(Press-News.org) CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Most of the parents included in a new study reported some infant feeding and activity behaviors that are believed to increase a child's risk for obesity later in life.
The study found that many of these "obesogenic" behaviors were highly prevalent among all of the parents, regardless of their race or ethnicity. Black parents were more likely to put children to bed with a bottle and report TV watching, while Hispanic parents were more likely to encourage children to finish feeding and to report less "tummy time" – when a baby lays on her belly to play while a parent supervises.
"These results from a large population of infants — especially the high rates of television watching — teach us that we must begin obesity prevention even earlier, " said Eliana M. Perrin, MD, MPH, lead author of the study, associate professor of pediatrics in the University of North Carolina School of Medicine and UNC-Chapel Hill's associate vice chancellor for research. The study will be published in the April 2014 issue of the journal Pediatrics.
The study included a large, diverse sample of 863 low-income parents participating in Greenlight, an obesity prevention trial taking place at four medical centers: UNC, New York University, Vanderbilt University and the University of Miami. Fifty percent of the parents were Hispanic, 27 percent were black and 18 percent were white. Most of the parents in the sample (86 percent) were on Medicaid.
Among all of the parents, behaviors that are thought related to later obesity were highly prevalent. Exclusive formula feeding was more than twice as common (45 percent) as exclusive breastfeeding (19 percent). Twelve percent had already introduced solid food, 43 percent put infants to bed with bottles, 23 percent propped bottles instead of holding the bottle by hand (which can result in overfeeding), 20 percent always fed when the infant cried, and 38 percent always tried to get their children to finish their milk.
In addition, 90 percent of the infants were exposed to television and 50 percent actively watched TV (meaning parents put their children in front of the television in order to watch).
"What this study taught us is that we can do better. While we don't know the exact causes of obesity, families of all races and ethnicities need early counseling to lead healthier lives. That counseling should be culturally-tailored, and we are hoping our research sheds light on the best ways to do that," said Dr. Perrin, who is a practicing pediatrician.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the study are Russell L. Rothman, MD, MPP; Lee M. Sanders, MD, MPH; Asheley C. Skinner, PhD; Svetlana K. Eden, MS; Ayumi Shintani, PhD, MPH; Elizabeth M. Throop, BA; and H. Shonna Yin, MD, MS.
Many parents have infant-feeding, TV, and activity practices which may increase obesity risk
2014-03-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Colon cancer incidence rates decreasing steeply in older Americans
2014-03-17
WASHINGTON, D.C. – March 17, 2014–Colon cancer incidence rates have dropped 30 percent in the U.S. in the last 10 years among adults 50 and older due to the widespread uptake of colonoscopy, with the largest decrease in people over age 65. Colonoscopy use has almost tripled among adults ages 50 to 75, from 19 percent in 2000 to 55 percent in 2010.
The findings come from Colorectal Cancer Statistics, 2014, published in the March/April issue of CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. The article and its companion report, Colorectal Cancer Facts & Figures, were released today ...
Study identifies most common, costly reasons for mental health hospitalizations for kids
2014-03-17
Nearly one in 10 children are hospitalized with a primary diagnosis of a mental health condition, and depression alone accounts for $1.33 billion in hospital charges annually, according to a new analysis led by UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital.
The study is the first to examine frequency and costs associated with specific inpatient mental health diagnoses for children, and is a step towards creating meaningful measures of the quality of pediatric hospital care.
"This is the first paper to give a clear picture of the mental health reasons kids are admitted to hospitals ...
Major 'third-hand smoke' compound causes DNA damage -- and potentially cancer
2014-03-17
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — Leftover cigarette smoke that clings to walls and furniture is a smelly nuisance, but now research suggests that it could pose a far more serious threat, especially to young children who put toys and other smoke-affected items into their mouths. Scientists reported today that one compound from this "third-hand smoke," which forms when second-hand smoke reacts with indoor air, damages DNA and sticks to it in a way that could potentially cause cancer.
Their talk was one of more than 10,000 presentations at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition ...
Three-quarters of people with seasonal and pandemic flu have no symptoms
2014-03-17
Around 1 in 5 of the population were infected in both recent outbreaks of seasonal flu and the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic, but just 23% of these infections caused symptoms, and only 17% of people were ill enough to consult their doctor.
These findings come from a major new community-based study comparing the burden and severity of seasonal and pandemic influenza in England over 5 years, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal.
"Reported cases of influenza represent the tip of a large clinical and subclinical iceberg that is mainly invisible to national ...
Potentially safer, greener alternative to BPA could come from papermaking waste
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — A waste product from making paper could yield a safer, greener alternative to the potentially harmful chemical BPA, now banned from baby bottles but still used in many plastics. Scientists made the BPA alternative from lignin, the compound that gives wood its
strength, and they say it could be ready for the market within five years.
They described the research here today in one of the more than 10,000 presentations at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society, taking ...
High-tech materials purify water with sunlight
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — Sunlight plus a common titanium pigment might be the secret recipe for ridding pharmaceuticals, pesticides and other potentially harmful pollutants from drinking water. Scientists combined several high-tech components to make an easy-to-use water purifier that could
work with the world's most basic form of energy, sunlight, in a boon for water purification in rural areas or developing countries.
The talk was one of more than 10,000 presentations at the 247th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest ...
Better-tasting reduced-fat desserts, dressings, sauces: Coming soon?
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — Adjusting the calcium level and acidity could be the key to developing new better-tasting, more eye-appealing and creamier reduced-fat sauces, desserts and salad dressings that could be on the market soon, researchers reported here today.
To date, a major problem with removing fat from these accompaniments is that in addition to reducing calories, it can negatively affect the flavor, appearance and texture, they said. But based on recent research it may not be too long before new, improved, lower-fat foods appear in grocery stores, the researchers ...
Tequila plant is possible sweetener for diabetics -- helps reduce blood sugar, weight
2014-03-16
DALLAS, March 16, 2014 — A sweetener created from the plant used to make tequila could lower blood glucose levels for the 26 million Americans and others worldwide who have type 2 diabetes and help them and the obese lose weight, researchers said here today.
The main reason it could be valuable, they explained, is that agavins, a natural form of sugar found in the agave plant, are non-digestible and can act as a dietary fiber, so they would not raise blood glucose. Their report was part of the 247th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's ...
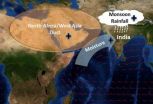
The rush to rain
2014-03-16
RICHLAND, Wash. -- A new analysis of satellite data reveals a link between dust in North Africa and West Asia and stronger monsoons in India. The study shows that dust in the air absorbs sunlight west of India, warming the air and strengthening the winds carrying moisture eastward. This results in more monsoon rainfall about a week later in India. The results explain one way that dust can affect the climate, filling in previously unknown details about the Earth system.
The study also shows that natural airborne particles can influence rainfall in unexpected ways, with ...
Researchers: Northeast Greenland ice loss accelerating
2014-03-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio—An international team of scientists has discovered that the last remaining stable portion of the Greenland ice sheet is stable no more.
The finding, which will likely boost estimates of expected global sea level rise in the future, appears in the March 16 issue of the journal Nature Climate Change [DOI:10.1038/NCLIMATE2161].
The new result focuses on ice loss due to a major retreat of an outlet glacier connected to a long "river" of ice - known as an ice stream - that drains ice from the interior of the ice sheet. The Zachariae ice stream retreated about ...