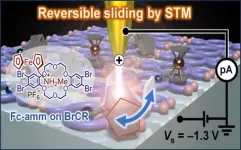
World’s smallest molecular machine: reversible sliding motion in ammonium-linked ferrocene
2024-12-12
Artificial molecular machines, nanoscale machines consisting of a few molecules, offer the potential to transform fields involving catalysts, molecular electronics, medicines, and quantum materials. These machines operate by converting external stimuli, like electrical signals, into mechanical motion at the molecular level. Ferrocene, a special drum-shaped molecule composed of an iron (Fe) atom sandwiched between two five-membered carbon rings, is a promising foundational molecule for molecular machinery. Its discovery earned the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1973, and it has since ...
Researchers reveal key factors behind Japan’s plastic waste removal rates in rivers
2024-12-12
Plastic pollution is an ever-growing problem in today’s world, as most societies have become overly dependent on plastics for packaging, medical supplies, and general goods. Plastic litter accumulation in the ocean, either through deliberate dumping or by being transported from a river, poses significant environmental challenges. Additionally, this plastic eventually degrades into small fragments called microplastics, which then impact diverse marine and land ecosystems by working their way up the food chain and into most living organisms. Though their negative effects on cell health are still under study, many nations have taken a cautionary stance, ...
Implantable sensors are helping scientists improve injury recovery
2024-12-12
EUGENE, Ore. — Dec. 12, 2024 — Tiny implantable sensors are helping University of Oregon researchers optimize the process of recovery from severe bone injuries.
Scientists at the UO’s Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact have developed miniature implantable sensors that transmit real-time data about what’s happening at an injury site. In a new study, they use the technology to show that a resistance-training rehabilitation program can significantly improve femur injuries in rats ...
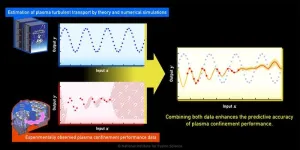
Improved predictive accuracy of fusion plasma performance by data science
2024-12-12
Fusion energy research is being pursued around the world as a means of solving energy problems. Magnetic confinement fusion reactors aim to extract fusion energy by confining extremely hot plasma in strong magnetic fields. Its development is a comprehensive engineering project involving many advanced technologies, such as superconducting magnets, reduced-activation materials, and beam and wave heating devices. In addition, predicting and controlling the confined plasma, in which numerous charged particles and electromagnetic fields interact in complex ...
Common brain network links brain atrophy patterns seen in schizophrenia
2024-12-12
A new study led by investigators from Mass General Brigham has identified a unique brain network that links varied patterns of brain atrophy, or shrinkage, associated with schizophrenia. By combining neuroimaging data from multiple studies involving more than 8,000 participants, the research team found a specific connectivity pattern of atrophy that was present across different stages and symptoms of schizophrenia — and distinct from brain networks associated with other psychiatric disorders. The findings will help to guide a clinical trial that will start recruiting patients soon and will ...
“Us” vs. “them” biases plague AI, too
2024-12-12
Research has long shown that humans are susceptible to “social identity bias”—favoring their group, whether that be a political party, a religion, or an ethnicity, and disparaging “outgroups.” A new study by a team of scientists finds that AI systems are also prone to the same type of biases, revealing fundamental group prejudices that reach beyond those tied to gender, race, or religion.
“Artificial Intelligence systems like ChatGPT can develop ‘us versus them’ biases similar to humans—showing favoritism toward their perceived ‘ingroup’ while expressing ...
Why deep sleep is helpful for memory
2024-12-12
It has been known for nearly 20 years that slow, synchronous electrical waves in the brain during deep sleep support the formation of memories. Why that is was previously unknown. Now, writing in the journal Nature Communications, a team of researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin posits an explanation. According to the study, the slow waves make the neocortex, the location of long-term memory, especially receptive to information. The findings could help to optimize the treatment approaches that are intended to support memory formation from outside.
How do permanent memories form? Experts believe that while we sleep, our brains replay the events of ...
Sleepers made from recycled plastic could make railways even more eco-friendly
2024-12-12
Railways, the most climate-friendly mode of transport bar long-distance buses, are bound to play an important role in the fight for net zero. The total emissions of railway travel are currently 31 grams of CO2 equivalents (CO2e) per passenger kilometer, half the amount as for the most economical electrical vehicles.
But the carbon emissions of railway traffic can be further reduced, shows a new study in Frontiers in Sustainability by authors in Finland. This is because typical construction materials such as steel and concrete are energetically costly to produce, transport, handle, and maintain. Even on the ...
