The chances of anything coming from Mars
2025-03-06
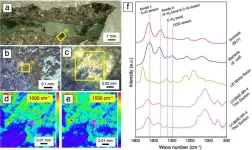
Within the next decade, space agencies plan to bring samples of rock from Mars to Earth for study. Of concern is the possibility these samples contain life, which could have unforeseen consequences. Therefore, researchers in this field strive to create methods to detect life. For the first time, researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo and NASA, successfully demonstrated a method to detect life in ancient rocks analogous to those found on Mars.
We’ve all seen the movies, in which “Scientists bring back something from space, ...
Scientists unlock clues to new treatments for muscular dystrophy
2025-03-06
A new discovery about how tiny protein clusters form in cells could pave the way for treatments for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), a rare genetic disorder that causes muscle weakness and heart problems.
Researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences combined advanced imaging techniques and theoretical physics to observe and explain how nanoclusters of the protein emerin form inside living cells. These clusters — about 100,000 times smaller than a human hair’s width — play a crucial role in how cells sense and respond to mechanical forces like stretching or pressure, ...
Anti-obesity drugs benefit kidney transplant recipients with type 2 diabetes
2025-03-06
Kidney transplant recipients with type 2 diabetes treated with a new class of anti-obesity drugs were less likely to experience organ failure and survived longer, a new study shows. Not only is obesity a known risk factor for diabetes, but it also increases risk of postsurgical complications, such as inflammation, organ rejection, and early death.
Previous research had suggested some benefit for kidney transplant recipients with a history of type 2 diabetes who took the medications, originally designed to treat diabetes, at some point after their transplant ...
Cases of Parkinson’s disease set to reach 25 million worldwide by 2050
2025-03-06
By 2050, there will be 25.2 million people living with Parkinson’s disease worldwide (a 112% increase from 2021), largely due to population ageing, suggests a modelling study published by The BMJ today.
Overall, the number of people living with Parkinson’s disease (all age prevalence) per 100,000 population is predicted to increase by 76%, and by 55% when corrected for age differences (age standardised prevalence), with rates projected to be highest in East Asia.
The researchers say these projections “could serve as an aid in promoting health research, ...
Throat microbiome holds clues to older Australians’ health
2025-03-06
New research by Flinders University has uncovered a potential marker that could provide valuable insights into the overall health of older adults living in long-term aged care facilities.
Led by PhD candidate Sophie Miller in the College of Medicine and Public Health, the study found that a simple swab from the back of the throat, known as the oropharynx, may offer clues about health challenges faced by aged care residents.
“Our findings suggest that certain bacteria detected in the back of the throat could indicate greater health vulnerability in older adults,” says Miller.
Identifying vulnerable individuals ...
Diabetes drug could help cancer patients make better recovery
2025-03-06
A common type of diabetes medication could help cancer patients make a better long-term recovery, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
Many cancer patients go on to develop heart failure - because of the cancer itself and also due to chemotherapy. This can lead to a reduced quality of life, multiple admissions to hospital or even death.
But a new study published today shows that a type of diabetes medication, called an SGLT2 inhibitor, may help protect the ...
Seismic study of Singapore could guide urban construction and renewable energy development
2025-03-05
A new seismic study of Singapore could guide urban growth and renewable energy development in the coastal city nation, where 5.6 million residents live within an area of 734 square kilometers.
The study, published in Seismological Research Letters, identifies areas with increased risk of ground shaking and a possible reservoir for geothermal energy production, as well as a glimpse at Singapore’s tectonic history.
Jiayuan Yao of China University for Geosciences and colleagues analyzed teleseismic data captured by a few permanent seismic stations and a nodal seismic array deployed in 2019 around the city. Their results provide the first detailed look at the top-kilometer ...
Tufts scientists develop open-source software for modeling soft materials
2025-03-05
When mechanical and structural engineers design machines, bridges, and buildings, they calculate loads, stresses, and deformation of metal, steel, concrete, glass, wood, and plastic to find the optimal geometry that bears loads with the minimum cost of material.
Designing for relatively hard materials that do not deform too much is commonly handled by software that calculates and optimizes structures using mathematical models that are well understood and easily applied.
But there is an expanding class of design challenges for things that incorporate soft materials—biological materials, engineered tissues, membranes, and even shape-shifting ...
