(Press-News.org) A new study published in the journal Science says that the total impact of switching to natural gas depends heavily on leakage of methane (CH4) during the natural gas life cycle, and suggests that more can be done to reduce methane emissions and to improve measurement tools which help inform policy choices.
Published in the February 14 issue of Science, the study, "Methane Leaks from North American Natural Gas Systems," presents a first effort to systematically compare North American emissions estimates at scales ranging from device-level to continental atmospheric studies. Because natural gas emits less carbon dioxide during combustion than other fossil fuels, it has been looked to as a 'bridge' fuel to a lower carbon energy system.
"With this study and our larger body of work focusing on natural gas and our transforming energy economy, we offer policymakers and investors a solid analytical foundation for decision making," said Doug Arent, executive director of the Joint Institute for Strategic Energy Analysis (JISEA) and a co-author to the study. "While we found that official inventories tend to under-estimate total methane leakage, leakage rates are unlikely to be high enough to undermine the climate benefits of gas versus coal."
The article was organized by Novim with funding from the Cynthia and George Mitchell Foundation and led by Stanford University's Adam Brandt. It was co-written by researchers from Stanford University, JISEA, Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), University of Michigan, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, University of Calgary, U.S. State Department, Harvard University, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, University of California Santa Barbara, and the Environmental Defense Fund.
"Recent life cycle assessments generally agree that replacing coal with natural gas has climate benefits," said Garvin Heath, a senior scientist at the NREL and a lead author of the report. "Our findings show that natural gas can be a bridge to a sustainable energy future, but that bridge must be traversed carefully. Current evidence suggests leakages may be larger than official estimates, so diligence will be required to ensure that leakage rates are actually low enough to achieve sustainability goals."
Among other key findings of the research:
Official inventories of methane leakage consistently underestimate actual leakage.
Evidence at multiple scales suggests that the natural gas and oil sectors are important contributors.
Independent experiments suggest that a small number of "super-emitters" could be responsible for a large fraction of leakage.
Recent regional atmospheric studies with very high emissions rates are unlikely to be representative of typical natural gas system leakage rates.
Hydraulic fracturing is not likely to be a substantial emissions source, relative to current national totals.
Abandoned oil and gas wells appear to be a significant source of current emissions.
Emissions inventories can be improved in ways that make them a more essential tool for policymaking.
INFORMATION:
JISEA is operated by the Alliance for Sustainable Energy, LLC on behalf of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the University of Colorado – Boulder, the Colorado School of Mines, the Colorado State University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Stanford University.
Study on methane emissions from natural gas systems indicates new priorities
Study findings published in Policy Forum of journal Science
2014-02-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Baby hearts need rhythm to develop correctly
2014-02-18
NASHVILLE, Tenn. – To develop correctly, baby hearts need rhythm...even before they have blood to pump.
"We have discovered that mechanical forces are important when making baby hearts," said Mary Kathryn Sewell-Loftin, a Vanderbilt graduate student working with a team of Vanderbilt engineers, scientists and clinicians attempting to grow replacement heart valves from a patient's own cells.
In an article published last month in the journal Biomaterials the team reported that they have taken an important step toward this goal by determining that the mechanical forces ...
Nitrogen-tracking tools for better crops and less pollution
2014-02-18
Stanford, CA— As every gardner knows, nitrogen is crucial for a plant's growth. But nitrogen absorption is inefficient. This means that on the scale of food crops, adding significant levels of nitrogen to the soil through fertilizer presents a number of problems, particularly river and groundwater pollution. As a result, finding a way to improve nitrogen uptake in agricultural products could improve yields and decrease risks to environmental and human health. Nitrogen is primarily taken up from the soil by the roots and assimilated by the plant to become part of DNA, ...
Regenerating orthopedic tissues within the human body
2014-02-18
By combining a synthetic scaffolding material with gene delivery techniques, researchers at Duke University are getting closer to being able to generate replacement cartilage where it's needed in the body.
