(Press-News.org) Alexandria, VA – On a beautiful, clear June morning in 1954, a massive wave suddenly swept out of Lake Michigan killing at least seven people along the Chicago waterfront. At the time, the wave was attributed to a storm that had earlier passed over northern Lake Michigan, but how it came to swamp faraway Chicago, with no warning, was not understood.
The Great Lakes, along with the Mediterranean, Japan and many other parts of the world, have a long history of such waves, which have characteristics similar to tsunamis triggered by earthquakes or landslides.
Only recently, however, have scientists unraveled how a storm can create and propagate these far-traveling waves — called meteorological tsunamis or meteotsunamis. The waves, which arise out of a complex interplay of storm speed, wave dynamics and ocean-bottom bathymetry, may be less common than seismic tsunamis, but they can still be destructive and deadly.
EARTH Magazine talks to scientists trying to forecast meteotsunamis and develop a warning system for coastal residents, particularly along the U.S. East Coast, where in June 2013, a series of large waves swept into Barnegat Bay, New Jersey, knocking fishermen off jetties, and sending scuba divers over a breakwater, causing some injuries.
INFORMATION:
Read the full article at: http://bit.ly/1fC7QEK.
Buy the complete March 2014 issue, or subscribe to EARTH Magazine for breaking stories about geoscience in our society, including reflections on the 50th anniversary of the 1964 "Good Friday" earthquake in Alaska, a look back at the intriguing Comet ISON, and how scientists are using hillslopes to reveal a mountain's tectonic history at http://www.earthmagazine.org.
Keep up to date with the latest happenings in Earth, energy and environment news with EARTH Magazine online at http://www.earthmagazine.org/. Published by the American Geosciences Institute, EARTH is your source for the science behind the headlines.
The American Geosciences Institute is a nonprofit federation of 50 geoscientific and professional associations that represents more than 250,000 geologists, geophysicists and other earth scientists. Founded in 1948, AGI provides information services to geoscientists, serves as a voice of shared interests in the profession, plays a major role in strengthening geoscience education, and strives to increase public awareness of the vital role the geosciences play in society's use of resources, resiliency to natural hazards, and interaction with the environment.
EARTH Magazine: Tsunamis from the sky
2014-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cardiovascular Institute researcher: Cancer drug may lower sudden cardiac death risk
2014-02-24
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – A researcher at the Cardiovascular Institute (CVI) at Rhode Island, The Miriam and Newport hospitals has found that a new class of drugs, originally developed to treat cancer, reduces sudden cardiac death risk after a heart attack. The findings were published online in advance of print in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
"Currently, there are limited options to reduce sudden cardiac death following a heart attack," said principal investigator Samuel C. Dudley, M.D., Ph.D., chief of cardiology at the CVI. "The benefit of most drugs ...
Toxic injection with elastic band
2014-02-24
This news release is available in German.
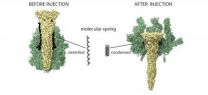
Bacteria have developed many different ways of smuggling their toxic cargo into cells. Tripartite Tc toxin complexes, which are used by bacteria like the plague pathogen Yersinia pestis and the insect pathogen Photorhabdus luminescens, are particularly unusual. Stefan Raunser from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology in Dortmund and his colleagues from the University of Freiburg have produced extremely accurate and detailed images of these "toxic injections"; they reveal from where the molecule complexes take ...
Precursor of multiple myeloma more common in blacks than whites, Mayo study finds
2014-02-24
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Feb. 24, 2014 — Blacks may be twice as likely as whites to develop multiple myeloma because they are more likely to have a precursor condition known as monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), a Mayo Clinic study has found. Not only is MGUS more common in blacks, but the type seen in the black population is also more apt to have features associated with a higher risk of progression to full-blown multiple myeloma, a cancer of a type of white blood cell in bone marrow.
The findings, which appear in the journal Leukemia, are from the ...
Higher risks among perinatal women with bipolar disorder
2014-02-24
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Pregnant and postpartum women with bipolar disorder more frequently have significant mental health and early mothering challenges than other perinatal women undergoing psychiatric treatment, according to a study in the Journal of Affective Disorders. The findings indicate the importance of properly identifying the disorder and developing specific treatments for women during and after pregnancy, the lead author said.
"Similar to what you find with bipolar disorder in the nonperinatal population, the overall level of clinical severity ...
In the eye of a chicken, a new state of matter comes into view
2014-02-24
Along with eggs, soup and rubber toys, the list of the chicken's most lasting legacies may eventually include advanced materials such as self-organizing colloids, or optics that can transmit light with the efficiency of a crystal and the flexibility of a liquid.
The unusual arrangement of cells in a chicken's eye constitutes the first known biological occurrence of a potentially new state of matter known as "disordered hyperuniformity," according to researchers from Princeton University and Washington University in St. Louis. Research in the past decade has shown that ...
Watching how the brain works
2014-02-24
Coral Gables, Fla (Feb. 19, 2014) -- There are more than a trillion cells called neurons that form a labyrinth of connections in our brains. Each of these neurons contains millions of proteins that perform different functions. Exactly how individual proteins interact to form the complex networks of the brain still remains as a mystery that is just beginning to unravel.
For the first time, a group of scientists has been able to observe intact interactions between proteins, directly in the brain of a live animal. The new live imaging approach was developed by a team of ...
Costs vary widely for care of children with congenital heart defects across US hospitals
2014-02-24
Ann Arbor, Mich. – Costs of care differ significantly across hospitals for children born with heart defects, according to new research led by a University of Michigan researcher. Congenital heart defects are known to be the most common birth defects, impacting nearly 1 in every 100 births.
The cost of care for children with congenital heart disease undergoing surgical repair varied as much as nine times across a large group of U.S. children's hospitals, says lead author Sara K. Pasquali, M.D., M.H.S., associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Michigan Medical ...
Opioid abuse initiates specific protein interactions in neurons in brain's reward system
2014-02-24
(New York) – Identifying the specific pathways that promote opioid addiction, pain relief, and tolerance are crucial for developing more effective and less dangerous analgesics, as well as developing new treatments for addiction. Now, new research from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai reveals that opiate use alters the activity of a specific protein needed for the normal functioning of the brain's reward center. Investigators were able to block the protein, as well as increase its expression in the mouse nucleus accumbens, a key component of the brain's reward ...
Abdominal fat accumulation prevented by unsaturated fat
2014-02-24
New research from Uppsala University shows that saturated fat builds more fat and less muscle than polyunsaturated fat. This is the first study on humans to show that the fat composition of food not only influences cholesterol levels in the blood and the risk of cardiovascular disease but also determines where the fat will be stored in the body. The findings have recently been published in the American journal Diabetes.
The study involved 39 young adult men and women of normal weight, who ate 750 extra calories per day for seven weeks. The goal was for them to gain three ...
Medical researchers use light to quickly and easily measure blood's clotting properties
2014-02-24
VIDEO:
This video shows the rapid "twinkling " or intensity fluctuations of the speckle pattern in a drop of unclotted whole blood. The rapid "twinkling " is due to the fast thermally-driven motion...
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, Feb. 24—Defective blood coagulation is one of the leading causes of preventable death in patients who have suffered trauma or undergone surgery. The body's natural defense against severe blood loss is the clotting ...