Repurposed ALS drug becomes imaging probe to help diagnose neurodegeneration
2025-03-05
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear imaging technique used to diagnose conditions such as cancer. An innovative advance from scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital is enhancing the technique’s ability to check for signs of neurological disease. The researchers repurposed the drug edaravone, an antioxidant used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), as a probe to be used with central nervous system PET imaging. With this technique, the researchers can ...
AI can open up beds in the ICU
2025-03-05
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals frequently ran short of beds in intensive care units. But even earlier, ICUs faced challenges in keeping beds available. With an aging American population, 11% of hospital stays included ICU stays.
Artificial intelligence offers a possible solution, says Indranil Bardhan, professor of information, risk, and operations management and Charles and Elizabeth Prothro Regents Chair in Health Care Management at Texas McCombs. AI models can predict the lengths of time patients will spend in the ICU, helping hospitals better manage their beds and, ideally, cut costs.
But although AI is good at predicting length of stay, ...
Are robotic hernia repairs still in the “learning curve” phase?
2025-03-05
For an abdominal wall hernia repair, also known as a ventral hernia repair, the most common surgical approaches have been laparoscopic and open techniques.
But a new approach for repairing hernias has been steadily growing in popularity: the surgical robot.
Supporters of using the robot method state multiple advantages over traditional laparoscopic and open approaches, including improved surgeon ergonomics.
But there may be downsides to the technology that are going undiscussed.
In a research article published in JAMA Surgery, Brian Fry, M.D., M.S., a ...
New STI impacts 1 in 3 women: Landmark study reveals men are the missing link
2025-03-05
A landmark study reveals that bacterial vaginosis (BV), a condition affecting nearly a third of women worldwide and causing infertility, premature births and newborn deaths, is in fact a sexually transmitted infection (STI), paving the way for a revolution in how it is treated.
Monash University and Alfred Health researchers at the Melbourne Sexual Health Centre say their findings, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, hold the key to driving down stubborn and distressing recurrence ...
Feeling is believing: Bionic hand “knows” what it’s touching, grasps like a human
2025-03-05
Johns Hopkins University engineers have developed a pioneering prosthetic hand that can grip plush toys, water bottles, and other everyday objects like a human, carefully conforming and adjusting its grasp to avoid damaging or mishandling whatever it holds.
The system’s hybrid design is a first for robotic hands, which have typically been too rigid or too soft to replicate a human’s touch when handling objects of varying textures and materials. The innovation offers a promising solution for people with hand loss and could improve how robotic arms interact with their environment.
Details about the device appear today in Science Advances.
“The ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $4.4 million to top young scientists
2025-03-05
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named 13 new Damon Runyon Fellows, exceptional postdoctoral scientists conducting basic and translational cancer research in the laboratories of leading senior investigators. The prestigious, four-year Fellowship encourages the nation's most promising young scientists to pursue careers in cancer research by providing them with independent funding ($300,000 total) to investigate cancer causes, mechanisms, therapies, and prevention.
The Foundation has also named ...
Over-the-counter pain relievers linked to improved recovery from concussion
2025-03-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 5, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Over-the-counter pain relievers linked to improved recovery from concussion
MINNEAPOLIS – People who take over-the-counter pain relievers after a concussion may recover faster than those who do not take pain relievers, according to a preliminary study released today, March 5, 2025, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 77th Annual Meeting taking place April 5–9, 2025, in San Diego ...
Stressed out? It may increase the risk of stroke
2025-03-05
MINNEAPOLIS — Some people living with chronic stress have a higher risk of stroke, according to a study published on March 5, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study looked at younger adults and found an association between stress and stroke, with no known cause, in female participants, but not male participants. This study does not prove that stress causes stroke; it only shows an association.
“Younger people often experience stress due to the demands and pressures associated with work, including long hours and job insecurity, as well as financial burdens,” ...
Nanoscale tweaks help alloy withstand high-speed impacts
2025-03-05
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led collaboration devised a new method for designing metals and alloys that can withstand extreme impacts, which could lead to the development of automobiles, aircraft and armor that can better endure high-speed impacts, extreme heat and stress.
The research, published in Communications Materials, introduces nanometer-scale speed bumps that suppress a fundamental transition that controls how metallic materials deform.
