(Press-News.org) MAYWOOD, Ill. (Date) – During the first 24 hours after a stroke, attention to detail --such as hospital bed positioning -- is critical to patient outcomes.
Most strokes are caused by blood clots that block blood flow to the brain. Sitting upright can harm the patient because it decreases blood flow and oxygen to the brain just when the brain needs more blood.
Thus, it's reasonable to keep patients lying flat or as nearly flat as possible, according to a report in the journal MedLink Neurology by Loyola University Medical Center neurologist Murray Flaster, MD, PhD and colleagues.
But strokes also can increase intracranial pressure (brain swelling) that can damage the brain. Sitting upright helps improve blood drainage and reduce intracranial pressure -- but at a cost of reduced blood flow to the brain.
"There are few data to guide decision making in this difficult situation," Flaster and colleagues write.
Further complicating stroke care, some patients have orthopnea (difficulty breathing while lying flat). In such patients, the head of the bed should be kept at the lowest elevation the patient can tolerate.
Finally, frequent changes in body position, regardless of head position, may help patients tolerate lying flat, while also minimizing the risk of bed sores, the Loyola neurologists write.
Bed position is among the complex issues that Flaster and colleagues address in their article, which summarizes the latest research on caring for ischemic stroke patients. (Most strokes are ischemic, meaning they are caused by blood clots.)
"The period immediately following an acute ischemic stroke is a time of significant risk," the Loyola neurologists write. "Meticulous attention to the care of the stroke patient during this time can prevent further neurologic injury and minimize common complications, optimizing the chance of functional recovery."
The authors discuss stroke-care issues that can affect outcomes. For example, there is considerable evidence of a link between hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and poor outcomes after stroke. The authors recommend strict blood sugar control, using frequent finger-stick glucose checks and aggressive insulin treatment, regardless of whether the patient has a known history of diabetes.
For each 1 degree C increase in the body temperature of a stroke patient, the risk of death or severe disability more than doubles. Therapeutic cooling has been shown to help cardiac arrest patients, and clinical trials are underway to determine whether such cooling could also help stroke patients. Until those trials are completed, the goal should be to keep normal temperatures (between 95.9 and 99.5 degrees F).
The authors discuss many other issues in stroke care, including blood pressure management; blood volume; statin therapy; management of complications such as pneumonia and sepsis; heart attack and other cardiac problems; blood clots; infection; malnutrition and aspiration; brain swelling; seizures; recurrent stroke; and brain hemorrhages.
Studies have shown that hospital units that specialize in stroke care decrease mortality, increase the likelihood of being discharged to home and improve functional status and quality of life.
INFORMATION:
Fifteen million people in the world have a stroke each year, and nearly six million people die. Every six seconds, someone dies from a stroke. The World Stroke Organization has designated Oct. 29 World Stroke Day to help spread public awareness of the world's high stroke risk and stroke prevalence
Flaster is a stroke specialist and an associate professor in the Department of Neurology of Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine. Co-authors are Sarkis Morales-Vidal, MD, Michael Schneck, MD, and Jose Biller, MD. Dr. Morales-Vidal is an assistant professor, Dr. Schneck is a professor and Dr. Biller is professor and chair in the Department of Neurology.
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Architecture imitates life, at least when it comes to those spiral ramps in multistory parking garages. Stacked and connecting parallel levels, the ramps are replications of helical structures found in a ubiquitous membrane structure in the cells of the body.
Dubbed Terasaki ramps after their discoverer, they reside in an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a network of membranes found throughout the cell and connected to and surrounding the cell nucleus. Now, a trio of scientists, including UC Santa Barbara biological physicist ...
The heart holds its own pool of immune cells capable of helping it heal after injury, according to new research in mice at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Most of the time when the heart is injured, these beneficial immune cells are supplanted by immune cells from the bone marrow, which are spurred to converge in the heart and cause inflammation that leads to further damage. In both cases, these immune cells are called macrophages, whether they reside in the heart or arrive from the bone marrow. Although they share a name, where they originate appears ...
BOSTON — Findings published in the Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation show that imperceptible vibratory stimulation applied to the soles of the feet improved balance by reducing postural sway and gait variability in elderly study participants. The vibratory stimulation is delivered by a urethane foam insole with embedded piezoelectric actuators, which generates the mechanical stimulation. The study was conducted by researchers from the Institute for Aging Research (IFAR) at Hebrew SeniorLife, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, the Wyss Institute for ...
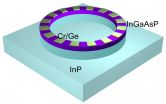
A significant breakthrough in laser technology has been reported by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley. Scientists led by Xiang Zhang, a physicist with joint appointments at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley, have developed a unique microring laser cavity that can produce single-mode lasing even from a conventional multi-mode laser cavity. This ability to provide single-mode lasing on demand holds ramifications for a wide range of applications including optical metrology and ...
Lab-grown tissues could one day provide new treatments for injuries and damage to the joints, including articular cartilage, tendons and ligaments.
Cartilage, for example, is a hard material that caps the ends of bones and allows joints to work smoothly. UC Davis biomedical engineers, exploring ways to toughen up engineered cartilage and keep natural tissues strong outside the body, report new developments this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"The problem with engineered tissue is that the mechanical properties are far from those ...
Washington, DC—The Endocrine Society today issued a Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) for the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly, a rare condition caused by excess growth hormone in the blood.
The CPG, entitled "Acromegaly: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline," appeared in the November 2014 issue of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM), a publication of the Endocrine Society.
Acromegaly is usually caused by a non-cancerous tumor in the pituitary gland. The tumor manufactures too much growth hormone and spurs the body to overproduce ...
Chicago, October 30, 2014—Analysis of data from an institutional patient registry on stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) indicates excellent long-term, local control, 79 percent of tumors, for medically inoperable, early stage lung cancer patients treated with SBRT from 2003 to 2012, according to research presented today at the 2014 Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology. The Symposium is sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), the International Association for the Study ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. – You have to be at least 2 years old to be covered by U.S. dietary guidelines. For younger babies, no official U.S. guidance exists other than the general recommendation by national and international organizations that mothers exclusively breastfeed for at least the first six months.
So what do American babies eat?
That's the question that motivated researchers at the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences to study the eating patterns of American infants at 6 months and 12 months old, critical ages for the development of ...
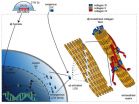
NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of the birth of the Eastern Pacific Ocean's twenty-first tropical depression, located far south of Acapulco, Mexico.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite gathered infrared data on newborn Tropical Depression 21E (TD 21E) and that data was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. At 1200 UTC (9 a.m. EDT), the GOES-West image showed that thunderstorms circled the low-level center and extended northeast of the center indicating that southwesterly wind shear was affecting ...
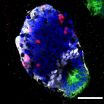
Professor Elly Tanaka and her research group at the DFG Research Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden - Cluster of Excellence at the TU Dresden (CRTD) demonstrated for the first time the in vitro growth of a piece of spinal cord in three dimensions from mouse embryonic stem cells. Correct spatial organization of motor neurons, interneurons and dorsal interneurons along the dorsal/ventral axis was observed.
This study has been published online by the American journal "Stem Cell Reports" on 30.10.2014.
For many years Elly Tanaka and her research group have been studying ...