Unlocking the hidden proteome: The role of coding circular RNA in cancer
2025-03-07
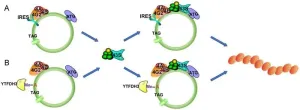
A new review article highlights the transformative role of circular RNA (circRNA) in cancer, revealing its potential as both a key player in tumor biology and a promising avenue for future therapies. Once thought to be noncoding RNA, circRNA has now been shown to encode functional proteins, challenging conventional RNA biology and opening up novel therapeutic possibilities.
Unlike traditional messenger RNA, circRNAs form a continuous loop, lacking the typical 5' cap and 3' tail. This unique structure was originally believed to preclude them from protein translation. However, recent discoveries demonstrate that specific internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) and N6-methyladenosine ...
Advancing lung cancer treatment: Understanding the differences between LUAD and LUSC
2025-03-07
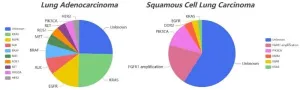
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) representing the most prevalent subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite their classification under the same umbrella, these two forms of lung cancer exhibit distinct genetic landscapes, therapeutic targets, and treatment responses.
Recent advancements in next-generation gene sequencing have identified key driver genes that differentiate LUAD and LUSC, influencing their respective clinical management approaches. LUAD is frequently associated ...
Study reveals widening heart disease disparities in the US
2025-03-07
A study published March 6 in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas highlights a growing divide in cardiovascular health in the U.S., showing that wealth and education play a significant role in heart disease risk.
The research, led by Salma Abdalla, MBBS, DrPH, an assistant professor of public health at Washington University in St. Louis, reveals that the top 20% of high-income, college-educated Americans have far lower rates of cardiovascular disease than the rest of the population — disparities ...
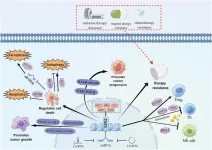
The role of ubiquitination in cancer stem cell regulation
2025-03-07
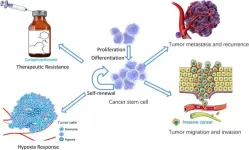
This review highlights the critical role of ubiquitination in governing the functionality of cancer stem cells (CSCs), shedding light on potential therapeutic targets for combating tumor progression, recurrence, and drug resistance. Published in Genes & Diseases, this article explores the intricate mechanisms through which the ubiquitin (Ub) system regulates key pathways essential for CSC maintenance and survival.
Ubiquitination, a fundamental post-translational modification, plays a pivotal role in protein stability, cellular signaling, and gene expression, particularly in the context of CSCs. Dysregulation ...
New insights into LSD1: a key regulator in disease pathogenesis
2025-03-07
A new review highlights the pivotal role of LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) in regulating critical cellular processes and its implications for human diseases. This article sheds light on how post-translational modifications (PTMs) influence LSD1 activity, impacting its function in gene regulation and disease progression.
LSD1 is a histone demethylase that plays a significant role in chromatin remodeling and gene expression by modifying histone H3 lysine residues. It interacts with various protein complexes, allowing it to serve as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. The intricate modifications ...
Vanderbilt lung transplant establishes new record
2025-03-07
Surgeons and teams with Vanderbilt Lung Transplant performed 99 lung transplants in 2024, the most ever in one year. Two of the procedures involved combined organ transplants.
For the second calendar year in a row, Vanderbilt Lung Transplant has the busiest program in the Southeast and leads the nation in innovation in organ preservation and regeneration.
The Vanderbilt Transplant Center is now home to the nation’s eighth largest lung transplant program by volume, and is among the best in long-term outcomes, demonstrating the ...
Revolutionizing cancer treatment: targeting EZH2 for a new era of precision medicine
2025-03-07
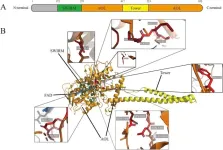
The critical role of EZH2, an essential epigenetic regulator, in cancer progression and treatment is underscored in this new review article published in Genes & Diseases. The study highlights the transformative potential of EZH2 inhibition, paving the way for a new generation of targeted therapies aimed at disrupting tumor growth and overcoming treatment resistance.
EZH2, a core component of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), plays a fundamental role in silencing tumor suppressor genes through histone methylation. Its overexpression has been ...
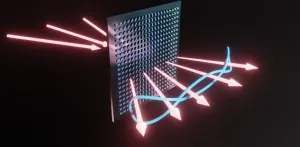
Metasurface technology offers a compact way to generate multiphoton entanglement
2025-03-07
Quantum information processing is a field that relies on the entanglement of multiple photons to process vast amounts of information. However, creating multiphoton entanglement is a challenging task. Traditional methods either use quantum nonlinear optical processes, which are inefficient for large numbers of photons, or linear beam-splitting and quantum interference, which require complex setups prone to issues like loss and crosstalk.
