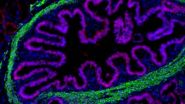
(Press-News.org) Scientists have uncovered a surprising way to reduce the brain damage caused by head injuries - stopping the body's immune system from killing brain cells. The study, published in the open access journal Acta Neuropathologica Communications, showed that in experiments on mice, an immune-based treatment reduced the size of brain lesions. The authors suggest that if the findings apply to humans, this could help prevent brain damage from accidents, and protect players of contact sports like American football, rugby and boxing.
To date, there are no effective treatments to prevent or reverse the damage sustained after brain injury. The researchers were testing the theory that blows to the head cause brain damage, in part, because of the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, allowing the immune cells in the blood to come into contact with brain cells and destroy them. They hypothesized that mice missing a vital immune component would have less brain damage from trauma, and that a treatment which blocks a component of the immune system would prevent damage.
The component they were working on was CD74, which plays a crucial part in the immune system's response to disease-causing agents. CD74 is broken into products that fit into the groove of cell surface immune response proteins as part of the chain of events that activates T cells – immune cells that normally attack infected (or damaged) cells in the body. It was thought that these cells might also attack the brain cells if the blood-brain barrier is down. A treatment known as CAP stops the T-cells from being activated, by fitting into the activation site in the proteins and blocking the interaction, meaning that the pathway cannot continue.
They tested this theory by a range of tests involving a total of 32 mice. The mice were divided into groups that had the different combinations of: CD74 deficient mice vs control mice; a sham brain injury or a real brain injury; and the CAP treatment or a saline injection as a control.
To test the hypothesis that the immune system causes brain damage after a trauma, the scientists compared the lesion size in CD74 deficient mice, vs control strain after a real brain trauma, with the saline injection. They found that the control mice with a fully working immune system had larger lesions, which suggests that the immune system is part of the reason for brain cells breaking down after a trauma.
To test whether the CAP treatment reduced brain damage after trauma, they compared control mice with a real brain injury that were given the CAP treatment against similar mice that were given the saline control. The mice that received the CAP treatment had smaller brain lesions, suggesting that it did reduce the damage caused by brain trauma. They found these lesions were as small as those in the CD74 deficient mice, further supporting the hypothesis that the treatment was successful because it stops the immune system from attacking the brain.
INFORMATION:
Media Contact
Alanna Orpen
PR Assistant
BioMed Central
T: +44 (0)20 3192 2054
E: alanna.orpen@biomedcentral.com
Notes to Editor
1. Research
Traumatic brain injury causes selective, CD74-dependent, peripheral lymphocyte activation that exacerbates neurodegeneration
Richard P Tobin, Sanjib Mukherjee, Jessica M Kain, Susannah K Rogers, Stephanie K Henderson, Heather L Motal, M. Karen Newell Rogers and Lee A Shapiro
Acta Neuropathologica Communications 2: 143
During embargo, please contact Alanna Orpen (alanna.orpen@biomedcentral.com) for a copy of the paper.
After embargo, article available at journal website here:
http://www.actaneurocomms.org/content/2/1/143
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BioMed Central's open access policy.
2. Acta Neuropathologica Communications publishes experimental and descriptive articles on the pathology of nervous system and skeletal muscle disorders and on mechanisms of neurological disease using morphological, molecular and cell biology methods.
3. BioMed Central (http://www.biomedcentral.com/) is an STM (Science, Technology and Medicine) publisher which has pioneered the open access publishing model. All peer-reviewed research articles published by BioMed Central are made immediately and freely accessible online, and are licensed to allow redistribution and reuse. BioMed Central is part of Springer Science+Business Media, a leading global publisher in the STM sector.
Viagra could be used as a safe treatment for heart disease, finds new research published today in the open access journal BMC Medicine. The study reveals that long-term daily treatment of Viagra can provide protection for the heart at different stages of heart disease, with few side effects.
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) is the main ingredient in Viagra and other drugs commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction. The inhibitor blocks the enzyme PDE5, which prevents relaxation of smooth muscle tissue. The presence of PDE5 in the heart has led to previous research ...
