Composite nanofibers developed by Penn scientists next chapter in orthopaedic biomaterials
2012-08-07
PHILADELPHIA – Bioengineered replacements for tendons, ligaments, the meniscus of the knee, and other tissues require re-creation of the exquisite architecture of these tissues in three dimensions. These fibrous, collagen-based tissues located throughout the body have an ordered structure that gives them their robust ability to bear extreme mechanical loading.
Many labs have been designing treatments for ACL and meniscus tears of the knee, rotator cuff injuries, and Achilles tendon ruptures for patients ranging from the weekend warrior to the elite Olympian. One popular ...
California's hydroelectricity production is vulnerable to climate change
2012-08-07
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — California's hydropower is vulnerable to climate change, a University of California, Riverside scientist has advised policymakers in "Our Changing Climate," a report released July 31 by the California Natural Resources Agency and the California Energy Commission (CEC).
"Climate change is expected to affect the quantity and timing of water flow in the state," explained Kaveh Madani, a former postdoctoral research scholar in UC Riverside's Water Science and Policy Center (WSPC), who led a research project on climate change effects on hydropower production, ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Aug. 7, 2012 issue
2012-08-07
1. Tuning into Contextual Clues May Help Doctors Improve Antibiotic Prescribing Habits
Appropriate use of antibiotics can improve patient outcomes and reduce risk for antibiotic resistance. Febrile respiratory illnesses, or FRI, often present with vague, cold-like symptoms, making it difficult to discern whether the illness is viral or bacterial. Since there are few bedside clues that reliably distinguish viral from bacterial, physicians rely on contextual factors to aid treatment decisions. Contextual factors include epidemiology (for example, flu pandemic period) and ...
Fainting: All in the family?
2012-08-07
MINNEAPOLIS – Fainting has a strong genetic predisposition, according to new research published in the August 7, 2012, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Fainting, also called vasovagal syncope, is a brief loss of consciousness when your body reacts to certain triggers, such as emotional distress or the sight of blood.
"The question of whether fainting is caused by genetic factors, environmental factors or a mixture of both has been the subject of debate," said study author Samuel F. Berkovic, MD, FRS, with the University ...
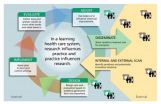
A 'learning health system' moves from idea to action
2012-08-07
In the United States, clinicians are struggling to provide better and more affordable health care to more people—while keeping up with new scientific developments. The idea of a "learning health system" is one proposed solution for rapidly applying the best available scientific evidence in real-time clinical practice. In the August 7 Annals of Internal Medicine, a Group Health Cooperative team describes the experience of turning this intriguing concept into action.
"In a learning health system, evidence and practice come together in a virtuous cycle, influencing each ...
Researchers peek at the early evolution of sex chromosomes
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Two new studies offer insight into sex chromosome evolution by focusing on papaya, a multimillion dollar crop plant with a sexual problem (as far as growers are concerned) and a complicated past. The findings are described in two papers in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research reveals that the papaya sex chromosomes have undergone dramatic changes in their short evolutionary histories (they are about 7 million years old; by comparison, human sex chromosomes began their evolution more than 167 million years ago). One of the ...
Researchers find evidence of ritual use of 'black drink' at Cahokia
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — People living 700 to 900 years ago in Cahokia, a massive settlement near the confluence of the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers, ritually used a caffeinated brew made from the leaves of a holly tree that grew hundreds of miles away, researchers report.
The discovery – made by analyzing plant residues in pottery beakers from Cahokia and its surroundings – is the earliest known use of this "black drink" in North America. It pushes back the date by at least 500 years, and adds to the evidence that a broad cultural and trade network thrived in the Midwest ...
Generic language helps fuel stereotypes, NYU, Princeton researchers find
2012-08-07
Hearing generic language to describe a category of people, such as "boys have short hair," can lead children to endorse a range of other stereotypes about the category, a study by researchers at New York University and Princeton University has found. Their research, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), also points to more effective methods to reduce stereotyping and prejudice.
The study focused on "social essentialism," or the belief that certain social categories, such as race or gender, mark fundamentally distinct kinds of people. ...
