BUSM researcher finds link between brain signaling and renal function
2012-06-05
(Boston) - Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) researchers recently uncovered a brain signaling pathway responsible for regulating the renal excretion of sodium. The findings appear in the Journal of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Hypertension, or chronic high blood pressure, affects one-third of adults, significantly increasing cardiovascular risk and mortality. Approximately 50 percent of hypertensive patients are salt-sensitive and exhibit an increase in blood pressure following salt-intake.
According to the researchers, little ...
New immune therapy shows promise in kidney cancer
2012-06-05
BOSTON – An antibody that helps a person's own immune system battle cancer cells shows increasing promise in reducing tumors in patients with advanced kidney cancer, according to researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
The results of an expanded Phase 1 trial presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology's annual conference in Chicago, showed that some patients treated with a fully human monoclonal antibody developed by Bristol Myers Squibb had a positive response to the effort by the agent, BMS-936558, to prolong the immune system's efforts to fight ...
Underground search for neutrino properties unveils first results
2012-06-05
Menlo Park, Calif. — Scientists studying neutrinos have found with the highest degree of sensitivity yet that these mysterious particles behave like other elementary particles at the quantum level. The results shed light on the mass and other properties of the neutrino and prove the effectiveness of a new instrument that will yield even greater discoveries in this area.
The Enriched Xenon Observatory 200 (EXO-200), an international collaboration led by Stanford University and the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, has begun one of ...
Vaccinations of US children declined after publication of now-refuted autism risk
2012-06-05
New University of Cincinnati research has found that fewer parents in the United States vaccinated their children in the wake of concerns about a purported link (now widely discredited) between the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine and autism.
Lenisa Chang, assistant professor of economics in UC's Carl H. Lindner College of Business, found that the MMR-autism controversy, which played out prominently in the popular media following publication in a 1998 medical journal, led to a decline of about two percentage points in terms of parents obtaining the MMR vaccine for ...
Physicists close in on a rare particle-decay process
2012-06-05
PASADENA, Calif.—In the biggest result of its kind in more than ten years, physicists have made the most sensitive measurements yet in a decades-long hunt for a hypothetical and rare process involving the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei.
If discovered, the researchers say, this process could have profound implications for how scientists understand the fundamental laws of physics and help solve some of the universe's biggest mysteries—including why there is more matter than antimatter and, therefore, why regular matter like planets, stars, and humans exists at all. ...
Emergency department algorithm may predict risk of death for heart failure patients
2012-06-05
Physicians can reduce the number of heart failure deaths and unnecessary hospital admissions by using a new computer-based algorithm developed at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) that calculates each patient's individual risk of death. Published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, the algorithm improves upon clinical decision-making and determines whether or not a patient with heart failure should be admitted to hospital. To bring this tool into the emergency departments, Peter Munk Cardiac Centre cardiologists are developing smartphone and web-based ...
June 2012 story tips from Oak Ridge National Laboratory
2012-06-05
MATERIALS – Transparent performance . . .
Windshields, windows, solar panels, eyeglasses, heart stents and hundreds of other products representing a multi-billion-dollar market are potential targets for Oak Ridge National Laboratory's thin-film superhydrophobic technology. Conventional commercially available products tend to lack transparency, suitable bonding capability or both, making them largely impractical, said Tolga Aytug, one of the developers. The ORNL product, based on glass, can be produced with manufacturing processes that are cost effective and easily scaled ...
Depression treatment can prevent adolescent drug abuse
2012-06-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- Treating adolescents for major depression can also reduce their chances of abusing drugs later on, a secondary benefit found in a five-year study of nearly 200 youths at 11 sites across the United States.
Only 10 percent of 192 adolescents whose depression receded after 12 weeks of treatment later abused drugs, compared to 25 percent of those for whom treatment did not work, according to research led by John Curry, a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University.
"It turned out that whatever they responded to -- cognitive behavioral therapy, ...
Life expectancy prolonged for esophageal cancer patients
2012-06-05
Reston, Va. (June 4, 2012) – For those with esophageal cancer, initial staging of the disease is of particular importance as it determines whether to opt for a curative treatment or palliative treatment. Research presented in the June issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine shows that physicians using positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) can discern incremental staging information about the cancer, which can significantly impact management plans.
In 2012, an estimated 17,500 people will be diagnosed with esophageal cancer and 15,000 will die from ...
