Scientists catch water molecules flipping before splitting
2025-03-05
For the first time, Northwestern University scientists have watched water molecules in real-time as they prepared to give up electrons to form oxygen.
In the crucial moment before producing oxygen, the water molecules performed an unexpected trick: They flipped.
Because these acrobatics are energy intensive, the observations help explain why water splitting uses more energy than theoretical calculations suggest. The findings also could lead to new insights into increasing the efficiency of water splitting, a process that holds promise for generating clean hydrogen fuel and for producing breathable oxygen during future missions to Mars.
The study will be published Wednesday (March 5) ...
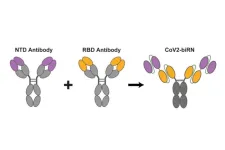
New antibodies show potential to defeat all SARS-CoV-2 variants
2025-03-05
The virus that causes COVID-19 has been very good at mutating to keep infecting people – so good that most antibody treatments developed during the pandemic are no longer effective. Now a team led by Stanford University researchers may have found a way to pin down the constantly evolving virus and develop longer-lasting treatments.
The researchers discovered a method to use two antibodies, one to serve as a type of anchor by attaching to an area of the virus that does not change very much and another to inhibit the virus’s ability ...
Mental health may be linked to how confident we are of our decisions
2025-03-05
A new study finds that a lower confidence in one’s judgement of decisions based on memory or perception is more likely to be apparent in individuals with anxiety and depression symptoms, whilst a higher confidence is more likely to be associated compulsivity, thus shedding light on the intricate link between cognition and mental health manifestations.
####
Article Title: Metacognitive biases in anxiety-depression and compulsivity extend across perception and memory
Author Countries: Germany, United Kingdom
Funding: TXFS is a Sir Henry Wellcome Postdoctoral Fellow (224051/Z/21/Z) based at the Max Planck UCL Centre for Computational Psychiatry ...
Research identifies key antibodies for development of broadly protective norovirus vaccine
2025-03-05
Scientists at The University of Texas at Austin, in collaboration with researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the National Institutes of Health, have discovered a strategy to fight back against norovirus, a leading cause of gastroenteritis worldwide. Their new study, published in Science Translational Medicine, identifies powerful antibodies capable of neutralizing a wide range of norovirus strains. The finding could lead to the design of broadly effective norovirus vaccine, as well as the development of new therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of norovirus-associated gastroenteritis.
Norovirus ...
NHS urged to offer single pill to all over-50s to prevent heart attacks and strokes
2025-03-05
The NHS could prevent thousands more heart attacks and strokes every year by offering everyone in the UK aged 50 and over a single “polypill” combining a statin and three blood pressure lowering drugs, according to academics from UCL.
In an opinion piece for The BMJ, the authors argued that a polypill programme could be a “flagship strategy” in Labour’s commitment to preventing disease rather than treating sickness. The programme would use age alone to assess eligibility, focusing on disease prevention rather than disease prediction.
They said such a strategy should replace the NHS Health Check, a five-yearly assessment ...
Australian researchers call for greater diversity in genomics
2025-03-05
A new study has uncovered that a gene variant common in Oceanian communities was misclassified as a potential cause of heart disease, highlighting the risk of the current diversity gap in genomics research which can pose a greater risk for misdiagnosis of people from non-European ancestries.
Led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and published in the European Heart Journal, the researchers describe the cases of two individuals of Pacific Island ancestries who carry a genetic variant previously thought to be a likely cause for their inherited ...
The pot is already boiling for 2% of the world’s amphibians: new study
2025-03-05
Scientists will be able to better identify what amphibian species and habitats will be most impacted by climate change, thanks to a new study by UNSW researchers.
Amphibians are the world’s most at-risk vertebrates, with more than 40% of species listed as threatened – and losing entire populations could have catastrophic flow-on effects.
Being ectothermic – regulating their body heat by external sources – amphibians are particularly vulnerable to temperature change in their habitats.
Despite this, the resilience of amphibians to rising temperatures ...
A new way to predict cancer's spread? Scientists look at 'stickiness' of tumor cells
2025-03-05
By assessing how “sticky” tumor cells are, researchers at the University of California San Diego have found a potential way to predict whether a patient’s early-stage breast cancer is likely to spread. The discovery, made possible by a specially designed microfluidic device, could help doctors identify high-risk patients and tailor their treatments accordingly.
The device, which was tested in an investigator-initiated trial, works by pushing tumor cells through fluid-filled chambers and sorting them based on how well they adhere to the chamber walls. When tested ...
