Discriminated groups create safe spaces online
2025-03-05
Online threats, hatred and harassment have led people who feel discriminated against to create digital spaces where they can feel safe. According to a new thesis from the University of Gothenburg, these spaces are characterised by clear rules and constant maintenance and monitoring.
Much of social life today takes place online. Unfortunately, the worst aspects of interpersonal relationships also appear in the digital world. A study of 51 countries revealed that 38% of women had personally experienced online harassment. Bullying and harassment have led people to create their own digital safe spaces, which is the topic ...
How one researcher equipped with a smartphone is creating detailed reports on the insides of stranded sea creatures
2025-03-05
What inspired you to become a researcher?
My interest in research began with an early love for nature, particularly the ocean and its wildlife. Drawn to conservation, I am fascinated by how technology can help study and protect marine mammals.
Can you tell us about the research you’re currently working on?
This research focuses on using accessible 3D scanning technologies, like LiDAR-equipped mobile devices and UAV photogrammetry, to document and analyze stranded marine mammals. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to determine the ...
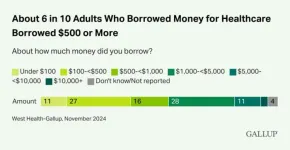
Americans borrowed $74 billion last year to cover healthcare costs
2025-03-05
WASHINGTON, D.C. – March 5, 2025 – More than 31 million Americans (12%) report needing to borrow about $74 billion last year to pay for healthcare despite most having some form of health insurance, according to a new survey from West Health and Gallup. Nearly one-third (28%) report being “very concerned” that a major health event could throw them into debt.
The survey found almost 20% of Americans aged 49 and under needed to borrow money to cover medical costs compared with just 9% of those 50 to 64. Women between the ages of 50 and 64 were twice as likely as men in the same age group to say they had to borrow (12% vs. 6%). Two percent ...
Iconic Australian bird reveals hidden farming talent
2025-03-05
A beloved Australian bird best known for its stunning tail and powers of mimicry may have a cunning hidden talent.
New research has revealed the superb lyrebird to be a resourceful farmer, creating micro-habitats to host and fatten its prey before returning later to feast.
Scientists from La Trobe University observed the ground-dwelling birds working to create habitats suitable for their diet of worms, centipedes and spiders.
In a new paper published in the Journal of Animal Ecology, the researchers found that lyrebirds arranged litter and soil on the forest floor in ways that promote more ...
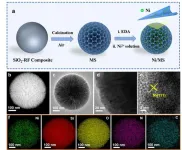
New method improves catalyst performance for hydrogenation reactions
2025-03-05
Recently, the research team led by Researcher WANG Guozhong from the Institute of Solid State Physics, the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed a method to precisely control the size of nickel particles in catalysts, improving their performance in hydrogenation reactions.
The related research results were published in Advanced Functional Materials.
Catalysts are essential in speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed, and the size of the metal particles in them plays a key role in their effectiveness. Larger particles have more high-coordination sites, while smaller ones are dominated ...
Cracking the code on gypsum and silica scaling in water desalination
2025-03-05
Mineral scaling, a significant issue in membrane desalination, reduces water recovery rates and diminishes system performance. Gypsum and silica, are two prevalent types of scaling, each form through different processes—crystallization for gypsum and polymerization for silica. These formation mechanisms lead to contrasting behaviors: gypsum scaling, marked by rapid kinetics and intrusive crystal growth, causes pore wetting, while silica scaling forms highly adhesive, irreversible layers. The impact of these scales on desalination efficiency underscores the need for a deeper understanding of their formation and mitigation.
On October 20, ...
Creativity boosts NAPLAN literacy and numeracy scores
2025-03-05
When ‘Elephant’ toothpaste erupts from the science lab, history deals up Pokémon playing cards, and maths bakes a batch of chocolate brownies, it might seem like chaos.
Yet, a groundbreaking study from University of South Australia researchers, shows that creativity plays an essential role in academic success, suggesting that students who think outside the box are more likely to excel in literacy and numeracy assessments.
It’s an important finding, particularly when the most recent National Assessment Program – Literacy and Numeracy (NAPLAN) data shows that one in three Australian students are behind in their numeracy ...
Beyond our solar system: scientists identify a new exoplanet candidate
2025-03-05
Scientists from UNSW Sydney have located a potential new exoplanet – a planet that orbits a star outside of our solar system – using a technique known as ‘transit timing variation’.
In research highlighted in a new paper, published today in The Astrophysical Journal, Scientia Senior Lecturer Ben Montet and PhD candidate Brendan McKee analysed changes in the timing of a known planet’s transit across its star, to infer the presence of a second exoplanet.