A team of researchers from Peking University, Southern University of Science and Technology, and the University of Science and Technology of China recently made ...
Effort seeks to increase cancer-gene testing in primary care
2025-03-07
Up to 10% of cancers are caused by genes that can be easily detected by commercially available tests. These include such common cancers as cancer of the breast, ovary, colon, stomach, uterus and pancreas.
“We don’t routinely screen for cancer susceptibility genes in primary-care settings because genetic testing is often considered too complicated and primary care doctors already have so many things they need to address,” noted lead author Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a UW Medicine gynecological oncologist. "But it is an opportunity lost.”
In the JAMA Network Open study published ...
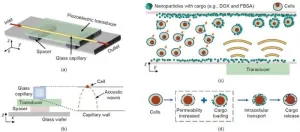
Acoustofluidics-based method facilitates intracellular nanoparticle delivery
2025-03-07
A recent study published in Engineering presents an innovative acoustofluidics-based approach for intracellular nanoparticle delivery. This method offers a new way to transport various functional nanomaterials into different cell types, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic applications and biophysical studies.
The efficient delivery of biomolecular cargos into cells is crucial for biomedical research, including gene therapies and drug delivery. However, traditional delivery methods such as endocytosis of nano-vectors, microinjection, and electroporation have limitations. They may require time-consuming processes, complex operations, or expensive equipment. ...
Sulfur bacteria team up to break down organic substances in the seabed
2025-03-07
Sulfate-reducing bacteria break down a large proportion of the organic carbon in oxygen-free zones of the Earth, and in the seabed in particular. Among these important microbes, the Desulfobacteraceae family of bacteria stands out because its members are able to break down a wide variety of compounds – including some that are poorly degradable – to their end product, carbon dioxide (CO2).
A team of researchers led by Dr Lars Wöhlbrand and Prof. Dr Ralf Rabus from the University of Oldenburg, Germany, has investigated the role ...
Stretching spider silk makes it stronger
2025-03-07
When spiders spin their webs, they use their hind legs to pull silk threads from their spinnerets. This pulling action doesn’t just help the spider release the silk, it’s also a crucial step in strengthening the silk fibers for a more durable web.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers have discovered why the role of stretching is so important. By simulating spider silk in a computational model, the team discovered the stretching process aligns the protein chains within the fibers and increases the number of bonds between those ...
Earth's orbital rhythms link timing of giant eruptions and climate change
2025-03-07
On ten thousand to million years time scales, climate dynamics on the Earth’s surface are driven by both external and internal processes. Earth`s interior provides heat from radioactive decay and chemical compounds by volcanic degassing, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Quasiperiodic changes in Earth’s orbit around the sun regulate the amount of incoming solar radiation on the planet’s surface as well as its distribution across latitudes, affecting the length and intensity ...
Ammonia build-up kills liver cells but can be prevented using existing drug
2025-03-07
High levels of ammonia kill liver cells by damaging the mitochondria that power the cells. But this can be prevented using an existing drug due to start clinical trials, finds a new study in mice led by researchers from UCL.
The study, published in Science Advances, is the first to observe that build-up of ammonia (hyperammonaemia) can harm liver cells and describe how this damage occurs in mouse models that are clinically relevant for humans.
Hyperammonaemia is known to cause brain dysfunction in those with liver disease, ...
New technical guidelines pave the way for widespread adoption of methane-reducing feed additives in dairy and livestock
2025-03-07
Philadelphia, March 7, 2025 – After many decades of research, the dairy sector has a significant body of peer-reviewed research showing that feed additives can effectively reduce methane, the greenhouse gas that makes up most of dairy’s environmental footprint. Yet the practical use of this knowledge on farms—as well as general awareness around additive effectiveness and safety—is still gaining momentum. At this critical point in the dairy sector’s pathway to a net-zero future, the Journal of Dairy Science, the leading general dairy research journal from ...
Eradivir announces Phase 2 human challenge study of EV25 in healthy adults infected with influenza
2025-03-07
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Eradivir, a clinical-stage small molecule immunotherapy biotech company, announced it has begun a Phase 2 challenge study with its antiviral therapeutic, EV25. The study will provide safety and efficacy data gathered from otherwise healthy participants infected with influenza then later treated with EV25.
EV25 was built on a platform created in Philip Low’s lab. Low is the Presidential Scholar for Drug Discovery and the Ralph C. Corley Distinguished Professor of Chemistry in Purdue University’s College of Science. Low is Eradivir’s chief scientific officer and on its board of directors.
The European Medicines ...