New research yields insights into Parkinson's disease
2012-06-05
Researchers at the University of Toronto Scarborough (UTSC) used an innovative technique to examine chemical interactions that are implicated in Parkinson's Disease.
The work details how a protein called alpha-synuclein interacting with the brain chemical dopamine can lead to protein misfolding and neuronal death.
Parkinson's Disease is a neurodegenerative disease which results in loss of motor control and cognitive function. Although the cause isn't known precisely, the disease involves the death of brain cells that produce dopamine, a chemical important in neuronal ...
Mature liver cells may be better than stem cells for liver cell transplantation therapy
2012-06-05
Tampa, Fla. (June 4, 2012) – After carrying out a study comparing the repopulation efficiency of immature hepatic stem/progenitor cells and mature hepatocytes transplanted into liver-injured rats, a research team from Sapporo, Japan concluded that mature hepatocytes offered better repopulation efficiency than stem/progenitor cells.
Until day 14 post-transplantation, the growth of the stem/progenitor cells was faster than the mature hepatocytes, but after two weeks most of the stem/progenitor cells had died. However, the mature hepatocytes continued to survive and proliferate ...
Cell transplantation of lung stem cells has beneficial impact for emphysema
2012-06-05
Tampa, Fla. (June 4, 2012) – When autologous (self-donated) lung-derived mensenchymal stem cells (LMSCs) were transplanted endoscopically into 13 adult female sheep modeled with emphysema, post-transplant evaluation showed evidence of tissue regeneration with increased blood perfusion and extra cellular matrix content. Researchers concluded that their approach could represent a practical alternative to conventional stem cell-based therapy for treating emphysema.
The study is published in Cell Transplantation (21:1), now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/.
...
Mosquitoes fly in rain thanks to low mass
2012-06-05
The mosquito is possibly summer's biggest nuisance. Sprays, pesticides, citronella candles, bug zappers — nothing seems to totally deter the blood-sucking insect. And neither can rain apparently.
Even though a single raindrop can weigh 50 times more than a mosquito, the insect is still able to fly through a downpour.
Georgia Tech researchers used high-speed videography to determine how this is possible. They found the mosquito's strong exoskeleton and low mass render it impervious to falling raindrops.
The research team, led by Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering ...
Energy-dense biofuel from cellulose close to being economical
2012-06-05
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A new Purdue University-developed process for creating biofuels has shown potential to be cost-effective for production scale, opening the door for moving beyond the laboratory setting.
A Purdue economic analysis shows that the cost of the thermo-chemical H2Bioil method is competitive when crude oil is about $100 per barrel when using certain energy methods to create hydrogen needed for the process. If a federal carbon tax were implemented, the biofuel would become even more economical.
H2Bioil is created when biomass, such as switchgrass or corn ...
Not ready to play nice: Online attacks by presidential candidates
2012-06-05
As voters increasingly rely on websites of presidential primary candidates for news, they run a risk because candidates' online attacks are not vetted through traditional "watchdog journalists" and other gatekeepers to determine accuracy or fairness, according to a study by Baylor University researchers.
"The primary danger is that constituents often use this one-sided information to decide how to vote," said Mia Moody, Ph.D., study co-author and an assistant professor of journalism, public relations and new media in Baylor's College of Arts & Sciences.
The study — "Not ...
Investigational diabetes drug may have fewer side effects
2012-06-05
AUDIO:
Drugs that are used to treat Type 2 diabetes also can contribute to unwanted side effects. But now, working with mice, researchers, led by scientists at Washington University School of...
Click here for more information.
Drugs for type 2 diabetes can contribute to weight gain, bone fractures and cardiovascular problems, but in mice, an investigational drug appears to improve insulin sensitivity without those troublesome side effects, researchers at Washington University ...
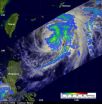
NASA looks at Typhoon Mawar, now heading to sea
2012-06-05
Over the weekend of June 2 and 3, Typhoon Mawar skirted the east coast of the Philippines bringing heavy surf, heavy rainfall and gusty winds that led to several missing and injured people. NASA's TRMM satellite and Aqua satellite showed heavy rainfall and cloud extent of the storm.
On June 1, Mawar (known as Ambo in the Philippines) had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots and it was about 245 miles east-northeast of Manila, Philippines. On that day, as Mawar continued north, some warnings were posted for the Philippines: Public storm warning signal #1 was up in the ...