After ...
Amphibians bounce-back from Earth’s greatest mass extinction
2025-03-05
Ancient frog relatives survived the aftermath of the largest mass extinction of species by feeding on freshwater prey that evaded terrestrial predators, University of Bristol academics have found.
In the study, published today in the journal Royal Society Open Science, their findings suggest the amphibians’ success lay in their generalist feeding ecology, enabling them to feed on a wide variety of prey despite the array of environmental changes happening all around them through the Triassic. Broader examination of Triassic ecosystems also indicates that the freshwater habitats they preferred provided them with a relatively stable variety of food resources, allowing them ...
Better semen quality is linked to men living longer
2025-03-05
Men’s semen quality is associated with how long they live according to a study of nearly 80,000 men, which is published today (Wednesday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals.
The study followed the men for up to 50 years and found that those with a total number of motile sperm (sperm that can move or ‘swim’) of more than 120 million could expect to live two to three years longer than men with a total motile sperm count of between 0 and 5 million.
This is the largest study to examine the link between semen quality and mortality. An accompanying editorial ...
Enhancing mosquito repellent effectiveness
2025-03-05
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- In a recent study, researcher Anandasankar Ray at the University of California, Riverside, and his team employed machine learning techniques combined with cheminformatics to predict novel mosquito repellents that could greatly improve global mosquito control efforts. Using the same approach to combat the global threat of mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue, Ray, the recipient of a $2.5 million, five-year grant from the National Institutes of Health, or NIH, will now work on identifying novel spatial mosquito repellents ...
Prenatal maternal stressors linked to higher blood pressure during first year after birth, study shows
2025-03-05
Psychosocial stress during pregnancy could lead to higher blood pressure during the first year postpartum according to research from Keck School of Medicine of USC.
The study, published in Hypertension and supported by the National Institutes of Health, investigated whether mothers who reported higher perceived stress and depressive symptoms during pregnancy, developed higher blood pressure in the four-year period after birth. The findings showed higher stress and depressive symptoms during pregnancy were associated with greater blood pressure during the first year postpartum, but associations diminished thereafter.
“Pregnancy ...
Resistance exercise may be best type for tackling insomnia in older age
2025-03-05
Resistance or muscle strengthening exercise, using weights or the body itself, may be the best type of exercise for tackling insomnia in older age, suggests a pooled data analysis of the available research, published in the open access journal Family Medicine and Community Health.
Aerobic exercise or a mix of strength, aerobic, balance, and flexibility exercises also seem to be effective, the analysis indicates.
Sleep quality tends to decline with age. And up to 1 in five older adults has insomnia, ...
Global 130%+ rise in postmenopausal osteoarthritis and associated disability over past 3 decades
2025-03-05
The global number of cases of osteoarthritis, as well the disability associated with the condition, have risen by more than 130% over the past 3 decades among women who have gone through the menopause, indicates a data analysis spanning 1990 to 2021, and published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
During this period, East Asia and high income Asia Pacific countries experienced the fastest growth in the condition while excess weight accounted for 20% of the total years lived with the resulting disability, the analysis indicates.
Osteoarthritis is primarily characterised by the deterioration and damage ...
OU Health Sciences rises to 102 in national ranking
2025-03-05
OKLAHOMA CITY – The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences has achieved its highest ranking ever in National Institutes of Health funding awarded for research. NIH funding increased to $75.2 million in the previous federal fiscal year, improving the campus’s ranking to 102 out of 2,838 institutions and other entities that receive NIH funding.
OU Health Sciences’ previous ranking was 122. Of the total amount of funding, $65.3 million was awarded to the OU College of Medicine, whose faculty members cross 23 academic departments ...
Bonobos and chimps offer clues to how our early ancestors had sex for social purposes
2025-03-05
We don’t just have sex to reproduce - new research suggests that using sex to manage social tension could be a trait that existed in the common ancestor of humans and apes six million years ago.
Humans share this behavioural strategy with our closest living ape relatives – bonobos and chimpanzees.
Now researchers, led by Durham University, UK, have undertaken what is thought to be one of the first direct comparisons of sexual behaviour amongst bonobos and chimpanzees during periods of social stress.
Their findings, published ...
Lebanon multidimensional crisis diminishing trust in public education and worsening inequality, study shows
2025-03-04
Diminished trust in public education in crisis-hit Lebanon is worsening inequality in the country and forcing parents to make difficult decisions, a new study warns.
