Breakthrough in worm research has implications for human disease studies
2010-12-18
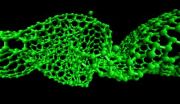
RENO, Nev. – It's just a worm, a tiny soil-dwelling nematode worm – but the implications are big for biomedicine and circadian biology as shown in a recent study authored by University of Nevada, Reno researcher Alexander van der Linden. The article on the circadian clock of the Caenorhabditis elegans worm was published in the peer-reviewed, open-access journal, PLoS Biology.
"Circadian rhythms are important in all organisms because they regulate biological functions such as food intake, temperature, metabolic rate and sleep," van der Linden said. "The discovery of clock-controlled ...
Novel drug offers hope for early intervention in cystic fibrosis patients
2010-12-18
Cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with normal to mildly impaired lung function may benefit from a new investigational drug designed to help prevent formation of the sticky mucus that is a hallmark of the disease, according to researchers involved in a phase 3 clinical trial of the drug. Called denufosol, the investigational medication can be given early in the CF disease process, and may help delay the progression of lung disease in these patients, the researchers found.
The findings were published online ahead of the print edition of the American Thoracic Society's American ...
Study: Customers who participate in eBay's 'community' become better buyers and sellers
2010-12-18
A new study from Rice University's Jones Graduate School of Business finds that customers of eBay who participate in the company's online communities become more conservative buyers and more selective and efficient sellers.
The study, "The Impact of Customer Community Participation on Customer Behaviors: An Empirical Investigation," appeared recently in the journal Marketing Science and was co-authored by Rice's Sharad Borle, associate professor of marketing; Siddharth Singh, assistant professor of marketing; and Utpal Dholakia associate professor of management, along ...
Beetroot juice could help people live more active lives
2010-12-18
New research into the health benefits of beetroot juice suggests it's not only athletes who can benefit from its performance enhancing properties – its physiological effects could help the elderly or people with heart or lung-conditions enjoy more active lives.
Beetroot juice has been one of the biggest stories in sports science over the past year after researchers at the University of Exeter found it enables people to exercise for up to 16% longer. The startling results have led to a host of athletes – from Premiership footballers to professional cyclists – looking into ...
Ben-Gurion U. researchers: High resistance rates among acute otitis media pathogens in children
2010-12-18
BEER-SHEVA, ISRAEL, December 17, 2010 – As middle ear infections increase during the winter months, researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) suggest that in many cases the most appropriate treatment is "watchful waiting" instead of using antibiotics immediately.
The review, published in the scientific journal Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy, does not suggest use of watchful waiting in all cases when the infection, also known as Acute Otitis Media (AOM), is suspected by a pediatrician, but notes that a large majority of cases can be treated this ...
550 million years ago rise in oxygen drove evolution of animal life
2010-12-18
Researchers funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) at the University of Oxford have uncovered a clue that may help to explain why the earliest evidence of complex multicellular animal life appears around 550 million years ago, when atmospheric oxygen levels on the planet rose sharply from 3% to their modern day level of 21%.
The team, led by Professor Chris Schofield, has found that humans share a method of sensing oxygen with the world's simplest known living animal - Trichoplax adhaerens - suggesting the method has been around since ...
The high price of sleep disorders
2010-12-18
Danish sleep researchers at the University of Copenhagen and the Danish Institute for Health Services Research have examined the socio-economic consequences of the sleep disorder hypersomnia in one of the largest studies of its kind. The sleep disorder has far-reaching consequences for both the individual and society as a whole.
Hypersomnia is characterised by excessive tiredness during the day. Patients who suffer from the disorder are extremely sleepy and need to take a nap several times a day. This can occur both at work, during a meal, in the middle of a conversation ...
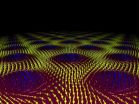
Electric current moves magnetic vortices
2010-12-18
VIDEO:
In this animated illustration, an electron (black ball) flies across a lattice of magnetic vortices. The forces transferred in the process allow the magnetic structures to be controlled with relatively...
Click here for more information.
One of the requirements to keep trends in computer technology on track – to be ever faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient – is faster writing and processing of data. In the Dec. 17 issue of the journal Science, physicists ...
Samples of vital human tumor tissue irradiated with ions for the first time
2010-12-18
Cancer treatment with ion beams developed at GSI is characterized by an excellent cure rate and only minor side effects. The therapy has been routinely in use for a little over one year. The effectiveness of the ion beams not only depends on the tumor type, but also on the genetic disposition and the personal circumstances of the individual patient. For the first time, scientists at GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung have irradiated samples of vital human tumor tissue in the scope of their systematical and fundamental research. Their long-term goal is to enhance ...