Gladstone scientists discover that epilepsy drug reverses memory loss in animal model of AD
2012-08-07
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—August 6, 2012— Scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have discovered that an FDA-approved anti-epileptic drug reverses memory loss and alleviates other Alzheimer's-related impairments in an animal model of the disease.
Scientists in the laboratory of Lennart Mucke, MD, who directs neurological research at Gladstone, conducted the research on mice genetically modified to simulate key aspects of Alzheimer's disease. In the study, they show how levetiracetam—a drug commonly prescribed for patients who suffer from epilepsy—suppresses abnormal brain activity ...
New genetic study defines the genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas
2012-08-07
VIDEO:
Harry Ostrer, M.D., discusses how his research into a new genetic analysis focusing on Jews from North Africa has provided an overall genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas. Dr....
Click here for more information.
August 6, 2012 — (Bronx, NY) — A new genetic analysis focusing on Jews from North Africa has provided an overall genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas. The findings support the historical record of Middle Eastern Jews settling in North Africa during Classical Antiquity, ...
Behavioral intervention can reduce tics in adults with Tourette syndrome
2012-08-07
Specially designed comprehensive behavioral therapy is more effective than sessions offering patient support and education in helping adults with Tourette syndrome manage their tics – sudden, repetitive motions or vocalizations – according to a study in the August issue of Archives of General Psychiatry. The findings come from a team of investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)/Harvard Medical School, Yale University, the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, and other institutions.
"The program we tested, which teaches patients new ways ...
Weight training associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes in study of men
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Weight training was linked with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in a study of male health professionals, and those men who engaged in weight training and aerobic exercise for at least 150 minutes a week had the greatest reduction in risk, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), but the role of weight training in the primary prevention of the disease is largely unknown, according to ...
Physical activity associated with lower risk of death in patients with diabetes
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Higher levels of physical activity were related to lower risk of death in patients with diabetes, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Increased physical activity (PA) has long been considered a key element in diabetes management. Patients with diabetes are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature death, so researchers note it is important to determine whether PA can produce similar beneficial effects in this high-risk population. While other studies have suggested that ...
Weight training associated with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
2012-08-07
Boston, MA – Men who do weight training regularly—for example, for 30 minutes per day, five days per week—may be able to reduce their risk of type 2 diabetes by up to 34%, according to a new study by Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) and University of Southern Denmark researchers. And if they combine weight training and aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or running, they may be able to reduce their risk even further—up to 59%.
This is the first study to examine the role of weight training in the prevention of type 2 diabetes. The results suggest that, because ...
Study examines racial/ethnic disparities in cranial CT among children
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – The odds of undergoing cranial computed tomography (CT) among children with minor blunt head trauma who were at higher risk for clinically important traumatic brain injury did not appear to differ by race/ethnicity in a secondary analysis of a study of injured children, according to a report in the August issue of Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, a JAMA Network publication. However, there may have been differences for children at intermediate or lowest risk.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of pediatric illness and death in the U.S., ...
Study examines effects of growth hormone-releasing hormone on cognitive function
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Treatment with growth hormone-releasing hormone appears to be associated with favorable cognitive effects among both adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults, according to a randomized clinical trial published Online First by Archives of Neurology, a JAMA Network publication.
"Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), growth hormone and insulinlike growth factor 1 have potent effects on brain function, their levels decrease with advancing age, and they likely play a role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease," the authors write as background ...
Study examines decision-making brain activity in patients with hoarding disorder
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Patients with hoarding disorder exhibited abnormal activity in regions of the brain that was stimulus dependent when deciding what to do with objects that did or did not belong to them, according to a report in the August issue of Archives of General Psychiatry, a JAMA Network publication.
Hoarding disorder (HD) is defined as the excessive collection of objects and an inability to discard them. It is characterized by marked avoidance of decisions about possessions, according to the study background.
David F. Tolin, Ph.D., of the Institute of Living, Hartford, ...
White children more likely to receive CT scans than Hispanic or African-American children
2012-08-07
White children are more likely to receive cranial (head) CT scans in an emergency department following minor head trauma, compared with African-American or Hispanic children, a study published by researchers at UC Davis has found.