New study finds that tooth size in Otaria byronia reflects historical shifts in population abundance
2025-03-07
Puerto Madryn, Argentina – A new study published in PeerJ Life and Environment reveals that the teeth of South American sea lions (Otaria byronia) hold valuable clues about past population dynamics. Researchers from the Instituto de Biología de Organismos Marinos, the Centro para el Estudio de Sistemas Marinos, and the Universidad Nacional de la Patagonia San Juan Bosco analysed changes intooth size and growth layer groups (GLGs) over the ...
nTIDE March 2025 Jobs Report: Employment rate for people with disabilities holds steady at new plateau, despite February dip
2025-03-07
East Hanover, NJ – March 7, 2024 – The employment rate for people with disabilities saw a slight dip in February but continued to fluctuate around a steady plateau of approximately 37.5%. While these dips can trigger speculation about broader policy implications, nTIDE experts cautioned that it is premature to attribute changes to recent shifts in federal employment policies. The employment-to-population ratio for people with disabilities remained stable. nTIDE is issued by Kessler Foundation and the ...
Breakthrough cardiac regeneration research offers hope for the treatment of ischemic heart failure
2025-03-07
Researchers in the Michael E. DeBakey Department of Surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute in Brisbane, Australia, and collaborating institutions report a groundbreaking discovery in cardiac regeneration that offers new hope for the treatment of ischemic heart failure. Published in npj Regenerative Medicine, the study reveals a novel approach to promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation.
“When the heart cannot replace injured cardiomyocytes with healthy ones, it becomes progressively ...
Fluoride in drinking water is associated with impaired childhood cognition
2025-03-07
Elevated concentrations of fluoride can occur in well water, and in some countries, it is added to drinking water to counteract caries in the population. A study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now supports a few previous studies indicating that exposure to fluoride during the fetal stage or early childhood may impair cognition in children. The study is published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
Fluoride occurs naturally as fluoride ions in drinking water, but the concentrations are generally low in ...
New composite structure boosts polypropylene’s low-temperature toughness
2025-03-07
A recent study published in Engineering presents a significant advancement in improving the toughness of polypropylene (PP), a widely used thermoplastic material. The research, led by Zhiyi Zhang and Qiang Zheng from Taiyuan University of Technology and Zhejiang University, focuses on developing a novel core–shell structured composite to enhance PP’s performance at low temperatures.
PP has many advantages, such as high thermal and chemical resistance, but its low-temperature toughness is a limiting ...
While most Americans strongly support civics education in schools, partisan divide on DEI policies and free speech on college campuses remains
2025-03-07
A new report looking at adults’ views on education topics shows more partisan agreement about how to educate students for citizenship than many might think, yet sharp partisan divide around issues of diversity, equity and inclusion policies on college campuses and free speech.
The report, published by the USC Center for Applied Research in Education, a center housed within USC Dornsife’s Center for Economic and Social Research, in partnership with the USC EdPolicy Hub, is based on a nationally representative, probability-based ...
Revolutionizing surface science: Visualization of local dielectric properties of surfaces
2025-03-07
Researchers from the University of Electro-Communications (Akira Sumiyoshi and Jun Nakamura) and Tohoku University (Kohei Yamasue and Yasuo Cho) have made a significant advancement in visualizing the local dipole moments at the semiconductor surface. This study offers unprecedented insights into the atomic-scale charge distribution and dipole configuration using a combination of the scanning nonlinear dielectric microscope (SNDM) and advanced density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
The ...
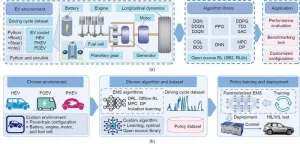
LearningEMS: A new framework for electric vehicle energy management
2025-03-07
A new study published in Engineering introduces LearningEMS, a unified framework and open-source benchmark designed to revolutionize the development and assessment of energy management strategies (EMS) for electric vehicles (EVs).
The automotive industry has recently undergone a transformative shift fueled by the growing global emphasis on sustainability and environmental conservation. EVs have become a crucial part of the future of transportation. However, effectively managing the energy in EVs, especially those with complex power ...
Nearly half of popular tropical plant group related to birds-of-paradise and bananas are threatened with extinction
2025-03-07
A new analysis from researchers at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History reveals that nearly half of the genus Heliconia, a group of tropical plants popular for their bright, beak-shaped flowers, are threatened with extinction. The findings, published today, March 7, in the journal Plants, People, Planet, reveal that many of these imperiled plants are not found within protected areas or botanical gardens, making additional conservation action crucial to saving these charismatic, horticulturally important and ecologically significant floras.
The new work places Heliconia among a select group of plants to undergo a detailed, comprehensive ...
[1] ... [642]
[643]
[644]
[645]
[646]
[647]
[648]
[649]
650
[651]
[652]
[653]
[654]
[655]
[656]
[657]
[658]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.