How religion promotes confidence about paternity
2012-06-05
ANN ARBOR, Mich.—Religious practices that strongly control female sexuality are more successful at promoting certainty about paternity, according to a study published in the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study analyzed genetic data on 1,706 father-son pairs in a traditional African population—the Dogon people of Mali, West Africa—in which Islam, two types of Christianity, and an indigenous, monotheistic religion are practiced in the same families and villages.
"We found that the indigenous religion allows males to achieve ...
UT Southwestern investigators provide first atomic-level images of the CLOCK complex
2012-06-05
DALLAS – June 4, 2012 – UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have taken a major step toward understanding the cellular clock, mapping for the first time the atomic-level architecture of a key component of the timekeeper that governs the body's daily rhythms.
The daily, or circadian, cycles guided by the body's clocks affect our ability to get a good night's sleep, how fast we recover from jet lag, and even the best time to give cancer treatments, said Dr. Joseph Takahashi, senior author of the Science study published online and a pioneer in the study of circadian ...
RHESSI will use Venus transit to improve measurements of the sun's diameter
2012-06-05
The RHESSI (Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager) satellite focuses on the highest energy x-rays and gamma-rays produced by the sun, helping to observe solar flares of all shapes and sizes. The satellite is pointed toward the sun, and constantly in rotation, which provides a serendipitous bit of side research: by monitoring the limb of the sun on its four second rotation cycle, RHESSI's Solar Aspect System (SAS) has produced ten years worth of precise measurements of the sun's diameter. This has already provided scientists with one of the most accurate measurements ...
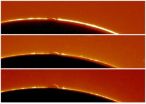
The mysterious arc of Venus
2012-06-05
When Venus transits the sun on June 5th and 6th, an armada of spacecraft and ground-based telescopes will be on the lookout for something elusive and, until recently, unexpected: The Arc of Venus.
"I was flabbergasted when I first saw it during the 2004 transit," recalls astronomy professor Jay Pasachoff of Williams College. "A bright, glowing rim appeared around the edge of Venus soon after it began to move into the sun."
For a brief instant, the planet had turned into a "ring of fire."
Researchers now understand what happened. Backlit by the sun, Venus's atmosphere ...
Ill, older patients who rely on emergency room often live final days in hospital, study finds
2012-06-05
Half of adults over age 65 made at least one emergency department (ED) visit in the last month of life, in a study led by a physician at the San Francisco VA Medical Center (SFVAMC) and UCSF.
Three quarters of ED visits led to hospital admissions, and more than two-thirds of those admitted to the hospital died there.
In contrast, the 10 percent of study subjects who had enrolled in hospice care at least one month before death were much less likely to have made an ED visit or died in the hospital.
"For too many older Americans, the emergency department is a conduit ...
New in Lithosphere: Mars, Iraq, Canada, and the Spanish Pyrenees
2012-06-05
Boulder, Colo., USA – New Lithosphere science posted online 4 June 2012 includes a study of the Valles Marineris fault zone, Mars, and asks why such a trough system occurs there, when such structures on Earth are mainly associated with plate tectonics. Other papers discuss landslides in the Pyrenees; first evidence of a "missing" Cretaceous arc assemblage in the Iraqi segment of the Zagros orogenic belt; and new information on the age of the Okanagan Valley shear zone, Canada.
Abstracts are online at http://lithosphere.gsapubs.org/content/early/recent. Representatives ...
Orange County Sports Medicine Specialist Adds Online Forms
2012-06-05
California sports medicine specialist Dr. Ralph Venuto (http://www.drvenuto.com) recently added downloadable forms on his website, helping patients get the resources they need before their first office visit. The Medical History form, Patient Financial Agreement, Notice of Privacy Practices Receipt, and Patient Information Form for the practice are all now available online. Dr. Venuto believes that giving patients access to medical forms online is a step that helps his team become more efficient in patient care.
"Online medical forms have become a norm at the modern ...
Practical tool can 'take pulse' of blue-green algae status in lakes
2012-06-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists have designed a screening tool that provides a fast, easy and relatively inexpensive way to predict levels of a specific toxin in lakes that are prone to blue-green algal blooms.
Blue-green algae is not your average pond scum - rather than consisting of plant-like organisms, blue-green algae actually are cyanobacteria, and some species are linked to the production and release of the toxin microcystin into the water. Human exposure to the toxin through drinking or recreational water contact can threaten public health by causing liver damage, ...
[1] ... [6474]
[6475]
[6476]
[6477]
[6478]
[6479]
[6480]
[6481]
6482
[6483]
[6484]
[6485]
[6486]
[6487]
[6488]
[6489]
[6490]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.