Performing tissue repair with stem cells typically requires applying copious amounts of growth factor proteins -- a task that is very expensive and becomes challenging once the developing material is implanted within a body. In a new study, however, Duke researchers found a way around this limitation by genetically altering the stem cells to make the necessary growth ...
Research of zebrafish neurons may lead to understanding of birth defects like spina bifida
2014-02-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The zebrafish, a tropical freshwater fish similar to a minnow and native to the southeastern Himalayan region, is well established as a key tool for researchers studying human diseases, including brain disorders. Using zebrafish, scientists can determine how individual neurons develop, mature and support basic functions like breathing, swallowing and jaw movement. Researchers at the University of Missouri say that learning about neuronal development and maturation in zebrafish could lead to a better understanding of birth defects such as spina bifida in ...
Prison-based education declined during economic downturn, study finds
2014-02-18
State-level spending on prison education programs declined sharply during the economic downturn, with the sharpest drop occurring in states that incarcerate the most prisoners, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Large states cut spending by an average of 10 percent between the 2009 and 2012 fiscal years, while medium-sized states cut spending by 20 percent, according to the study.
"There has been a dramatic contraction of the prison education system, particularly those programs focused on academic instruction versus vocational training," said Lois Davis, the ...
Miriam Hospital study shows social gaming site effective weight loss tool
2014-02-18
(PROVIDENCE, R.I.) -- Researchers from The Miriam Hospital have found that DietBet, a web-based commercial weight loss program that pairs financial incentives with social influence, delivers significant weight losses. The study and its findings have been published in the current issue of the open access publication JMIR Serious Games.
Tricia Leahey, Ph.D., lead researcher at The Miriam Hospital Weight Control and Diabetes Research Center, sought to examine weight losses associated with the social gaming website and contributing factors to gauge the success of such web-based ...
Rife with hype, exoplanet study needs patience and refinement
2014-02-18
Imagine someone spent months researching new cities to call home using low-resolution images of unidentified skylines. The pictures were taken from several miles away with a camera intended for portraits, and at sunset. From these fuzzy snapshots, that person claims to know the city's air quality, the appearance of its buildings, and how often it rains.
This technique is similar to how scientists often characterize the atmosphere — including the presence of water and oxygen — of planets outside of Earth's solar system, known as exoplanets, according to a review of exoplanet ...
Frequent flyers, bottle gourds crossed the ocean many times
2014-02-18
Bottle gourds traveled the Atlantic Ocean from Africa and were likely domesticated many times in various parts of the New World, according to a team of scientists who studied bottle gourd genetics to show they have an African, not Asian ancestry.
"Beginning in the 1950s we thought that bottle gourds floated across the ocean from Africa," said Logan Kistler, post-doctoral researcher in anthropology, Penn State. "However, a 2005 genetic study of gourds suggested an Asian origin."
Domesticated bottle gourds are ubiquitous around the world in tropical and temperate areas ...
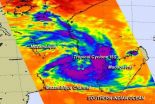
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone 15S form in the Mozambique Channel
2014-02-18
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone 15S as it formed in the Mozambique Channel on Feb. 18 and the AIRS instrument aboard gathered infrared data on its cloud top temperatures and potential.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical cyclone 15S on Feb. 18 at 10:53 a.m. EST. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument captured infrared data on the tropical system that showed the highest cloud tops and strongest thunderstorms were in a band that stretched from the east to the south of the center. Cloud top temperatures were near -63F/-52C, indicating ...
Agricultural productivity loss as a result of soil and crop damage from flooding
2014-02-18
URBANA, Ill. – The Cache River Basin, which once drained more than 614,100 acres across six southern Illinois counties, has changed substantively since the ancient Ohio River receded. The basin contains a slow-moving, meandering river; fertile soils and productive farmlands; deep sand and gravel deposits; sloughs and uplands; and one of the most unique and diverse natural habitats in Illinois and the nation.
According to a recent University of Illinois study, the region's agricultural lands dodged a bullet due to the timing of the great flood of April 2011 when the Ohio ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Study on methane emissions from natural gas systems indicates new prioritiesStudy findings published in Policy Forum of journal Science