How plants counteract against the shade of larger neighbors
2010-12-18
Plants that "lose the battle" during competitiveness for light because they are shaded by larger neighbours, counteract. They adapt by rapid shoot elongation and stretch their leaves towards the sun. The molecular basis of this so-called shade avoidance syndrome had been unclarified to date. Research scientists from the Utrecht University in the Netherlands and the Ruhr University in Bochum have now been able to unravel a regulation pathway. A specific transport protein (PIN3) enables the accumulation of the plant hormone auxin, which plays an important role during this ...
Typically Italian, isn't it?
2010-12-18
"I have ready!" With this sentence the FC Bayern Munich coach Giovanni Trapattoni finished a furious rant about his team's performance in 1998. And "Mr Angelo" in a coffee advert points out to his neighbour with a mischievous smile: "I don't have a car at all". In both cases the Italians are unmistakeably recognizable and so the exuberant temperament of the first and the charming way of the second are seemingly "typically Italian".
The accent someone talks in plays a crucial role in the way we judge this person, psychologists of the Friedrich Schiller University Jena ...
How do you cut a nanotube? Lots of compression
2010-12-18
VIDEO:
Compression causes nanotubes to buckle and twist and eventually to lose atoms from their lattice-like structure.
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A pipefitter knows how to make an exact cut on a metal rod. But it's far harder to imagine getting a precise cut on a carbon nanotube, with a diameter 1/50,000th the thickness of a human hair.
In a paper published this month in the British journal Proceedings of the Royal Society ...
K-State research looks at pathogenic attacks on host plants
2010-12-18
MANHATTAN, KAN. -- Two Kansas State University researchers focusing on rice genetics are providing a better understanding of how pathogens take over a plant's nutrients.
Their research provides insight into ways of reducing crop losses or developing new avenues for medicinal research.
Frank White, professor of plant pathology, and Ginny Antony, postdoctoral fellow in plant pathology, are co-authors, in partnership with researchers at three other institutions, of an article in a recent issue of the journal Nature. The article, "Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange ...
Study reveals major shift in how eczema develops
2010-12-18
Like a fence or barricade intended to stop unwanted intruders, the skin serves as a barrier protecting the body from the hundreds of allergens, irritants, pollutants and microbes people come in contact with every day. In patients with eczema, or atopic dermatitis, the most common inflammatory human skin disease, the skin barrier is leaky, allowing intruders – pollen, mold, pet dander, dust mites and others – to be sensed by the skin and subsequently wreak havoc on the immune system.
While the upper-most layer of the skin – the stratum corneum – has been pinned as the ...
Ancient raindrops reveal a wave of mountains sent south by sinking Farallon plate
2010-12-18
50 million years ago, mountains began popping up in southern British Columbia. Over the next 22 million years, a wave of mountain building swept (geologically speaking) down western North America as far south as Mexico and as far east as Nebraska, according to Stanford geochemists. Their findings help put to rest the idea that the mountains mostly developed from a vast, Tibet-like plateau that rose up across most of the western U.S. roughly simultaneously and then subsequently collapsed and eroded into what we see today.
The data providing the insight into the mountains ...
Computer games and science learning
2010-12-18
Computer games and simulations are worthy of future investment and investigation as a way to improve science learning, says LEARNING SCIENCE: COMPUTER GAMES, SIMULATIONS, AND EDUCATION, a new report from the National Research Council. The study committee found promising evidence that simulations can advance conceptual understanding of science, as well as moderate evidence that they can motivate students for science learning. Research on the effectiveness of games designed for science learning is emerging, but remains inconclusive, the report says.###
The report is available ...
You only live once: our flawed understanding of risk helps drive financial market instability
2010-12-18
Our flawed understanding of how decisions in the present restrict our options in the future means that we may underestimate the risk associated with investment decisions, according to new research by Dr Ole Peters from Imperial College London. The research, published today in the journal Quantitative Finance, suggests how policy makers might reshape financial risk controls to reduce market instability and the risk of market collapse.
Investors know that there are myriad possibilities for how a financial market might develop. Before making an investment, they try to capture ...
