in their colons.
The team have now found that E. coli bacteria, which carry pks genes that encode a toxin that damages DNA in the cells of the gut lining, are more commonly found in the colons of patients that have inflammatory bowel disease ...
What's best for very low birth weight babies
2012-08-17
While the health benefits of breast feeding baby are well known, a new study published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Pediatrics finds that, for very low birth weight (VLBW) babies, a small amount of fortification can improve growth rates without sacrificing the benefits associated with mother's milk.
Human milk provides babies with exactly the right nutrients for growth and also helps protect against infections and diseases. Breast fed babies are less likely to have diarrhea or vomiting, they have fewer chest and ear infections, and long term are less likely ...
Treatment for cervical disease is not linked to increased risk of preterm births
2012-08-17
Treatment for cervical disease does not appear to increase the risk of subsequently giving birth prematurely, according to a study of over 44,000 women in England. The study, published online in the British Medical Journal [1] today (Friday), is the largest in the UK to investigate this and contradicts previous research suggesting treatment could be linked to an increased risk.
Professor Peter Sasieni, professor of cancer epidemiology and biostatistics at the Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine, part of Queen Mary, University of London (UK), led the study. "This ...
[1] ... [6148]
[6149]
[6150]
[6151]
[6152]
[6153]
[6154]
[6155]
6156
[6157]
[6158]
[6159]
[6160]
[6161]
[6162]
[6163]
[6164]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.