(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
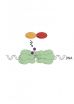
This is an animation of a recording from a trial with two male bats competing for prey. Red and blue each represent a bat (red = GR41 and blue =...
Click here for more information.
As big brown bats wake up from their winter slumber and start zooming around in pursuit of insects to eat, how do they coordinate their activities in the dark of night? For one thing, according to researchers who report their findings on March 27 in the Cell Press journal Current Biology, males do it by telling other males to back off. In so doing, those vocal males—each with their own distinctive calls—increase their chances of a meal.
The study is the first to describe the bats' ultrasonic food-claiming calls as distinct from those the animals use to locate their bug prey.
"Despite decades of study, many things about common bat behaviors such as foraging remain mysterious," says Genevieve Wright of the University of Maryland. "We were able to study a social call that is likely occurring thousands of times a night all over North America during the summer months, yet had not been described or studied before now."
Wright and her colleagues first got curious after examining audio recordings from two bats flying and foraging together. They noticed calls that seemed to differ from typical echolocation calls.
To find out more, the researchers let male and female big brown bats fly alone and in pairs while tempting them with tethered mealworms. Careful analysis of video and audio recordings of the bats' flight paths and calls, respectively, revealed sequences of three to four calls, both longer in duration and lower in frequency than the big brown bats' echolocation pulses. For reasons that the researchers can't entirely explain yet, only males make those calls.
The males who emitted those calls were more likely to attack the mealworm while the other male moved farther away. Almost always—96% of the time, to be exact—the researchers could trace calls back to the specific male that made them, based on the calls' unique features.
Wright says she doesn't really know why only males make the foraging calls. Females do have to eat, but they may more often forage near related individuals in comparison to males. Some male bats also make mating calls that are similar in some respects to the newly described foraging calls, suggesting that they may have carried them over from use in one context to another. Whatever the answer, the findings are a reminder of the impressive social lives of bats as they go about their fast-paced, night lives.
"Male big brown bats use individually distinct social calls to repel other bats and increase their own chances of getting a meal," Wright says.
"Acoustic communication in bats may be more sophisticated than was previously understood."
INFORMATION:
Current Biology, Wright et al.: "Social Calls Predict Foraging Success in Big Brown Bats."
Big brown bat males call 'dibs' on food
2014-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The multiplication of cells under close observation
2014-03-27
Our cells must grow and divide optimally to ensure that our bodies functions properly. It is essential, however, that these processes are carefully controlled in order to prevent unrestrained proliferation that can lead to the formation of tumours. David Shore, a professor at the Faculty of Sciences, University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, and his team have uncovered a cellular factor that regulates the timing of DNA replication. This molecule, called Rif1, ensures that only a fraction of the origins of DNA replication is activated at specified times of the cell cycle. ...
Scientists find potential target for treating mitochondrial disorders
2014-03-27
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (March 27, 2014) – Mitochondria, long known as "cellular power plants" for their generation of the key energy source adenosine triphosphate (ATP), are essential for proper cellular functions. Mitochondrial defects are often observed in a variety of diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease, and are the hallmarks of a number of genetic mitochondrial disorders whose manifestations range from muscle weakness to organ failure. Despite a fairly strong understanding of the pathology of such genetic mitochondrial disorders, efforts ...
In mapping feat, Scripps Florida scientists pinpoint neurons where select memories grow
2014-03-27
JUPITER, FL – March 27, 2014 – Memories are difficult to produce, often fragile, and dependent on any number of factors—including changes to various types of nerves. In the common fruit fly—a scientific doppelganger used to study human memory formation—these changes take place in multiple parts of the insect brain.
Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have been able to pinpoint a handful of neurons where certain types of memory formation occur, a mapping feat that one day could help scientists predict disease-damaged neurons in humans ...
Foraging bats can warn each other away from their dinners
2014-03-27
VIDEO:
In this animated graphic of bats' calls in flight, two bats are represented by different colors, red and blue. The bats' movements and vocalizations have been slowed by a factor...
Click here for more information.
Look into the spring sky at dusk and you may see flitting groups of bats, gobbling up insect meals in an intricately choreographed aerial dance. It's well known that echolocation calls keep the bats from hitting trees and each other. But now scientists have learned ...
Researchers at IRB discover a key regulator of colon cancer
2014-03-27
Barcelona, Thursday 27 March 2014.- A team headed by Angel R. Nebreda at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB) identifies a dual role of the p38 protein in colon cancer. The study demonstrates that, on the one hand, p38 is important for the optimal maintenance of the epithelial barrier that protects the intestine against toxic agents, thus contributing to decreased tumour development. Intriguingly, on the other hand, once a tumour has formed, p38 is required for the survival and proliferation of colon cancer cells, thus favouring tumour growth. The study is published ...
Researchers: Biomarkers predict effectiveness of radiation treatments for cancer
2014-03-27
An international team of researchers, led by Beaumont Health System's Jan Akervall, M.D., Ph.D., looked at biomarkers to determine the effectiveness of radiation treatments for patients with squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. They identified two markers that were good at predicting a patient's resistance to radiation therapy. Their findings were published in the February issue of the European Journal of Cancer.
Explains Dr. Akervall, co-director, Head and Neck Cancer Multidisciplinary Clinic, Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak, and clinical director of Beaumont's BioBank, ...
Cancer researchers find key protein link
2014-03-27
HOUSTON – (March 27, 2014) – A new understanding of proteins at the nexus of a cell's decision to survive or die has implications for researchers who study cancer and age-related diseases, according to biophysicists at the Rice University-based Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP).
Experiments and computer analysis of two key proteins revealed a previously unknown binding interface that could be addressed by medication. Results of the research appear this week in an open-source paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The proteins ...
Sleep may stop chronic pain sufferers from becoming 'zombies'
2014-03-27
Chronic pain sufferers could be kept physically active by improving the quality of their sleep, new research suggests.
The study by the University of Warwick's Department of Psychology, published in PLoS One, found that sleep was a worthy target for treating chronic pain and not only as an answer to pain-related insomnia.
"Engaging in physical activity is a key treatment process in pain management. Very often, clinicians would prescribe exercise classes, physiotherapy, walking and cycling programmes as part of the treatment, but who would like to engage in these activities ...
First sightings of solar flare phenomena confirm 3-D models of space weather
2014-03-27
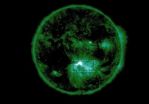
Scientists have for the first time witnessed the mechanism behind explosive energy releases in the Sun's atmosphere, confirming new theories about how solar flares are created.
New footage put together by an international team led by University of Cambridge researchers shows how entangled magnetic field lines looping from the Sun's surface slip around each other and lead to an eruption 35 times the size of the Earth and an explosive release of magnetic energy into space.
The discoveries of a gigantic energy build-up bring us a step closer to predicting when and where ...
Corporate layoff strategies are increasing workplace gender and racial inequality
2014-03-27
Research from Prof. Alexandra Kalev of Tel Aviv University's Department of Sociology and Anthropology reveals that current workplace downsizing policies are reducing managerial diversity and increasing racial and gender inequalities. According to the study, layoff practices focusing on positions and tenure, rather than worker performance, minimized the share of white women in management positions by 25 percent and of black men by 20 percent. Prof. Kalev found that a striking two-thirds of the companies surveyed used tenure or position as their core criteria for downsizing. ...