The study findings do not indicate that CT (computed tomography) scans are underused in African-American and Hispanic children. Rather, the researchers suggested that white children may receive too many CT scans and thus may be exposed to unnecessary radiation.
The results are online and appear in the August issue of the Archives of Pediatrics ...
Holy bat detector! Ecologists develop first Europe-wide bat ID tool
2012-08-07
Just as differences in song can be used to distinguish one bird species from another, the pips and squeaks bats use to find prey can be used to identify different species of bat. Now, for the first time, ecologists have developed a Europe-wide tool capable of identifying bats from their echolocation calls.
The new free online tool – iBatsID – will be a major boost to conserving bats, whose numbers have declined significantly across Europe over the past 50 years. Details are published today in the British Ecological Society's Journal of Applied Ecology.
Working with ...
Research represents major breakthrough in macular degeneration
2012-08-07
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Aug. 6 , 2012) — University of Kentucky researchers, led by Dr. Jayakrishna Ambati, have made an exciting finding in the "dry" form of age-related macular degeneration known as geographic atrophy (GA). GA is an untreatable condition that causes blindness in millions of individuals due to death of retinal pigmented epithelial cells. The paper, "ERK1/2 Activation is a Therapeutic Target in Age-Related Macular Degeneration" appears in the current online issue of the premier journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Ambati, professor of physiology, ...
More education, socioeconomic benefits equals longer life
2012-08-07
Despite advances in health care and increases in life expectancy overall, Americans with less than a high school education have life expectancies similar to adults in the 1950s and 1960s.
"The most highly educated white men live about 14 years longer than the least educated black men," says S. Jay Olshansky, professor of epidemiology at the University of Illinois at Chicago School of Public Health and lead author of the study. "The least educated black women live about 10 years less than the most educated white women."
The research, funded by The MacArthur Foundation ...
Bariatric surgery does not increase risk of broken bones
2012-08-07
An international study, led by researchers at the Medical Research Council Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit (MRC LEU) at the University of Southampton, has found that obese patients who undergo bariatric surgery are not at an increased risk of broken bones in the first few years after the operation.
However, the study, published in the British Medical Journal today (DATE) has shown that there is a possibility of an increase in fracture risk after three to five years.
Generally, a higher Body Mass Index (BMI) protects the bone against most types of fracture because a higher ...
Despite financial challenges, safety-net hospitals provide high quality care
2012-08-07
A Yale study of the care quality received at safety-net hospitals — which provide care for the majority of uninsured and other vulnerable populations — found that quality at these facilities is similar to non-safety-net hospitals. This is despite the unique financial challenges at safety-net hospitals in the face of rising costs and the potential impact of the health care law.
Published in the August issue of Health Affairs, the study was conducted by Elizabeth E. Drye, M.D., of the Yale Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, Joseph S. Ross, M.D., assistant professor ...
Long-term use of blood pressure meds promoting sun sensitivity may raise lip cancer risk
2012-08-07
OAKLAND, Calif., August 6, 2012 – Long-term use of commonly used blood pressure medications that increase sensitivity to sunlight is associated with an increased risk of lip cancer in non-Hispanic whites, according to a Kaiser Permanente study that appears in the current online issue of Archives of Internal Medicine.
Funded by the National Cancer Institute, the study found that photosensitizing antihypertensive drugs such as nifedipine and hydrochlorothiazide were associated with cancer of the epithelial cells known as squamous cells—which are the main part of the outermost ...
Implantable defibrillators lead to decrease in cardiac arrests
2012-08-07
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators account for one-third of the decrease in cardiac arrests caused by ventricular fibrillation in North-Holland, according to research in Circulation, an American Heart Association journal.
VF is an abnormal heart rhythm that makes the heart quiver so it can't pump blood.
ICDs are small electronic devices implanted in the chest that detect potentially fatal abnormal heart rhythms and try to stop them with electric shocks. Generally, only people with a high risk of sudden cardiac death — mostly those at high risk of abnormal heartbeats ...
[1] ... [6176]
[6177]
[6178]
[6179]
[6180]
[6181]
[6182]
[6183]
6184
[6185]
[6186]
[6187]
[6188]
[6189]
[6190]
[6191]
[6192]
... [8806]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.