Heart rate recovery predicts clinical worsening in pulmonary hypertension
2011-11-21
Heart rate recovery at one minute after a six-minute walking distance (6MWD) test is highly predictive of clinical worsening and time to clinical worsening in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH), according to a new study.
"Ours is the first study to show that heart rate recovery at one minute of rest (HRR1) following a 6MW test is a strong predictor of clinical worsening in IPAH patients," said Omar A. Minai, MD, staff physician in the Department of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic. "Predicting long-term ...
Metabolic syndrome biomarkers predict lung function impairment after exposure to WTC dust
2011-11-21
Metabolic syndrome biomarkers predict subsequent decline in lung function after particulate exposure, according to new research involving rescue personnel exposed to World Trade Center (WTC) dust.
In a nested case-control study of 327 non-smoking FDNY 9/11 rescue workers, metabolic syndrome biomarkers measured within six months of exposure to WTC dust predicted decline of forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) over the next six years.
"Study participants with dyslipidemia, elevated heart rate or elevated leptin levels had a significantly increased risk of developing ...
As probiotics use grows for gut health, VSL#3 has designations for specific GI issues
2011-11-21
GAITHERSBERG, MD, Nov. 18 – As clinical studies continue to validate the use of probiotics to help promote general gastrointestinal health, a growing U.S. market1 for probiotics indicates that the U.S. healthcare community and consumers alike are recognizing the value of these beneficial microorganisms. However, because most probiotics are classified as dietary supplements, directing patients to the best probiotic for their individual needs can be challenging. And, as the category matures, one probiotic preparation -- VSL#3 -- stands apart and ahead because it is not a ...
The protest vote prevails when a landslide victory is expected
2011-11-21
Researchers at the Juan March foundation and the Duke University (USA) have analysed the reason for casting a protest vote as a way of expressing unhappiness with a party during elections. Moderate voters are more likely to vote in this way than those at the extreme left or extreme right of the political spectrum.
Daniel Kselman, researcher at the Juan March Foundation and co-author of the study that analyses such behaviour states that "the protest vote is just a way of expressing discontent. In order for it to be effective, a lot more voters from your party need to vote ...
NRL Monterey develops more accurate tropical cyclone prediction model
2011-11-21
WASHINGTON -- Researchers at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) Marine Meteorology Division (MMD), Monterey, Calif., have developed the Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System Tropical Cyclone (COAMPS-TC™) model, achieving a significant research milestone in predictions of tropical cyclone intensity and structure.
While the predictions of the paths or tracks of hurricanes, more generally referred to as tropical cyclones (TC), have steadily improved over the last few decades, improvements in the predictions of storm intensity have proven much more difficult.
"Over ...
Protection from severe malaria explained
2011-11-21
Why do people with a hereditary mutation of the red blood pigment hemoglobin (as is the case with sickle-cell anemia prevalent in Africa) not contract severe malaria? Scientists in the group headed by Prof. Michael Lanzer of the Department of Infectious Diseases at Heidelberg University Hospital have now solved this mystery. A degradation product of the altered hemoglobin provides protection from severe malaria. Within the red blood cells infected by the malaria parasite, it blocks the establishment of a trafficking system used by the parasite's special adhesive proteins ...
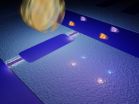
Chalmers scientists create light from vacuum
2011-11-21
Scientists at Chalmers University of Technology have succeeded in creating light from vacuum – observing an effect first predicted over 40 years ago. The results is published tomorrow (Wednesday) in the journal Nature. In an innovative experiment, the scientists have managed to capture some of the photons that are constantly appearing and disappearing in the vacuum.
The experiment is based on one of the most counterintuitive, yet, one of the most important principles in quantum mechanics: that vacuum is by no means empty nothingness. In fact, the vacuum is full of various ...
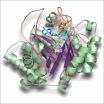
Enzymatic synthesis of pyrrolysine, the mysterious 22nd amino acid
2011-11-21
This press release is available in German.
With few exceptions, all known proteins are built up from only twenty amino acids. 25 years ago scientists discovered a 21st amino acid, selenocysteine and ten years ago a 22nd, the pyrrolysine. However, how the cell produces the unusual building block remained a mystery. Now researchers at the Technische Universitaet Muenchen have elucidated the structure of an important enzyme in the production of pyrrolysine. The scientific journal Angewandte Chemie reports on their results in its "Early View" online section.
Proteins ...
