(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
On March 14, 2014, at 1 a.m. EDT this simulated 3-D flyby of the TRMM satellite showed rain falling at the rate of over 116 mm/4.5 inches per hour (red),...
Click here for more information.
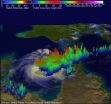
Heavy rainfall rates and powerful towering thunderstorms were spotted in what appeared to be the rebirth process of Tropical Cyclone Gillian in the Gulf of Carpentaria between Australia's Northern Territory and Queensland.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite called TRMM flew above northern Australia on March 14, 2014 at 0500 UTC/1 a.m. EDT capturing rainfall data. Very strong convective storms in this area are the remnants of tropical cyclone Gillian and may signal a rebirth. TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) instrument found rain falling at the rate of over 116 mm/4.5 inches per hour in these powerful storms in the northeastern Gulf of Carpentaria.
TRMM PR data were also used to create a 3-D view of the strong convective storms in the northern Gulf of Carpentaria. Some towering convective storms were found to be very energetic. Several tall storms were shown to reach altitudes greater than 16.75 km/10.4 miles. Some heavy rain within these storms returned reflectivity values greater than 52dBZ to the satellite. TRMM is a joint satellite mission of NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
Animated multispectral satellite imagery today, March 16, showed a system that has become more symmetric. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted on March 14 at 01:40 UTC, that a composite radar loop from Weipa showed formative bands of thunderstorms had begun to spiral into a low level circulation center that has become better defined.
Computer models indicate that Ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian will re-intensify to at least 35 knots/40 mph/62 kph over the next 24 to 36 hours. Maximum sustained surface winds are estimated at 25 to 30 knots/ 28.7 to 34.5 mph/46.3 to 55.5 kph. Minimum sea level pressure is estimated to be near 1001 millibars.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology has posted a warning and a watch for Ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian. A Cyclone Warning continues for coastal and island communities from Elcho Island to Numbulwar, including Alyangula and Nhulunbuy. A Cyclone Watch continues for coastal areas from Croker Island to Elcho Island.
The warning stated that Gillian is expected to approach the coast near Nhulunbuy early Sunday (March 16) morning then continue heading west near the northern coast of the Top End.
Residents between Numbulwar and Nhulunbuy, including Alyangula can expect gusty winds today, March 14, and those conditions will spread west on March 16. In addition to the winds, heavy rainfall, higher than normal tides and large waves will accompany Gillian as it moves west.
The Australian Bureau of Meteorology expects Gillian's remnants to meander in the Gulf of Carpentaria for the next day before setting course to the northwest and moving past Nhulumbuy and Elcho Island, Northern Territory on March 16 and 17. For updated watches and warnings, visit: http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone.
INFORMATION:
NASA's TRMM satellite eyeing Tropical Cyclone Gillian's rebirth
2014-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Parents receiving heart disease diagnosis for infants need better information
2014-03-14
LOS ANGELES – Based on a survey of parents of children with congenital heart disease, physicians delivering the diagnosis need to do a better job of showing compassion, ensuring parents understand all their options and providing easily understandable information, according to a new study published in the February edition of the journal, Pediatric Cardiology.
Researchers at Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute (LA BioMed) worked with the California Heart Connection, a nonprofit organization of parents of children with congenital heart disease, to conduct an online ...
Tension triggers muscle building
2014-03-14
In order to move the body, skeletal muscles are pulling on the skeleton. For efficient muscle and skeletal movements it is essential that the muscle contracts only along a defined axis, for instance for the leg movement along the thigh. Such a directed contraction is achieved by the myofibrils that span through the entire length of the muscle. At both ends, the myofibrils are anchored to the tendon cells, which themselves are linked to the skeleton. "Thereby, the entire force is transduced from the muscle to the skeleton," Frank Schnorrer describes. How can the regular ...
