'Good cholesterol' structure identified, could help explain protective effects
2011-03-13
CINCINNATI—University of Cincinnati (UC) researchers have determined the structure of human HDL cholesterol and say the finding could help explain how this "fat packet" protects against cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke.
The study, led by W. Sean Davidson, PhD, professor in UC's pathology and laboratory medicine department, appears online ahead of print March 13, 2011, in the journal Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
HDL (high-density lipoproteins) also known as "good cholesterol," are packets of protein and fat that deliver fat to specific ...
Combination overcomes breast cancer resistance to herceptin
2011-03-13
HOUSTON - Breast cancer tumors take numerous paths to resist the targeted drug Herceptin, but a single roadblock at a crucial crossroads may restore a tumor's vulnerability to treatment, scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center report on line at Nature Medicine.
Adding the drug saracatinib to Herceptin treatment shrinks previously resistant tumors by cutting off at least five different molecular pathways, each of which can resist, said senior author Dihua Yu, M.D., Ph.D., professor in MD Anderson's Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology.
"Scientists ...
Bigmouthmedia Expands Analytics Services with Nedstat Professional Accreditation
2011-03-13
Bigmouthmedia has expanded the range of analytics services on offer to clients after announcing that the agency has been awarded global professional accreditation status by Nedstat.
Underlining bigmouthmedia's expertise in web analytics, two members of its team recently passed Nedstat's prestigious Sitestat professional exam qualifications. The accreditation, which will allow the agency to work as a Sitestat Authorized Partner, represents the latest step in the company's strategy to expand and diversify the range of services on offer to clients.
"This is a significant ...
With new method, CSHL team is able to infer how tumors evolve and spread
2011-03-13
Cold Spring Harbor, NY -- A new method of analyzing cancerous tumors developed by scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) suggests that tumors may not evolve gradually, but rather in punctuated or staccato-like bursts. It is a finding that has already shed new light on the process of tumor growth and metastasis, and may help in the development of new methods to clinically evaluate tumors.
The new analytic method, devised by CSHL Professor Michael Wigler and colleagues, features a process called single cell sequencing (SNS), which enables accurate quantification ...
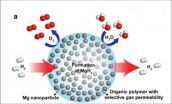
Berkeley Lab scientists achieve breakthrough in nanocomposite for high-capacity hydrogen storage
2011-03-13
Since the 1970s, hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels due to its clean combustion —unlike hydrocarbon-based fuels, which spew greenhouse gases and harmful pollutants, hydrogen's only combustion by-product is water. Compared to gasoline, hydrogen is lightweight, can provide a higher energy density and is readily available. But there's a reason we're not already living in a hydrogen economy: to replace gasoline as a fuel, hydrogen must be safely and densely stored, yet easily accessed. Limited by materials unable to leap these conflicting ...
Key Assets Presents New Career Opportunities in Fostering
2011-03-13
Key Assets, a 'not for profit' non-government fostering agency operating in South Australia, is providing carers with the opportunity to commit to fostering on a full-time basis with 24-hour support and a rewarding fostering fee. This will enable carers to commit the time and attention that this fulfilling career deserves.
Working in partnership with the Department for Families and Communities, Key Assets provides foster care placements for a wide range of children and young people across South Australia. Through the delivery of Team Parenting, an approach based upon ...
Bet 365 Wins Deepstack Media's "Best Cheltenham Festival Free Bet 2011" Award
2011-03-13
With so many free bets available for the upcoming Cheltenham Festival, it is difficult for punters to decide which the most suitable and best value is. As part of Free Bet Finder's online Cheltenham betting microsite, over twenty five bookmakers' promotions have been reviewed and rated to determine the best Cheltenham free bet.
With just hours to go before the start of the Cheltenham Festival, and most punters already deciding who their fancied horses and best bets are, Free Bet Finder have announced that Bet 365 are the winner of this award.
Following a number ...
Evans Consoles Acquires DAS/NKI Group
2011-03-13
Evans Consoles, the leader in design and manufacturing of 24/7 mission critical environments, is pleased to announce the acquisition of both Dutch Airport Solutions B.V. (DAS) and the assets relating to the airport interiors division of NKI Solutions B.V. (NKI), both based in the Netherlands.
NKI has a 35-year history and is recognized worldwide, with a reputation for excellence in the design, manufacturing, installation and project management of airport counters, terminal interiors and signage.
These entities have been acquired by the newly created airport division ...
4Hotels.co.uk: Cheltenham Spa - More Than Just A Racecourse Town!
2011-03-12
Everyone has heard of the Cheltenham Festival - the 4 day extravaganza of horse racing that takes place every year in March - but did you know there are four other festivals that Cheltenham is world renowned for, as well as it being a town made famous by its architecture and numerous other points of historical interest?