Prehistoric bone tool ‘factory’ hints at early development of abstract reasoning in human ancestors
2025-03-05
UCL Press Release
Under embargo until Wednesday 5 March 2025, 16:00 UK time / 11:00 US Eastern time
Prehistoric bone tool ‘factory’ hints at early development of abstract reasoning in human ancestors
The oldest collection of mass-produced prehistoric bone tools reveal that human ancestors were likely capable of more advanced abstract reasoning one million years earlier than thought, finds a new study involving researchers at UCL and CSIC- Spanish National Research Council.
The paper, published in Nature, describes a collection of 27 now-fossilised bones that had been shaped into hand tools 1.5 million years ago by human ancestors.
It’s ...
Study: Vaping does not help US tobacco smokers quit
2025-03-05
Researchers at the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science and Moores Cancer Center at University of California San Diego have found that, among smokers in the United States, e-cigarette use does not increase smoking cessation and is actually associated with reduced tobacco abstinence. The findings, published March 5 in JAMA, refute the notion that e-cigarettes can help people quit, a common misperception among tobacco users and e-cigarette proponents.
“Most smokers think vaping will help you quit ...
Insect populations are declining — and that is not a good thing
2025-03-05
Insect populations, foundational to food chains and pollination, have dramatically declined over the past 20 years due to rapid climate change
Scientists identify two ways fly species from different climates (high-altitude forest and hot desert) have adapted to temperature
Paper provides evidence that changes in brain wiring and heat sensitivity contributed to shifting preference to hot or cold conditions, respectively
Results may help predict the impact of ongoing climate change on insect distribution and behavior
EVANSTON, Ill. --- Tiny, cold-blooded animals like flies depend on their environment to regulate body temperature, ...
Scientists discover genes to grow bigger tomatoes and eggplants
2025-03-05
Bigger, tastier tomatoes and eggplants could soon grace our dinner plates thanks to Johns Hopkins scientists who have discovered genes that control how large the fruits will grow.
The research—led by teams at Johns Hopkins University and Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory—could lead to the development of new varieties of heirloom tomatoes and eggplants, including those that help support agriculture in areas around the world where local varieties are currently too small for large-scale production.
Findings were published in the journal Nature.
“Once ...
Effects of combining coronary calcium score with treatment on plaque progression in familial coronary artery disease
2025-03-05
About The Study: The combination of coronary artery calcium (CAC) score with a primary prevention strategy in intermediate-risk patients with a family history of coronary artery disease was associated with reduction of atherogenic lipids and slower plaque progression compared with usual care. These data support the use of CAC score to assist intensive preventive strategies in intermediate-risk patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Thomas H. Marwick, MBBS, PhD, MPH, email Tom.Marwick@bakeridi.edu.au.
To ...
Cancer screening 3 years after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-05
About The Study: In 2023, reported breast and colorectal cancer screening rebounded from COVID-19 pandemic–related declines and surpassed pre-pandemic estimates. These findings are encouraging given larger-than-expected declines in early-stage breast and colorectal cancer diagnoses in 2020 and increases in distant-stage breast cancer diagnoses through 2021. Cervical cancer screening rates remained below pre-pandemic levels, a troubling trend as early-stage diagnoses continued to decrease in 2021. The persistent decline may in part reflect longer-term declines in patient knowledge and clinician recommendation of cervical cancer ...
Trajectories of sleep duration, sleep onset timing, and continuous glucose monitoring in adults
2025-03-05
About The Study: In this cohort study of middle-aged and older participants, persistent inadequate sleep duration and late sleep onset, whether alone or in combination, were associated with greater glycemic variability. These findings emphasize the importance of considering both sleep duration and timing for optimizing glycemic control in the general population.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Ju-Sheng Zheng, PhD, (zhengjusheng@westlake.edu.cn) and Yu-ming Chen, PhD, (chenyum@mail.sysu.edu.cn).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Sports gambling and drinking behaviors over time
2025-03-05
About The Study: This study found that over time, the trajectory of sports gambling frequency was associated with the trajectory of alcohol-related problems. Screening and treatment interventions are recommended for sport gamblers who also drink concurrently, especially because this group appears to be at an elevated risk for developing greater alcohol-related problems over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joshua B. Grubbs, PhD, email joshuagrubbs12@unm.edu
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2025.0024)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
For better quantum sensing, go with the flow
2025-03-05
Combine a garden-variety green laser, microwaves with roughly the energy of your wi-fi, and some diamond dust in drops of water, and what do you get? A precise chemical detection tool.
