(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES – Based on a survey of parents of children with congenital heart disease, physicians delivering the diagnosis need to do a better job of showing compassion, ensuring parents understand all their options and providing easily understandable information, according to a new study published in the February edition of the journal, Pediatric Cardiology.
Researchers at Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute (LA BioMed) worked with the California Heart Connection, a nonprofit organization of parents of children with congenital heart disease, to conduct an online survey of 841 parents of children who were either diagnosed before birth or shortly afterward with congenital heart disease. The researchers said physicians remain the primary source of information for parents at diagnosis. So they analyzed the survey's findings to offer suggestions for how physicians and other health care providers can most effectively tell parents their child has a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition.
"Parents confronted with a diagnosis of congenital heart disease face very difficult choices – from selecting a treatment to determining whether to continue a pregnancy, if they receive the diagnosis prenatally," said Ruey-Kang Chang, MD, an LA BioMed researcher and the corresponding author of the study. "All of these decisions depend on the information they are given at the time of diagnosis and how well they can understand and retain the information at such a difficult time."
Upon learning of their children's diagnosis, most of the parents surveyed said they received no information on support groups, Internet resources or success rates at other hospitals. Two-thirds of the parents were told their children's heart conditions were "rare." More than half of them believed that meant fewer than one in a million infants had the condition or there were few people alive with the defect. In reality, congenital heart disease occurs in about eight in 1,000 births in the United States, with approximately one-third of those cases requiring invasive treatment during the first year of life.
Of those surveyed, 13% reported feeling pressured to terminate the pregnancy by their pediatric cardiologist, and 15% felt their physician showed a lack of compassion. More than a fourth of the respondents said they sought a second opinion, and 71% of them chose the second physician for long-term follow-up care. The two most commonly cited stress factors were "uncertainty" about their child's future (87%) and "not knowing about survivors with this defect" (52%).
In the United Kingdom, parents have access to a database of information about the number of procedures and mortality rates among children with congenital heart disease. In the U.S., Dr. Chang said no such database is available to the public so physicians continue to be a vital source of information.
"The information parents receive at diagnosis and the manner in which it is conveyed often determines their assessment of their children's chances for survival and may shape the parents' decisions," said Dr. Chang. "To ensure the parents have the information they need to make these critical decisions about their children's health, physicians should provide context for the parents, including information on success rates at different hospitals, Internet resources and referrals to support networks. Physicians should also be aware of how their demeanor and the words they use will be interpreted by the parents."
Debra Hilton-Kamm of the California Heart Connection, and Mark Sklansky, MD, of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, co-authored the study. The 82-question survey was distributed to online support groups for parents of children with congenital heart disease. A total of 1,001 responses were received and 160 were excluded because they were incomplete or didn't meet the study's criteria.
INFORMATION:
About LA BioMed
Founded in 1952, LA BioMed is one of the country's leading nonprofit independent biomedical research institutes. It has approximately 100 principal researchers conducting studies into improved treatments and cures for cancer, inherited diseases, infectious diseases, illnesses caused by environmental factors and more. It also educates young scientists and provides community services, including prenatal counseling and childhood nutrition programs. LA BioMed is academically affiliated with the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and located on the campus of Harbor-UCLA Medical Center. For more information, please visit http://www.LABioMed.org
Parents receiving heart disease diagnosis for infants need better information
LA BioMed survey finds more compassion and resources required to help guide treatment choices
2014-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tension triggers muscle building
2014-03-14
In order to move the body, skeletal muscles are pulling on the skeleton. For efficient muscle and skeletal movements it is essential that the muscle contracts only along a defined axis, for instance for the leg movement along the thigh. Such a directed contraction is achieved by the myofibrils that span through the entire length of the muscle. At both ends, the myofibrils are anchored to the tendon cells, which themselves are linked to the skeleton. "Thereby, the entire force is transduced from the muscle to the skeleton," Frank Schnorrer describes. How can the regular ...
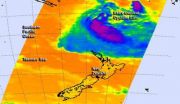
NASA sees an extra-tropical Lusi north of New Zealand
2014-03-14
NASA's Aqua satellite caught an infrared picture of Tropical Cyclone Lusi after it transitioned into an extra-tropical storm, north of New Zealand. Gale Warnings are in effect in Northern New Zealand.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Lusi on March 13 at 13:41 UTC/9:41 a.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument captured infrared data on the storm that revealed it had become a cold-core system. When a storm becomes extra-tropical and its core changes from warm to cold, the strongest winds spread out and the storm expands.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center ...