Ugh, my stomach: Identifying amino acids that prevent sporulation in food poisoning
2024-12-12
Food poisoning is a common, yet unpleasant, illness caused by eating contaminated items. It is sometimes caused by Clostridium perfringens, a pathogen widely found in soil and the intestinal tracts of animals.
The pathogen multiplies in environments with little oxygen, for example, curry stored in a pot. After ingestion of the pathogen, they form spores in the small intestinal tracts. The toxins produced during spore formation cause diarrhea and abdominal pain, but the underlying mechanism of spore formation has not been fully understood.
Associate Professor Mayo Yasugi’s team at Osaka Metropolitan University’s ...
Air pollution in India linked to millions of deaths
2024-12-12
A new study from Karolinska Institutet shows that long-term exposure to air pollution contributes to millions of deaths in India. The research, published in The Lancet Planetary Health, emphasises the need for stricter air quality regulations in the country.
Air pollution consisting of particles smaller than 2.5 micrometres in diameter, PM2.5, can enter the lungs and bloodstream and is a major health risk in India. Researchers have now examined the link between these particles and mortality over a ten-year ...
Study finds widening inequalities in child vaccination rates across England
2024-12-12
Inequalities in childhood vaccination are widening in England, with uptake rates of five key vaccines consistently lower in young children living in areas of higher deprivation from 2019 to 2023, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say vaccine uptake was below the World Health Organization’s recommended 95% target for all vaccinations studied and call for urgent action to strengthen systems for childhood vaccination.
Protecting children from vaccine preventable diseases ...
Investigation raises new concerns over landmark trial for top selling anti-platelet drug
2024-12-12
An investigation published by The BMJ today raises new concerns over the landmark clinical trial (PLATO) that was used to gain worldwide approval for the anti-platelet drug ticagrelor (Brilinta in the US and Brilique in Europe), manufactured by AstraZeneca.
Peter Doshi, senior editor at The BMJ, reveals new details that show problems in data reporting after obtaining primary PLATO trial records and unpublished data through a freedom of information request.
The PLATO trial was published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) in 2009. Assessing over 18,000 patients in 43 countries, investigators reported that ticagrelor ...
Making chemotherapy for Hodgkin lymphoma kinder to patients
2024-12-12
A simple change to the chemotherapy regimen for people with Hodgkin lymphoma could reduce the long-term health impacts that can result from treatment, according to researchers in Cambridge. The findings could lead to the national guidance on chemotherapy treatment for these patients being revised.
The study, published today in The Lancet Oncology was led by Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (CUH) and the Wellcome Sanger Institute. It compares the lasting effects of two chemotherapy regimens used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma in younger adults. Hodgkin lymphoma ...
ACS study finds early-onset colorectal cancer cases surge globally
2024-12-12
ATLANTA, December 11, 2024 — A new study led by American Cancer Society (ACS) researchers shows that early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) incidence rates are rising in 27 of 50 countries/territories worldwide, 20 of which have either exclusive or faster increases for early-onset disease. In 14 countries, including the United States, rates are increasing in young adults while stabilizing in those 50 years and older. The research is published today in the journal The Lancet Oncology.
“The ...
Fluctuating blood pressure tied to problems with thinking skills
2024-12-11
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 11, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Older adults whose blood pressure fluctuates over time may be more likely to have problems with thinking and memory skills, according to a study published in the December 11, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The association was found in Black participants but not in white participants in the study.
The study does not prove that fluctuations in blood pressure cause problems with thinking skills; it only shows an association.
“These results suggest ...
Scientists find promising new target for antidepressants—in the gut
2024-12-11
Researchers have discovered new connections between the gut and brain that hold promise for more targeted treatments for depression and anxiety, and could help prevent digestive issues in children by limiting the transmission of antidepressants during pregnancy.
The study, published in the journal Gastroenterology, shows that increasing serotonin in the gut epithelium—the thin layer of cells lining the small and large intestines—improves symptoms of anxiety and depression in animal studies. The researchers also found ...
Antidepressants may act in gut to reduce depression and anxiety
2024-12-11
NEW YORK, NY (Dec. 11, 2024)--Most of us have experienced the effects of moods and emotions on our gastrointestinal tract, from “butterflies” in the stomach caused by nervousness to a loss of appetite when we’re feeling blue.
A new study in animals suggests that targeting antidepressant medications to cells in the gut could not only be an effective treatment of mood disorders like depression and anxiety but may also cause fewer cognitive, gastrointestinal, and behavioral side effects for patients and their children than current treatments.