The project was led by Mostafa Hassani, assistant professor of mechanical ...
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
2025-03-05
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
Article URL: https://plos.io/4baFCW5
Article title: AI-determined similarity increases likability and trustworthiness of human voices
Author countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during
2025-03-05
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during the Pliocene or Miocene epochs
Article URL: https://plos.io/4gQHlB2
Article title: Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes of Theobroma cacao from northern Peru
Author countries: Perú
Funding: This study was supported by the Programa Nacional de Investigación Científica y Estudios Avanzados (PROCIENCIA) funded by the Project through the Contract N° 026-2016-FONDECYT “Círculo de Investigación ...
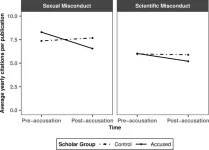
After sexual misconduct accusations, scholars’ work is cited less
2025-03-05
In a new analysis, scholars publicly accused of sexual misconduct experienced a significant decrease in the rate at which other scholars cited their published research. Giulia Maimone of the University of California, Los Angeles, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on March 5, 2025.
In academia, scholars cite other scholars’ publications as a widely agreed-upon way to reference existing research and promote scientific advancement. A scholar with a high number of citations may be considered particularly impactful in their field. Prior research ...
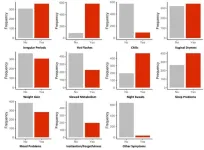
Menopause symptoms associated with future memory and neuropsychiatric problems
2025-03-05
Women who exhibit more menopausal symptoms are more likely to later have poorer cognitive function and mild behavioral impairments – both markers of dementia. That is the conclusion of a study of 896 postmenopausal females published March 5, 2025, in the open-access journal PLOS One by Zahinoor Ismail of University of Calgary, Canada, and colleagues.
Females are known to have a three-fold greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, and will be disproportionately ...
Findings may advance understanding of infertility in mothers
2025-03-05
Oxytocin, a hormone already known for its role in childbirth, milk release, and mother-infant bonding, may have a newfound purpose in mammalian reproduction. In times of maternal stress, the hormone can delay an embryo’s development for days to weeks after conception, a new study in rodents shows. According to the authors, the findings about so-called “diapause” may offer new insights into pregnancy and fertility issues faced by humans.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the study explored diapause, in which an embryo temporarily stops growing early in ...
Engineered cartilage from nasal septum cells helps treat complex knee injuries
2025-03-05
Injuries to the articular cartilage in different joints, including the knee, are painful and limit mobility. Therefore, researchers at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel are developing cartilage implants using cells from the patient’s nasal septum. A recent study shows that giving these cartilage implants more time to mature significantly improved clinical efficacy, even in patients with complex cartilage injuries. This suggests that the method could also be suitable for the treatment of degenerated cartilage in osteoarthritis.
An unlucky fall while skiing or playing ...
Damaged but not defeated: Bacteria use nano-spearguns to retaliate against attacks
2025-03-05
Some bacteria deploy tiny spearguns to retaliate against rival attacks. Researchers at the University of Basel mimicked attacks by poking bacteria with an ultra-sharp tip. Using this approach, they have uncovered that bacteria assemble their nanoweapons in response to cell envelope damage and rapidly strike back with high precision.
In the world of microbes, peaceful coexistence goes hand in hand with fierce competition for nutrients and space. Certain bacteria outcompete rivals and fend off attackers by injecting them with a lethal cocktail using tiny, ...
Among older women, hormone therapy linked to tau accumulation, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease
2025-03-05
A new study from Mass General Brigham researchers has found faster accumulation of tau—a key indicator of Alzheimer’s disease—in the brains of women over the age of 70 who took menopausal hormone therapy (HT) more than a decade before. Results, which are published in Science Advances, could help inform discussions between patients and clinicians about Alzheimer’s disease risk and HT treatment.
While the researchers did not see a significant difference in amyloid beta accumulation, they did find a significant difference in how fast regional tau accumulated in the brains of women over the age of 70, with women who had taken HT showing faster tau accumulation ...
[1] ... [638]
[639]
[640]
[641]
[642]
[643]
[644]
[645]
646
[647]
[648]
[649]
[650]
[651]
[652]
[653]
[654]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.