Pain relief through distraction -- it's not all in your head
2012-05-18
Mental distractions make pain easier to take, and those pain-relieving effects aren't just in your head, according to a report published online on May 17 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication.
The findings based on high-resolution spinal fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) as people experienced painful levels of heat show that mental distractions actually inhibit the response to incoming pain signals at the earliest stage of central pain processing.
"The results demonstrate that this phenomenon is not just a psychological phenomenon, but an active neuronal ...
When you eat matters, not just what you eat
2012-05-18
When it comes to weight gain, when you eat might be at least as important as what you eat. That's the conclusion of a study reported in the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism published early online on May 17th.
When mice on a high-fat diet are restricted to eating for eight hours per day, they eat just as much as those who can eat around the clock, yet they are protected against obesity and other metabolic ills, the new study shows. The discovery suggests that the health consequences of a poor diet might result in part from a mismatch between our body clocks and our ...
New study shows that workplace inspections save lives, don't destroy jobs
2012-05-18
Research to be published in Science on May 18, 2012, sheds light on a hot-button political issue: the role and effectiveness of government regulation. Does it kill jobs or protect the public?
The new study, co-authored by Harvard Business School Professor Michael Toffel, Professor David Levine of the Haas School of Business at the University of California, Berkeley, and Boston University doctoral student Matthew Johnson, examines workplace safety inspections conducted by California's Division of Occupational Safety and Health (Cal/OSHA). The authors carried out the first ...
Religion is a potent force for cooperation and conflict, research shows
2012-05-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich.--- Across history and cultures, religion increases trust within groups but also may increase conflict with other groups, according to an article in a special issue of Science.
"Moralizing gods, emerging over the last few millennia, have enabled large-scale cooperation and sociopolitical conquest even without war," says University of Michigan anthropologist Scott Atran, lead author of the article with Jeremy Ginges of the New School for Social Research.
"Sacred values sustain intractable conflicts like those between the Israelis and the Palestinians ...
Google goes cancer: Researchers use search engine algorithm to find cancer biomarkers
2012-05-18
The strategy used by Google to decide which pages are relevant for a search query can also be used to determine which proteins in a patient's cancer are relevant for the disease progression. Researchers from Dresden University of Technology, Germany, have used a modified version of Google's PageRank algorithm to rank about 20,000 proteins by their genetic relevance to the progression of pancreatic cancer. In their study, published in PLoS Computational Biology, they found seven proteins that can help to assess how aggressive a patient's tumor is and guide the clinician ...
Researchers reveal an RNA modification influences thousands of genes
2012-05-18
###
Weill Cornell Medical College
Weill Cornell Medical College, Cornell University's medical school located in New York City, is committed to excellence in research, teaching, patient care and the advancement of the art and science of medicine, locally, nationally and globally. Physicians and scientists of Weill Cornell Medical College are engaged in cutting-edge research from bench to bedside, aimed at unlocking mysteries of the human body in health and sickness and toward developing new treatments and prevention strategies. In its commitment to global health and ...
Untangling the development of breast cancer
2012-05-18
In two back-to-back reports published online on 17 May in Cell, researchers have sequenced the genomes of 21 breast cancers and analysed the mutations that emerged during the tumours' development. The individual results are described below.
Led by researchers from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, the team created a catalogue of all the mutations in the genomes of the 21 cancer genomes and identified the mutational processes that lead to breast cancer. They found that these mutations accumulate in breast cells over many years, initially rather slowly, but picking up ...
Resolving the ortholog conjecture
2012-05-18
Researchers at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute have confirmed the long-held conjecture that studying the genes we share with other animals is a viable means of extrapolating information about human biology. The study, published in the open access journal PLoS Computational Biology, shows how bioinformatics makes it possible to test the conjecture.
Scientists have long looked to model species – mice, for example – to understand human biology. This is at the root of what is called the 'ortholog conjecture': the idea ...
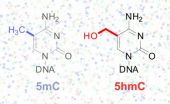
New technique reveals unseen information in DNA code
2012-05-18
Imagine reading an entire book, but then realizing that your glasses did not allow you to distinguish "g" from "q." What details did you miss?
Geneticists faced a similar problem with the recent discovery of a "sixth nucleotide" in the DNA alphabet. Two modifications of cytosine, one of the four bases that make up DNA, look almost the same but mean different things. But scientists lacked a way of reading DNA, letter by letter, and detecting precisely where these modifications are found in particular tissues or cell types.