“Antidepressants like Prozac and Zoloft that raise serotonin levels are important first-line ...
New PROSPECT-lung trial launches to advance treatment options for operable non-small cell lung cancer
2024-12-11
The highly anticipated PROSPECT-Lung trial has officially opened, marking a significant step forward in the quest to improve treatment strategies for patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. The trial, which is the first to open through the newly formed National Cancer Institute (NCI) Clinical Trials Innovation Unit (CTIU), aims to evaluate the role of immunotherapy before and after surgery in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
The PROSPECT-Lung trial is a large, multicenter trial developed and led by the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology and the SWOG Cancer Research Network and conducted within the NIH-funded NCI National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN), ...
The Welch Foundation honors Rice’s Wang for pioneering contributions to sustainable energy solutions
2024-12-11
The Welch Foundation, one of the nation’s leading private funders of basic chemistry research, has awarded the 2025 Norman Hackerman Award in Chemical Research to Haotian Wang, an associate professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at Rice University. Wang is recognized for his groundbreaking contributions to carbon dioxide electrochemistry, which pave the way for sustainable energy solutions.
Wang’s innovative research focuses on harnessing the catalyst-electrolyte ...
Hospital payment caps could save millions of dollars for state employee health plans
2024-12-11
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — State employee health plans could have saved $7.1 billion nationwide by capping hospital payments at 200% of Medicare rates in 2022, a study led by researchers at the Brown University School of Public Health found.
“States are under growing budgetary pressure due to rising health care spending, primarily through increases in hospital and drug prices,” said study author Roslyn Murray, an assistant professor of health services, policy and practice ...
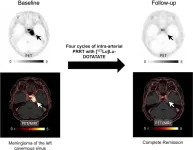
Intraarterial radionuclide therapy safe and effective for advanced meningioma patients
2024-12-11
Reston, VA (December 10, 2024)—Radionuclide therapy delivered directly to an artery is safe and feasible for patients with advanced meningioma, according to new research published in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. In the first long-term study of intraarterial peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) in advanced meningioma, patients saw improved radiologic and clinical disease control compared with intravenous PRRT, with no additional toxicity.
Meningiomas are the most common primary neoplasms of the central nervous system and account for more than one-third of all cases. Meningiomas are mostly ...
University of Tennessee and Sheffield sign MOU to facilitate collaborations
2024-12-11
The University of Tennessee and the University of Sheffield recently signed a memorandum of understanding to facilitate educational and research collaborations, share best practices, and promote student and staff exchanges between the institutions.
Tickle College of Engineering Dean Matthew Mench, the Wayne T. Davis Dean’s Chair, traveled to England in late November to tour the Sheffield facilities, meet with faculty, and sign the MOU with Malcolm Butler, the vice president and director of global engagement of the University of Sheffield.
There ...
Nemours Children’s Health Initiative to start HPV vaccination at age 9 improved completion rates
2024-12-11
WILMINGTON, Del. (December 11, 2024) — A quality improvement program designed to increase earlier uptake of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine raised vaccination rates significantly, according to a study by Nemours Children’s Health researchers.
In a new study published in Academic Pediatrics, Caitlin J. Miller, medical student at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University and Jonathan Miller, MD, Associate Chief of Primary Care, Nemours Children’s ...
Nova SBE and New York University Tandon School of Engineering launch transatlantic dual degree program
2024-12-11
Nova School of Business and Economics (Nova SBE) has partnered with NYU Tandon School of Engineering to create a transatlantic program focusing on two strategic and complementary fields: Management (Nova SBE) and Management of Technology (NYU Tandon).
This new program allows students to earn distinct master’s degrees from two of the world’s most prestigious academic institutions, located in key cultural and economic centers: Lisbon and New York.
Under this partnership agreement, students enrolled in either the International Master’s in Management or the Master’s in Management (both from Nova SBE) ...
2025 SPIE-Franz Hillenkamp Postdoctoral Fellowship awarded to Morgan Fogarty
2024-12-11
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA — SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, has announced Morgan Fogarty, who is expected to receive her PhD in Imaging Science from Washington University in St. Louis (WashU) in February, as the recipient of the 2025 SPIE-Franz Hillenkamp Postdoctoral Fellowship in Problem-Driven Biomedical Optics and Analytics. The annual award of $75,000 supports interdisciplinary problem-driven research and provides opportunities for translating new technologies ...
[1] ... [781]
[782]
[783]
[784]
[785]
[786]
[787]
[788]
789
[790]
[791]
[792]
[793]
[794]
[795]
[796]
[797]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.