Situated on the edge of the Cotswolds, in the south-west region of England, Cheltenham is a wealthy spa town which became a health and holiday resort in 1716 when mineral springs were discovered. The spring waters are the only consumable alkaline waters ...
The Gay-Friendly Source Is Open For Business
2011-03-12
The Gay-Friendly Source is a website that was built to foster community and dialogue between the LGBT community and the world at large. The site was created for the gay community and beyond. The Gay-Friendly Source was designed to be used by all ages, both by those who are gay and by their families, friends, and coworkers, as well as by those who seek to gain greater insight and understanding of gay issues. The Gay-Friendly Source offers news, editorials, and an extensive listing of gay-friendly events nationwide. The site appeals to a wide audience and is an ideal venue ...
LiveVox Delivers Burstable Predictive Dialer to Teleservices
2011-03-12
LiveVox Inc., the leading provider of cloud contact center solutions, today announced deployment of its fully burstable inbound/outbound cloud platform with integrated hosted predictive dialer, ACD, IVR, call recording and sub-second global call routing to telesales organizations.
The integrated LiveVox platform is unique in its ability to scale and enable seamlessly integrated "virtual agent groups" that can combine onshore, offshore and at-home agent pools. LiveVox is also differentiated by its ability to deliver ongoing cost efficiency and reliability through the ...
Aitan Releases New EP Top Of The World, Announces Tour Dates During SXSW
2011-03-12
Pop / Rock artist Aitan released his new studio EP Top Of The World this week through iTunes and most other online retailers. Aitan worked on Top Of The World with producer Stewart Cararas (Katie Cole, All Time Low, American Idol) in his Los Angeles based studio.
In addition, Aitan has posted new tour dates surrounding this year's SXSW festival in Austin, TX. Dates include a very special interactive and live experience on March 15th at Michael Nesmith's VideoRanch 3D and two additional festival dates.
03.15.2011 - Michael Nesmith's VideoRanch 3D *live at the Austin ...
Howell, NJ's Hunter Brook Horse Farm Named to Hulafrog.com's 31 Cool Camps List
2011-03-12
Hulafrog.com, a parent's guide to life with kids in the greater Red Bank area of NJ, is helping local moms find fun, unique and educational summer camps and programs for their kids. Each day in March, starting today, editors will highlight One Cool Summer Camp in Monmouth County, New Jersey.
And Today's Summer Camp Pick is: Hunter Brook Horse Farm's Horse Lovers Camp
Horse Lovers Camp | Hunter Brook Farm
Have a horse lover? Hunter Brook Farm has three weeks of camp that focus on all things horses! Campers will participate in daily riding and grooming activities ...
Gleneagles Kuala Lumpur's Women Support Group Launched in conjunction with International Women's Day
2011-03-12
A century ago, when the first International Women's Day was held in Europe, women holding high-level positions such as a CEO or an editor of a well-known magazine or even a doctor would have been unbelievable to many.
In 1911, most women in Malaysia were struggling to raise families amid economic challenges and social disparity.
Fast-forward to 100 years after that, women today, especially in Malaysia, are recognized for their achievements and hold many key decision-making positions in the corporate and government sectors.
According to a recent published report, ...
Foxit Shows Business Ready PDF Solutions at CeBIT 2011
2011-03-12
Foxit Corporation would like to thank those people who took the time to visit the Foxit booth at CeBIT 2011, the world¡¯s leading ICT tradeshow in Hannover, Germany. Customers came away impressed with Foxit¡¯s award winning PDF solutions due to their affordability, blazing speed, tight security, and lightweight architecture. Foxit provides the right features at the right price with the quality and support you expect from an enterprise solution.
Foxit is a leading provider of solutions for reading, creating, organizing, and securing PDF documents. Customers of Foxit¡¯s ...
Chris Brennan Instructional DVD's and Special Gi Unveiled by Budo Videos
2011-03-12
Budo Videos, which proclaims to have the largest selection of martial arts products in the world, recently unveiled a new line of products that should excite those who practice BJJ or who are just interested in the martial art. These include a series of instructional DVD's by Brazilian Jujitsu legend Chris Brennan, as well as a new Shoyoroll Gi called the White Mamba.
The first DVD by Chris "The Westside Strangler" Brennan is titled 'Nogi Guard Passes'. This DVD is designed to show practitioners the best ways to pass the Nogi guard. The DVD can be used by both BJJ practitioners ...
Empower your Journey to Success with these Trafford Publishing Offers for March
2011-03-12
In line of International Women's History month, Trafford Publishing is empowering authors with value laden publishing and book marketing offers. Discover the power of publishing with these deals:
Publishing Services Savings
Avail any of Trafford's book publishing packages and they will automatically upgrade the purchased package at no cost. Or get any of Trafford Publishing's Black and White, Full Color, or Children's Publishing packages and move a step up, without any additional charges.