The findings suggest that this disturbing trend could be due the emergence of more virulent group B streptococcal strains and call for a renewed evaluation of preventive strategies to reduce neonatal disease.
Passed from mother to child during birth, group B streptococcus is the most common cause of infection in newborns. Guidelines for the prevention of disease have been widely adopted in high-income countries. But despite these efforts, the bacterium remains a leading cause of blood stream infections and meningitis worldwide, typically affecting babies younger than ...
BETHESDA, MD – Breaking down complex conditions such as Type 2 Diabetes and obesity into the specific metabolic proteins and processes that underlie them offers a new approach to studying the genetics of these diseases and how they are interrelated, according to research presented today at the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) 2014 Annual Meeting in San Diego.
By studying specific proteins that contribute to such conditions – and the genes that encode them – scientists can develop new drugs that directly target the metabolic processes that do ...
Improving household electricity access in India over the last 30 years contributed only marginally to the nation's total carbon emissions growth during that time, according to a new study published in the journal Nature Climate Change.
"Energy access is fundamental to development: it brings improvements to all aspects of life, including education, communication, and health," says IIASA researcher Shonali Pachauri, who conducted the study.
While increased energy access is widely agreed to be an important goal for development efforts, such as the UN Sustainable Energy ...
VIDEO:
Michael Helmrath, M.D., M.S., surgical director of the Intestinal Rehabilitation Program at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, talks about researchers successfully growing human intestinal tissue in mice. The study describes...
Click here for more information.
CINCINNATI --Researchers have successfully transplanted "organoids" of functioning human intestinal tissue grown from pluripotent stem cells in a lab dish into mice – creating an unprecedented ...
DNA has garnered attention for its potential as a programmable material platform that could spawn entire new and revolutionary nanodevices in computer science, microscopy, biology, and more. Researchers have been working to master the ability to coax DNA molecules to self assemble into the precise shapes and sizes needed in order to fully realize these nanotechnology dreams.
For the last 20 years, scientists have tried to design large DNA crystals with precisely prescribed depth and complex features – a design quest just fulfilled by a team at Harvard's Wyss Institute ...
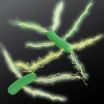
AMHERST, Mass. ¬– The claim by microbiologist Derek Lovley and colleagues at the University of Massachusetts Amherst that the microbe Geobacter produces tiny electrical wires, called microbial nanowires, has been mired in controversy for a decade, but the researchers say a new collaborative study provides stronger evidence than ever to support their claims.
UMass Amherst physicists working with Lovley and colleagues report in the current issue of Nature Nanotechnology that they've used a new imaging technique, electrostatic force microscopy (EFM), to resolve ...
Berlin, 19th October 2014 What's in a name? Doctors have found that the name of the drug you are prescribed significantly influences how the patient sees the treatment. Now in a significant shift, the world's major psychiatry organisations are proposing to completely change the terminology of the drugs used in mental disorders shifting it from symptom based (e.g. antidepressant, antipsychotic etc.) to pharmacologically based (e.g. focusing on pharmacological target (serotonin, dopamine etc.) and the relevant mode of action). This will mean that patient will no longer have ...
Scientists at The University of Manchester hope a major breakthrough could lead to more effective methods for detoxifying dangerous pollutants like PCBs and dioxins. The result is a culmination of 15 years of research and has been published in Nature. It details how certain organisms manage to lower the toxicity of pollutants.
The team at the Manchester Institute of Biotechnology were investigating how some natural organisms manage to lower the level of toxicity and shorten the life span of several notorious pollutants.
Professor David Leys explains the research: ...
Kansas City, MO - While megakaryocytes are best known for producing platelets that heal wounds, these "mega" cells found in bone marrow also play a critical role in regulating stem cells according to new research from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research. In fact, hematopoietic stem cells differentiate to generate megakaryocytes in bone marrow. The Stowers study is the first to show that hematopoietic stem cells (the parent cells) can be directly controlled by their own progeny (megakaryocytes).
The findings from the lab Stowers Investigator Linheng Li, Ph.D., described ...