Now, a team of scientists from the University ...
Salk study may offer drug-free intervention to prevent obesity and diabetes
2012-05-18
VIDEO:
This is an interview with Dr. Panda.
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA, CA----It turns out that when we eat may be as important as what we eat. Scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies have found that regular eating times and extending the daily fasting period may override the adverse health effects of a high-fat diet and prevent obesity, diabetes and liver disease in mice.
In a paper published May 17 in Cell Metabolism, scientists from Salk's ...
We can learn a lot from other species
2012-05-18
Researchers at the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute have confirmed the long-held belief that studying the genes we share with other animals is useful. The study, published today in the open access journal PLoS Computational Biology, shows how bioinformatics makes it possible to test the fundamental principles on which life science is built.
Studying genes helps life science researchers understand how our bodies work and how diseases progress. Scientists have long looked to model species – mice, for example – to understand ...
Technology convergence may widen the digital divide
2012-05-18
Technology is helping communication companies merge telephone, television and Internet services, but a push to deregulate may leave some customers on the wrong side of the digital divide during this convergence, according to a Penn State telecommunications researcher.
"Moving away from copper lines is an example of abandoning obsolete technology and embracing technology that is faster, better, cheaper and more convenient," said Rob Frieden, Pioneers Chair in Cable Television and professor of telecommunications and law. "But the risk is that we may be creating a digital ...
In chemical reactions, water adds speed without heat
2012-05-18
MADISON – An international team of researchers has discovered how adding trace amounts of water can tremendously speed up chemical reactions—such as hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis—in which hydrogen is one of the reactants, or starting materials.
Led by Manos Mavrikakis, the Paul A. Elfers professor of chemical and biological engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, and Flemming Besenbacher, a professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Aarhus, Denmark, the team published its findings in the May 18 issue of the journal Science.
Hydrogenation ...
Weight management in pregnancy with diet is beneficial and safe and can reduce complications
2012-05-18
For pregnant women, including those who are overweight and obese, following a healthy calorie controlled diet during pregnancy is safe and can reduce the risk of serious complications such as pre-eclampsia, diabetes and premature birth, finds a study published on bmj.com today.
In the UK, more than half the women of reproductive age are overweight or obese, and across Europe and the US, up to 40% of women gain more than the recommended weight in pregnancy. Excessive weight gain during pregnancy is associated with a number of serious health problems.
Pregnancy is thought ...
Bringing home (less) of the bacon
2012-05-18
The recent excesses of Wall Street may be big news but behind the headlines there's another story: When it comes to men and women stockbrokers, someone is taking home a bigger paycheck.
New research shows that women stockbrokers sometimes earn as much as 20 percent less than their male counterparts. "Stockbrokers are among the highest paid workers, yet they have the greatest gender inequality among all sales worker jobs," says Prof. Janice Fanning Madden, who conducted the research.
Her paper "Performance-Support Bias and the Gender Pay Gap Among Stockbrokers," will ...
Western Springs Orthodontist Offers Online Appointment Request Form
2012-05-18
Dr. Joseph Kizior, Brookfield orthodontist, is pleased to offer an easy to use online appointment request form as a part of his practice's comprehensive website. The appointment request form is just one of the features on the Western Springs orthodontist's website designed to make dealing with Dr. Kizior's practice easy for patients.
To schedule an appointment, patients simply have to navigate to the appointment request form on Dr. Kizior's website. Once there, patients can request the date and time that they wish to come in for an appointment and the practice's scheduling ...
Hot Ink Slots Tattoo Trail to Facebook
2012-05-18
This week's slot promotion at Spin and Win Casino not only gives players a chance to win a share of GBP250 as the top wagerer but in addition upload photos of their own tattoos to win free cash prizes on the Spin and Win Facebook Page.
A 50 loyalty point booster will be credited to players SpinandWin.com account for sharing their photo plus they'll be entered into a competition for an additional 1000 points for the best tattoo.
The Facebook page for SpinandWin.com is a hub for players to get involved with enjoying promotions, games and freebies! Just 'liking' the ...