The country’s dual education system, reinforced by religious and political policies, continues to favour the upper classes, exacerbating educational disparities between social groups.
Lebanon’s sectarian government and weak state has led parents to perceive the academic and non-academic outcomes of most private schools as better than those of public schools.
Many said this perception has intensified recently due to declining government funding, ...
Cold atoms on a chip
2025-03-04
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — UC Santa Barbara researchers are working to move cold atom quantum experiments and applications from the laboratory tabletop to chip-based systems, opening new possibilities for sensing, precision timekeeping, quantum computing and fundamental science measurements.
“We’re at the tipping point,” said electrical and computer engineering professor Daniel Blumenthal.
In an invited article that was also selected for the cover of Optica Quantum, Blumenthal, along with graduate student researcher Andrei Isichenko and postdoctoral researcher Nitesh Chauhan, lays out the latest developments ...
Rice University study reveals how rising temperatures could lead to population crashes
2025-03-04
Researchers at Rice University have uncovered a critical link between rising temperatures and declines in a species’ population, shedding new light on how global warming threatens natural ecosystems. The study, published in Ecology and led by Volker Rudolf, revealed that rising temperatures exacerbate competition within populations, ultimately leading to population crashes at higher temperatures. It offers one of the first clear experimental confirmations that rising temperatures alter the forces that control population dynamics in nature.
“Our research provides an essential ...
WVU research reveals adults with disabilities misuse prescription drugs at high rates
2025-03-04
Adults with disabilities are nearly twice as likely to misuse prescription drugs as adults without disabilities, according to West Virginia University research.
Jeanette Garcia, associate professor at the WVU College of Applied Human Sciences, said the findings point to the urgency of curbing prescription misuse among adults with disabilities.
“Almost 10% of the individuals with disabilities in our sample reported misusing prescription drugs within the past year, compared to 4.4% of individuals without disabilities,” Garcia said. “We saw the highest ...
Consumers value domestic vanilla -- when informed, research shows
2025-03-04
UF/IFAS researchers are investigating the economic potential of growing vanilla in Florida with the aim of establishing an alternative – and potentially lucrative – crop to oranges.
“With citrus in decline, we’re searching for crops that can generate profits for producers,” said Jaclyn Kropp, a professor in the food and resource economics department. “Vanilla is a high-value crop, so there’s immense revenue potential.”
No large-scale, commercial production ...
Are higher doses of folic acid in pregnancy safe?
2025-03-04
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, TUESDAY, MARCH 4, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Are higher doses of folic acid in pregnancy safe?
MINNEAPOLIS – Taking a higher dose of folic acid during the first trimester of pregnancy was safe and associated with improved verbal abilities in children at age six as well as improved behavior skills, according to a preliminary study released today, March 4, 2025, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 77th Annual Meeting taking ...
Survey confirms radiation and orthopedic health hazards in cardiac catheterization laboratories are ‘unacceptable’
2025-03-04
WASHINGTON—A survey conducted by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) highlights ongoing radiation and orthopedic hazards faced by interventional cardiologists and cardiac catheterization laboratory (“cath lab” or CCL) staff. The survey revealed that despite technological advancements, significant risks often remain unaddressed despite advances in protective equipment.
“Occupational Health Hazards in the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory: Results of the 2023 SCAI Survey” highlights alarming trends in radiation exposure and orthopedic ...
Study finds consumer devices can be used to assess brain health
2025-03-04
(Boston) — Technology is changing how physicians think about assessing patients and, in turn, how patients expect to be able to measure their own health. Apps designed for smartphones and wearable devices can provide unique insights into users’ brain health.
It is estimated that 55 million individuals worldwide suffer from some form of dementia. Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias being the leading causes, with numbers expected to triple by 2050. Early education and detection of cognitive changes empower individuals to enact lifestyle modifications and initiate pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic approaches to slow or prevent decline. In fact, up to 45% of ...
Teachers' negative emotions impact engagement of students, new study finds
2025-03-04
In their study, University of Delaware Associate Research Professor Leigh McLean and co-author Nathan Jones of Boston University, found that teachers displayed far more positive emotions than negative ones. But they also found that some teachers showed high levels of negative emotions. In these cases, teachers’ expressions of negative emotions were associated with reduced student enjoyment of learning and engagement. These findings add to a compelling body of research highlighting the importance of teachers’ and students’ emotional experiences within ...
[1] ... [649]
[650]
[651]
[652]
[653]
[654]
[655]
[656]
657
[658]
[659]
[660]
[661]
[662]
[663]
[664]
[665]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.