With these book publishing offers, authors can celebrate their rights to speak ...
Access Display Group Boosts Sales by 52% in 2010
2011-03-12
2010 brought a 52% increase in sales for Access Display Group (ADG), a leading designer, manufacturer and distributor of changeable poster displays, sign frames and other signage display frame fixtures.
2010 was a busy, productive year for ADG. In addition to increasing its sales by 52% from 2009, the company was also ranked among the fastest growing private companies in America for the second year in a row, according to Inc. Magazine. The company was ranked #7 among manufacturers in New York State.
ADG attributes its most recent successes to the creation of 11 new ...
Micro Keylogger 1.70 Released
2011-03-12
Micro Keylogger Inc., the company specializing in awarding ¡V winning monitoring solutions, announced the release of Micro Keylogger 1.70. Micro Keylogger is a powerful undetectable computer monitoring solution for parental control, catching cheating spouse and employee monitoring, which allows you to secretly track all activities from all computer users.
What you can do with Micro Keylogger?
Monitor and protect your kids
Have you ever encountered that your kids spend all days on the Internet but you have no clue what they are doing, who they are talking to, what ...
Aneesoft Corporation Gives Away YouTube Converter for Free
2011-03-12
Aneesoft Corporation, a leading digital multimedia software company, launches a YouTube Converter giveaway for a limited time on their official website. The program is designed to download multiple YouTube videos and convert YouTube videos to any common video format and audio format.
This Aneesoft YouTube Converter is easy to use. Just copy the YouTube URL to Aneesoft YouTube Converter, the YouTube videos will be downloaded easily with great speed. It also can help users to convert YouTube videos for playing back on the mobile devices, such as iPad 2, iPad, iPod, iPhone, ...
DMG Productions is currently in production of a new episode on "Aerospace & Defense" as part of their "Business Update" television program
2011-03-12
This fall, DMG and Business Update invite our viewers to join us on an informative and exciting exploration behind the aerospace and defense industry.
Senior producer for the series, Vince Moss, explained, "Aerospace and defense is a pivotal aspect of not just our economy, but of our future. Additionally, it's an industry that the general public is not too familiar with, he added. "Our mission with this episode is to educate the television audience on the role aerospace and defense plays in our society as well as highlighting the latest advancements and innovations ...
Galapagos Now Welcomes Families with Young Children With Expanding Inventory of Land-Based Programs and Accommodations
2011-03-12
Families with toddlers to tweens, can now comfortably experience the Galapagos that heretofore has been nearly off limits for them because cruise ships often exclude young children and land stays were difficult to come by.
Ecuador's leading hospitality company for active adventure, Red Mangrove Galapagos and Ecuador Lodges http://www.redmangrove.com/, offers a variety of land-based itineraries and sufficient multi-island room capacity in five separate lodges to entice active young families.
"My wife and seven-month-old daughter went on several of our island tours ...
Aircraft Never Built Now Take Wing Online at The Magazine Collector
2011-03-12
What does it feel like to fly a high-performance fighter plane that never went beyond the concept stage? Those who had that experience did so as armchair aviators in the mid-1920s to the late '30s. They were at the controls of futuristic flying machines engaging in dogfights against advanced-design enemy aircraft. All they had to do was read the aviation adventure novels published in 10 pulp-fiction magazines.
Each issue featured aircraft that were created in the minds of the most talented aviation artists of the day. These sleek concept planes were so futuristic that ...
Wine and Design Raises Over $1,500 for National Pancreatic Cancer Foundation
2011-03-12
Wine and Design recently held a fundraiser to raise funds and awareness for the National Pancreatic Cancer Foundation. The two-hour painting party attracted 35 participants and was held on behalf of long-time patron, Jackie Woodcock, whose husband Phil died of the disease. Wine and Design donated 100% of the event's profits to the Foundation and gave an additional gift of $612.50—bringing their total donation to $1,575.
"Offering the fundraiser at Wine and Design on February 12th was special to me," says Woodcock. "Valentine's Day is our wedding anniversary. Each year ...
Sims Recycling Solutions Facilities in California Receive Environmental and Safety Management Certifications
2011-03-12
Sims Recycling Solutions, the world's largest electronics recycler announced today that all of their electronics recycling facilities in California have received OHSAS 18001:2007 certification and ISO 14001:2004 certification from Bureau Veritas. These certifications require adherence to specified requirements of environmental, health and safety management.
"We have always had exceptionally high standards for the safety of our employees, contractors, and visitors, and will continue to work hard to secure our vision of continuous improvement and excellence in recycling" ...
[1] ... [7720]
[7721]
[7722]
[7723]
[7724]
[7725]
[7726]
[7727]
7728
[7729]
[7730]
[7731]
[7732]
[7733]
[7734]
[7735]
[7736]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.