Efficient phosphorus use by phytoplankton
2010-12-18
Rapid turnover and remodelling of lipid membranes could help phytoplankton cope with nutrient scarcity in the open ocean.
A team led by Patrick Martin of the National Oceanography Centre has shown that a species of planktonic marine alga can rapidly change the chemical composition of its cell membranes in response to changes in nutrient supply. The findings indicate that the process may be important for nutrient cycling and the population dynamics of phytoplankton in the open ocean.
Tiny free-floating algae called phytoplankton exist in vast numbers in the upper ocean. ...
Effect of college on volunteering greatest among disadvantaged college graduates
2010-12-18
Sociologists have long known that a college education improves the chances that an individual will volunteer as an adult. Less clear is whether everyone who goes to college gets the same boost in civic engagement from the experience.
In an innovative study that compared the volunteering rates of college graduates with those of non–college graduates with similar social backgrounds and high school achievement levels, UCLA sociologist Jennie Brand found something striking: A college education has a much greater impact on volunteering rates among individuals from underprivileged ...
Ion channel responsible for pain identified by UB neuroscientists
2010-12-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- University at Buffalo neuroscience researchers conducting basic research on ion channels have demonstrated a process that could have a profound therapeutic impact on pain.
Targeting these ion channels pharmacologically would offer effective pain relief without generating the side effects of typical painkilling drugs, according to their paper, published in a recent issue of The Journal of Neuroscience.
"Pain is the most common symptom of injuries and diseases, and pain remains the primary reason a person visits the doctor," says Arin Bhattacharjee, PhD, ...
A total lunar eclipse and winter solstice coincide on Dec. 21
2010-12-18
With frigid temperatures already blanketing much of the United States, the arrival of the winter solstice on December 21 may not be an occasion many people feel like celebrating. But a dazzling total lunar eclipse to start the day might just raise a few chilled spirits.
Early in the morning on December 21 a total lunar eclipse will be visible to sky watchers across North America (for observers in western states the eclipse actually begins late in the evening of December 20), Greenland and Iceland. Viewers in Western Europe will be able to see the beginning stages of ...
NASA's LRO creating unprecedented topographic map of moon
2010-12-18
NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter is allowing researchers to create the most precise and complete map to date of the moon's complex, heavily cratered landscape.
"This dataset is being used to make digital elevation and terrain maps that will be a fundamental reference for future scientific and human exploration missions to the moon," said Dr. Gregory Neumann of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "After about one year taking data, we already have nearly 3 billion data points from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter on board the LRO spacecraft, with near-uniform ...
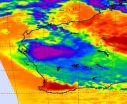
NASA satellite tracks soaking System 91S in western Australia
2010-12-18
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a series of images from its Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument over the last two days and saw the low pressure area known as System 91S make landfall in Australia. System 91S may not have become a tropical depression, but it's dropping heavy rainfall in Western Australia.
NASA's AIRS infrared instrument showed System 91S's center making landfall on Dec. 16 at 0647 UTC (1:47 a.m. EST) near the town of Carnavon in Western Australia. At that time, there was a large area of strong thunderstorms around the center of circulation, ...
New Article On OffTheGridNews.com Points to Some Challenging Questions; is Outrage Over WikiLeaks Revelations Misguided?
2010-12-18
The controversy surrounding whistle-blowing website WikiLeaks along with its creator Julian Assange continues to gain momentum as liberal Democrats and conservative Republicans have joined together in one voice to condemn the most recent leaks that Senator Diane Feinstein has described as "a serious breach of national security and could be used to severely harm the United States and its worldwide interests."
If you're looking to score popularity points in Washington now is the time to jump on the anti-Assange bandwagon and condemn the Aussie for his complicity in weakening ...
Louisiana Plastic Surgeons Caution on Laser Liposuction
2010-12-18
The Louisiana plastic surgeons of The Wall Center for Plastic Surgery (www.wallcenter.com) note a surge in the number of patients who have turned to them for corrective surgery after undergoing laser liposuction from plastic surgeons and unqualified physicians alike. While liposuction has gained acceptance and popularity with a constant stream of technological advances since its inception in the late 1970s, not all treatments and providers will be able to deliver the results patients seek.
"Many doctors are expanding into services they were never trained to perform, ...
[1] ... [8183]
[8184]
[8185]
[8186]
[8187]
[8188]
[8189]
[8190]
8191
[8192]
[8193]
[8194]
[8195]
[8196]
[8197]
[8198]
[8199]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.