MU researchers develop tool that saves time, eliminates mistakes in diabetes care
2011-11-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. – In the fast-paced world of health care, doctors are often pressed for time during patient visits. Researchers at the University of Missouri developed a tool that allows doctors to view electronic information about patients' health conditions related to diabetes on a single computer screen. A new study shows that this tool, the diabetes dashboard, saves time, improves accuracy and enhances patient care.
The diabetes dashboard provides information about patients' vital signs, health conditions, current medications, and laboratory tests that may need to be ...
Colon cancer screening campaign erases racial, gender gaps in use of colonoscopy
2011-11-21
Since the 1970s, U.S. mortality rates due to colorectal cancer have declined overall, yet among blacks and Hispanics, the death rates rose. Evidence suggests that underuse of colonoscopy screening among these groups is one reason for the large disparities. In 2003, New York City launched a multifaceted campaign to improve colonoscopy rates among racial and ethnic minorities and women. A new study conducted by researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and the NYC Department of Health and Mental Hygiene demonstrates the notable success of the campaign. ...
A corny turn for biofuels from switchgrass
2011-11-21
Many experts believe that advanced biofuels made from cellulosic biomass are the most promising alternative to petroleum-based liquid fuels for a renewable, clean, green, domestic source of transportation energy. Nature, however, does not make it easy. Unlike the starch sugars in grains, the complex polysaccharides in the cellulose of plant cell walls are locked within a tough woody material called lignin. For advanced biofuels to be economically competitive, scientists must find inexpensive ways to release these polysaccharides from their bindings and reduce them to fermentable ...
Great Plains river basins threatened by pumping of aquifers
2011-11-21
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Suitable habitat for native fishes in many Great Plains streams has been significantly reduced by the pumping of groundwater from the High Plains aquifer – and scientists analyzing the water loss say ecological futures for these fishes are "bleak."
Results of their study have been published in the journal Ecohydrology.
Unlike alluvial aquifers, which can be replenished seasonally with rain and snow, these regional aquifers were filled by melting glaciers during the last Ice Age, the researchers say. When that water is gone, it won't come back – at ...
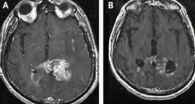
Old drugs find new target for treating brain tumor
2011-11-21
Scientists at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center, in collaboration with colleagues in Boston and South Korea, say they have identified a novel gene mutation that causes at least one form of glioblastoma (GBM), the most common type of malignant brain tumor.
The findings are reported in the online edition of the journal Cancer Research.
Perhaps more importantly, the researchers found that two drugs already being used to treat other forms of cancer effectively prolonged the survival of mice modeling this particular ...
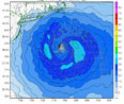
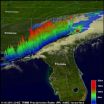
GOES satellite eyeing late season lows for tropical development
2011-11-21
Its late in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific hurricane seasons, but the calendar isn't stopping the tropics. The GOES-13 satellite is keeping forecasters informed about developing lows like System 90E in the eastern Pacific and another low pressure area in the Atlantic.
System 90E and the Atlantic low pressure area were both captured in one image from the NOAA's GOES-13 satellite today, November 18, 2011 at 1145 UTC (7:45 a.m. EST). The image was created by the NASA GOES Project (in partnership with NOAA) at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The ...
New NASA missions to investigate how Mars turned hostile
2011-11-21
Maybe because it appears as a speck of blood in the sky, the planet Mars was named after the Roman god of war. From the point of view of life as we know it, that's appropriate. The Martian surface is incredibly hostile for life. The Red Planet's thin atmosphere does little to shield the ground against radiation from the Sun and space. Harsh chemicals, like hydrogen peroxide, permeate the soil. Liquid water, a necessity for life, can't exist for very long here --any that does not quickly evaporate in the diffuse air will soon freeze out in subzero temperatures common over ...
Walking through doorways causes forgetting, new research shows
2011-11-21
We've all experienced it: The frustration of entering a room and forgetting what we were going to do. Or get. Or find.
New research from University of Notre Dame Psychology Professor Gabriel Radvansky suggests that passing through doorways is the cause of these memory lapses.
"Entering or exiting through a doorway serves as an 'event boundary' in the mind, which separates episodes of activity and files them away," Radvansky explains.
"Recalling the decision or activity that was made in a different room is difficult because it has been compartmentalized."
The study ...
NASA's TRMM satellite sees deadly tornadic thunderstorms in Southeastern US
2011-11-21
Tornadoes are expected to accompany severe storms in the springtime in the U.S., but this time of year they also usually happen. When a line of severe thunderstorms associated with a cold front swept through the U.S. southeast on Nov. 16, TRMM collected rainfall data on the dangerous storms from space.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over the southeastern United States on November 16, 2011 at 2310 UTC (6:10 p.m. EST) when tornadoes were occurring with a line of thunderstorms that stretched from western Florida north through North Carolina. ...