For the first time, researchers have combined nanodiamonds in microdroplets of liquid for quantum sensing. The new technique is precise, fast, sensitive, and requires only small amounts of the material to be studied – helpful when studying trace chemicals or individual cells. The results were published in the journal Science Advances in December.
“We weren’t even sure ...
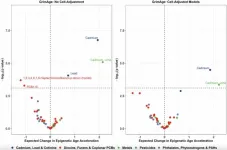
Toxic environmental pollutants linked to faster aging and health risks in US adults
2025-03-05
“Environmental chemical exposures represent a key modifiable risk factor impacting human health and longevity, and our findings provide evidence for associations between several environmental exposures and epigenetic aging in a large sample representative of the US adult population.”
BUFFALO, NY — March 5, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 11, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Exposome-wide association study of environmental chemical exposures ...
Jerome Morris voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
2025-03-05
Jerome E. Morris, the E. Desmond Lee Endowed Professor of Urban Education at the University of Missouri–St. Louis, has been voted president-elect of the American Educational Research Association (AERA). Morris joins the AERA Council in 2025–2026 as president-elect, and his presidency begins at the conclusion of the association’s 2026 Annual Meeting.
Morris leverages his upbringing in public housing and attending predominantly Black public schools in Birmingham, Alabama, to inform his research, which examines the intersection of ...
Study reveals how agave plants survive extreme droughts
2025-03-05
WASHINGTON — Agave plants may be best known for their role in tequila production, but they are also remarkably adept at retaining water in extremely dry environments. In a new study, researchers used terahertz spectroscopy and imaging to gain new insights into how these succulents store and manage water to survive in dry conditions.
“Understanding how plants adapt to dry conditions could lead to better farming practices and be used to develop crops that require less water,” said Monica Ortiz-Martinez ...
Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) launches a second funding opportunity to accelerate novel tool development to advance Parkinson's disease research
2025-03-05
The Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) initiative opened applications for research community members to apply for funding to develop novel tools to advance Parkinson’s disease (PD) research. The Collaborative Research Network (CRN) 2025 Technical Track grants will support the development of sustainable tools to accelerate validation and therapeutic research and discovery for emerging targets identified through ASAP discoveries, offering funding of up to $2M per year over three years, up to $6M total.
"By bringing researchers together to generate new preclinical tools for targets studied in our ASAP programs, our goal ...
New study: Eating mangos daily shown to improve insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control
2025-03-05
ORLANDO, Fla. – Mar. 5 2025 – New research has uncovered a potential gamechanger for improving cardiometabolic health: fresh mangos. A study recently published in the journal Nutrients finds that eating two cups of mango, just about 100 calories-worth, daily may help lower insulin concentration levels and improve insulin sensitivity in adults who are overweight or obese with chronic low-grade inflammation. The findings underscore how simple dietary choices could contribute to reducing the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes, ...
Highly radioactive nuclear waste – how to keep it from oblivion
2025-03-05
Sweden’s radioactive nuclear waste will be stored in a sealed bedrock repository for 100,000 years. It will be hazardous for a very long time. So how can we ensure that humanity does not forget that it is there? Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have come up with a proposal for how to keep the memory alive over generations.
“We’re trying to do something that no one has ever done before. The person who eventually reads this might not even be human, but perhaps a kind of AI or something ...
Generations ‘sync’ up in rural ‘glades’ to boost technology use for health
2025-03-05
Given the growing role of mobile technology in supporting older adults, it’s essential to implement initiatives that encourage its adoption among this population. However, older adults are often unfamiliar with mobile technology, especially those in rural areas with limited digital access or literacy.
To bridge this gap, researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing, and collaborators, implemented a pilot study to test an intergenerational program involving high school students, older adults and local faith-based health educators in the “Glades,” a rural community nestled at the ...
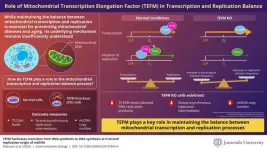
Unveiling the mechanism of maintenance of replication and transcription in mitochondria
2025-03-05
Mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (mtDNA) is essential for cellular energy production and overall cell function. Abnormalities in mtDNA are linked to various diseases and are also implicated in aging. Understanding the process of replication and transcription of mtDNA is crucial for improving our knowledge of human health, disease, and aging. However, the mechanisms that regulate the balance between transcription and replication of mtDNA remain unclear.
To unveil the mechanisms, a team of researchers ...
[1] ... [639]
[640]
[641]
[642]
[643]
[644]
[645]
[646]
647
[648]
[649]
[650]
[651]
[652]
[653]
[654]
[655]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.