Abundance of rare DNA changes following population explosion may hold clues to common diseases
2012-05-18
One-letter switches in the DNA code occur much more frequently in human genomes than anticipated, but are often only found in one or a few individuals.
The abundance of rare variations across the human genome is consistent with the population explosion of the past few thousand years, medical geneticists and evolutionary biologists report in the May 17 advanced online edition of Science.
"This is a dramatic example of how recent human history has profoundly shaped patterns of genetic variation," said Joshua Akey, University of Washington associate professor of genome ...
RHS Chelsea Flower Show
2012-05-18
This year the show will commence on May 22nd and wrap up on May 26th. The RHS Chelsea Flower Show contains many different aspects including unique exhibits every year, showcases from emerging talents and seminars to help amateurs solve the many challenges of gardening in both an urban and country setting.
Held in the grounds of the Royal Hospital Chelsea, the RHS Chelsea Flower Show quite literally takes over south-west London during the 5 days which it is held in May. Many of the feature gardens require some assembly so massive awnings and screens are erected to not ...
Scientists study serious immune malfunction
2012-05-18
Defects in the gene that encodes the XIAP protein result in a serious immune malfunction. Scientists used biochemical analyses to map the protein's ability to activate vital components of the immune system. Their results have recently been published in Molecular Cell, a journal of international scientific repute.
Researchers at The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Protein Research at the University of Copenhagen have mapped how the XIAP protein activates a vital component of the immune defence system, specifically the component that fights bacterial infections in the ...
Genetic testing may not trigger more use of health services
2012-05-18
SEATTLE—People have more and more chances to participate in genetic testing that can indicate their range of risk for developing a disease. Receiving these results does not appreciably drive up— or diminish—test recipients' demand for potentially costly follow-up health services, according to a new study in the May 17, 2012 early online issue of Genetics in Medicine.
The study was done by researchers with the Multiplex Initiative, a multi-center collaborative initiative involving investigators from the National Institutes of Health's Intramural Research Program, Group ...
Kefalonia Holiday Packages Have Become Inexpensive Following Greek Finance Worries
2012-05-18
Greece is a yet to recover completely from the economic turmoil that it was going through, but the tourism industry seems to have taken an excellent initiative to make sure that the flow of foreign currency remains intact - almost the entire tourism department of Greece seems to have gone on a price slashing spree and the industry is mainly banking on Kefalonia.
The property owners and the hotel owners catering to tourists to Greece have reduced their prices considerably and that has made Kefalonia an exotic destination less the price tag associated with such destinations.
Kefalonia ...
A new category of heel: The customer service saboteur
2012-05-18
PULLMAN, Wash.—There are jerks, and then there are jerks.
Joel Anaya has given them a fair amount of study, focusing on that very special jerk who can take a routine service experience—dining out, paying at a cash register, air travel—and make it a nightmare.
Anaya has even coined a term for it—"customer service sabotage"—and discerned seven different categories of rude customers who can be a serious liability for the service industry.
"Customers don't just go to a restaurant to enjoy a burger," he says. "They go to have a good time, to enjoy the ambience of the establishment. ...
Governor Christie Signs Tough Road Rage Bill Into Law
2012-05-18
New Jersey Governor Chris Christie recently signed a bill into law that increases penalties for bodily harm caused by aggressive driving.
Jessica Rogers' Law
Jessica Rogers was 16 when she was involved in an automobile accident that left her paralyzed from the chest down and necessitated 24 surgeries. Jessica's accident was the result of aggressive and reckless driving behavior, known commonly as "road rage."
After her accident, Jessica's parents lobbied for tougher laws for those that commit road rage crashes, believing that current laws did not penalize ...
New York Lawmakers Debate Reforms to Scaffolding Law
2012-05-18
Some New York lawmakers and other tort reform advocates wish to reform the state's scaffolding laws, reducing the liability of contractors and property owners and leaving injured employees at risk.
Current New York Scaffolding Law
New York is the only state in the nation that holds contractors and property owners absolutely liable for any worker injury sustained from a fall or a falling object, otherwise known as a fall injury. This type of liability is known as "strict liability."
The law also requires employers to take all reasonable action to prevent ...
[1] ... [6470]
[6471]
[6472]
[6473]
[6474]
[6475]
[6476]
[6477]
6478
[6479]
[6480]
[6481]
[6482]
[6483]
[6484]
[6485]
[6486]
... [8800]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.