A failing sense of smell can be reversed
2011-11-21
NEW YORK, November 20, 2011 – In a new study scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center have shown that the sense of smell can be improved. The new findings, published online November 20, 2011, in Nature Neuroscience, suggest possible ways to reverse the loss of smell due to aging or disease.
Smell is unique among our senses, explains Donald A. Wilson, PhD, professor of child and adolescent psychiatry at NYU Langone Medical Center and senior research scientist at the Emotional Brain Institute at Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research, who led the study. The ...
U-M researchers find genetic rearrangements driving 5 to 7 percent of breast cancers
2011-11-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Researchers at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have discovered two cancer-spurring gene rearrangements that may trigger 5 to 7 percent of all breast cancers.
These types of genetic recombinations have previously been linked to blood cancers and rare soft-tissue tumors, but are beginning to be discovered in common solid tumors, including a large subset of prostate cancers and some lung cancers.
Looking at the genetic sequencing of 89 breast cancer cell lines and tumors, researchers found two distinct types of genetic rearrangements ...
Style-Passport Launches New "Winter Sun" Collection for Year-Round Jetsetters
2011-11-21
Winter is great; who doesn't love wrapping up warm, sipping hot cocoa, making snowmen and - of course - Christmas? However, for those heading abroad and swapping frosty paths for sun-kissed beaches, buying your holiday clothes at this time of year can be more daunting than Christmas dinner with the in-laws! Help is at hand, as online fashion retailer Style-Passport have launched their winter sun collection.
Boasting beautiful bikinis, stunning sarongs and contemporary kaftans (amongst other things), Style-Passport's winter sun range is perfect for picking up the beach ...
Huskies lend insight into mercury risk
2011-11-21
Researchers have highlighted the serious health risks associated with the diets of indigenous people by linking the accumulation of mercury in their primary food source to a decrease in the power of antioxidants.
Published today, 21 November, in IOP Publishing's journal Environmental Research Letters, the study used Alaskan huskies to demonstrate the risk posed by contaminants, such as mercury, in the subsistence diets that both indigenous people and huskies live on.
Huskies are an ideal model for humans as they are exposed to the same environmental hazards and have ...
Climate change effect on release of CO2 from peat far greater than assumed
2011-11-21
Climate change effect on release of CO2 from peat far greater than assumed
Drought causes peat to release far more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than has previously been realised.
Much of the world's peatlands lie in regions predicted to experience increased frequency and severity of drought as a result of climate change- leading to the peat drying out and releasing vast stores of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. It's the very wetness of the peat that has kept the air out, locking in centuries of carbon dioxide that would normally be released from the ...
Novel ALS drug slows symptom progression, reduces mortality in phase 2 trial
2011-11-21
Treatment with dexpramipexole – a novel drug believed to prevent dysfunction of mitochondria, the subcellular structures that provide most of a cell's energy – appears to slow symptom progression in the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Promising results of a phase 2 trial of dexpramipexole are receiving advance online publication in Nature Medicine. Some preliminary results of the study were presented at the 2009 International Symposium on ALS/MND and the 2010 American Academy of Neurology annual meeting.
"Today there are only two FDA-approved ...
UGA scientists invent long-lasting, near infrared-emitting material
2011-11-21
Athens, Ga. – Materials that emit visible light after being exposed to sunlight are commonplace and can be found in everything from emergency signage to glow-in-the-dark stickers. But until now, scientists have had little success creating materials that emit light in the near-infrared range, a portion of the spectrum that only can be seen with the aid of night vision devices.
In a paper just published in the early online edition of the journal Nature Materials, however, University of Georgia scientists describe a new material that emits a long-lasting, near-infrared glow ...
Study finds sex a significant predictor of happiness among married seniors
2011-11-21
The more often older married individuals engage in sexual activity, the more likely they are to be happy with both their lives and marriages, according to new research presented in Boston at The Gerontological Society of America's (GSA) 64th Annual Scientific Meeting.
This finding is based on the 2004� General Social Surveys, a public opinion poll conducted on a nationally representative sample of non-institutionalized English and Spanish-speaking person 18 years of age or older living in the U.S. The data analysis was conducted by Adrienne Jackson, PT, PhD, MPA, ...
[1] ... [6895]
[6896]
[6897]
[6898]
[6899]
[6900]
[6901]
[6902]
6903
[6904]
[6905]
[6906]
[6907]
[6908]
[6909]
[6910]
[6911]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.