Salad at concession stands!?
2014-03-14
Pep-rallies, the marching band, cheers and chants, and savory, indulgent foods sold at the concession stand are all beloved features of the American high school sports tradition.
In contrast to the nutrition requirements on breakfast and lunches sold in school cafeterias, foods sold at concession stands do not follow the standard nutrition guidelines because they are typically sold for fundraising purposes. Is there something that can be done to improve the healthful features of concession stand food, and preserve the profits they generate? According to this new study ...
Older age at onset of Type 1 diabetes associated with lower brain connectivity
2014-03-14
SAN FRANCISCO, March 14, 2014 – Children and adolescents older than age 8 at the onset of type 1 diabetes had weaker brain connectivity when tested later in life relative to those who had earlier ages of diagnosis, University of Pittsburgh Schools of the Health Sciences researchers discovered.
The findings, presented today at the American Psychosomatic Society's annual meeting, were made by analyzing the brain scans of 44 middle-age adults diagnosed with type 1 diabetes as children.
"Adolescence is a time when the brain matures and makes connections in networks responsible ...
Study: Losing or gaining weight after joint replacement affects how well patients do
2014-03-14
While many overweight patients have the best intentions to lose weight after joint replacement, a study at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) finds that although some are able to achieve this goal, equal numbers of patients actually gain weight after hip or knee replacement. Researchers also determined that patients who lose weight do better in terms of function and activity level two years down the road.
"Our findings represent the first report to present evidence that weight loss is associated with improved clinical outcomes, while weight gain is associated with inferior ...
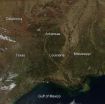
Southeastern fires consist of prescribed and wild
2014-03-14
According to the Southern Area Coordination Center, which monitors and coordinates response to incidents throughout the Southeast, there are currently seven large fires burning in this area of the country. Six of them are located in the state of Oklahoma and the seventh is in the Gulf area of Louisiana. These fires currently have burned over 7,600 acres. The majority of the fires on this image, though, are not wildfires, but are prescribed fires. The Chicasaw Journal of Mississippi wrote this regarding prescribed fires: "Prescribed fire, also known as controlled burning, ...
Researchers find significant increase in painkillers prescribed to US adults in the ER
2014-03-14
WASHINGTON (March 14, 2014) —George Washington University (GW) researchers report dramatic increases in prescriptions of opioid analgesics, such as Percocet, Vicodin, oxycodone and Dilaudid, during U.S. emergency department visits from 2001 to 2010. These findings were not explained by higher visit rates for painful conditions, which only increased modestly during the time period. This report was published today in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine.
"This trend is especially concerning given dramatic increases in opioid-related overdoses and fatalities in recent ...
In the lab, scientists coax E. coli to resist radiation damage
2014-03-14
MADISON, Wis. – Capitalizing on the ability of an organism to evolve in response to punishment from a hostile environment, scientists have coaxed the model bacterium Escherichia coli to dramatically resist ionizing radiation and, in the process, reveal the genetic mechanisms that make the feat possible.
The study, published in the online journal eLife, provides evidence that just a handful of genetic mutations give E. coli the capacity to withstand doses of radiation that would otherwise doom the microbe. The findings are important because they have implications for better ...
Researchers find high acceptability of 3-colored raspberry jelly
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—Raspberries are among the most popular berries in the world and are high in antioxidants that offer significant health benefits to consumers. The red raspberry is most commonly used in processed products like juices, jams, jellies and preserves because of its short shelf life. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), found that the production of a mixed raspberry jelly with black and yellow raspberries could be a good alternative to just one-colored jelly.
Black raspberries, which produce clusters of ...
Gluten-free crackers made with hemp flour and decaffeinated green tea leaves
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—The market for gluten-free foods with functional properties is growing immensely across virtually all food categories on a global level. The need to replace wheat proteins, fibers, and minerals is very important in order to provide a better selection and more nutritious food for consumers that belong to this segment of the population. At the same time, the use of by-products of the food processing industry as a source of functional ingredients such as antioxidants, phenols, fibers and proteins is on the rise, which supports global sustainability.
A team of food ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Parents receiving heart disease diagnosis for infants need better informationLA BioMed survey finds more compassion and resources required to help guide treatment choices