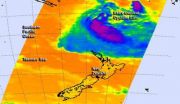
NASA sees an extra-tropical Lusi north of New Zealand
2014-03-14
NASA's Aqua satellite caught an infrared picture of Tropical Cyclone Lusi after it transitioned into an extra-tropical storm, north of New Zealand. Gale Warnings are in effect in Northern New Zealand.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Lusi on March 13 at 13:41 UTC/9:41 a.m. EDT and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument captured infrared data on the storm that revealed it had become a cold-core system. When a storm becomes extra-tropical and its core changes from warm to cold, the strongest winds spread out and the storm expands.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center ...
Salad at concession stands!?
2014-03-14
Pep-rallies, the marching band, cheers and chants, and savory, indulgent foods sold at the concession stand are all beloved features of the American high school sports tradition.
In contrast to the nutrition requirements on breakfast and lunches sold in school cafeterias, foods sold at concession stands do not follow the standard nutrition guidelines because they are typically sold for fundraising purposes. Is there something that can be done to improve the healthful features of concession stand food, and preserve the profits they generate? According to this new study ...
Older age at onset of Type 1 diabetes associated with lower brain connectivity
2014-03-14
SAN FRANCISCO, March 14, 2014 – Children and adolescents older than age 8 at the onset of type 1 diabetes had weaker brain connectivity when tested later in life relative to those who had earlier ages of diagnosis, University of Pittsburgh Schools of the Health Sciences researchers discovered.
The findings, presented today at the American Psychosomatic Society's annual meeting, were made by analyzing the brain scans of 44 middle-age adults diagnosed with type 1 diabetes as children.
"Adolescence is a time when the brain matures and makes connections in networks responsible ...
Study: Losing or gaining weight after joint replacement affects how well patients do
2014-03-14
While many overweight patients have the best intentions to lose weight after joint replacement, a study at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) finds that although some are able to achieve this goal, equal numbers of patients actually gain weight after hip or knee replacement. Researchers also determined that patients who lose weight do better in terms of function and activity level two years down the road.
"Our findings represent the first report to present evidence that weight loss is associated with improved clinical outcomes, while weight gain is associated with inferior ...
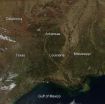
Southeastern fires consist of prescribed and wild
2014-03-14
According to the Southern Area Coordination Center, which monitors and coordinates response to incidents throughout the Southeast, there are currently seven large fires burning in this area of the country. Six of them are located in the state of Oklahoma and the seventh is in the Gulf area of Louisiana. These fires currently have burned over 7,600 acres. The majority of the fires on this image, though, are not wildfires, but are prescribed fires. The Chicasaw Journal of Mississippi wrote this regarding prescribed fires: "Prescribed fire, also known as controlled burning, ...
Researchers find significant increase in painkillers prescribed to US adults in the ER
2014-03-14
WASHINGTON (March 14, 2014) —George Washington University (GW) researchers report dramatic increases in prescriptions of opioid analgesics, such as Percocet, Vicodin, oxycodone and Dilaudid, during U.S. emergency department visits from 2001 to 2010. These findings were not explained by higher visit rates for painful conditions, which only increased modestly during the time period. This report was published today in the journal Academic Emergency Medicine.
"This trend is especially concerning given dramatic increases in opioid-related overdoses and fatalities in recent ...
In the lab, scientists coax E. coli to resist radiation damage
2014-03-14
MADISON, Wis. – Capitalizing on the ability of an organism to evolve in response to punishment from a hostile environment, scientists have coaxed the model bacterium Escherichia coli to dramatically resist ionizing radiation and, in the process, reveal the genetic mechanisms that make the feat possible.
The study, published in the online journal eLife, provides evidence that just a handful of genetic mutations give E. coli the capacity to withstand doses of radiation that would otherwise doom the microbe. The findings are important because they have implications for better ...
Researchers find high acceptability of 3-colored raspberry jelly
2014-03-14
CHICAGO—Raspberries are among the most popular berries in the world and are high in antioxidants that offer significant health benefits to consumers. The red raspberry is most commonly used in processed products like juices, jams, jellies and preserves because of its short shelf life. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), found that the production of a mixed raspberry jelly with black and yellow raspberries could be a good alternative to just one-colored jelly.
Black raspberries, which produce clusters of ...