(Press-News.org) The use of fenced areas to protect threatened species in the wild should be a last resort, argue scientists from the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) and the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS).
In an article published in the journal Science, the authors state that there is a need to review the use of fencing as the conservation community develops a clearer understanding of the ecological changes caused when an area is fenced.
Fencing can have a disruptive impact on predator-prey dynamics, with species such as the African wild dog learning to chase prey into fences. For migratory herbivores such as elephants and wildebeest, fenced areas can also limit access to the vast areas of land needed to support their populations.
Human–wildlife conflict is an issue that fencing is frequently used to tackle. However, a study of 37 fences in Southern India showed that almost 50 per cent failed to prevent the passage of elephants, demonstrating the difficulty in designing and maintaining fences. As a barrier to people, fences can also spark hostility towards conservation efforts within local communities.
Lead author Prof Rosie Woodroffe of ZSL says: "In some parts of the world, fencing is part of the culture of wildlife conservation – it's assumed that all wildlife areas have to be fenced.
"But fencing profoundly alters ecosystems, and can cause some species to disappear. We're asking that conservationists carefully weigh up the biodiversity costs and benefits of new and existing wildlife fences."
Climate change is also now a factor for consideration, as barriers intended to protect species from other threats may put them at risk if they prevent animals from migrating when faced with changing climatic conditions.
The authors highlight that fencing still has a role to play in protecting species in ecosystems already badly damaged by people. For the hihi bird in New Zealand 'mainland islands' have been created using fencing to provide much needed protection from alien species, and a similar approach has been proposed to restore native wildlife, such as wolves and lynx, to fenced areas of Scotland.
But they stress that where habitat is more extensive, the priority should be to provide connected environments that can support the free movement of species, while working with local communities to help them live alongside wildlife, rather than on the other side of a fence.
Co-author Simon Hedges of WCS says: "A variety of alternative approaches – including better animal husbandry, community-based crop-guarding, insurance schemes, and wildlife-sensitive land-use planning – can be used to mitigate conflicts between people and wildlife without the need for fencing."
INFORMATION:
Editors' Notes
Copies of the embargoed Science Perspectives paper 'To Fence or Not to Fence' are available from the Science press office: +1-202-326-6440 or scipak@aaas.org.
ZSL
Founded in 1826, the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is an international scientific, conservation and educational charity whose mission is to promote and achieve the worldwide conservation of animals and their habitats. Our mission is realised through our groundbreaking science, our active conservation projects in more than 50 countries and our two Zoos, ZSL London Zoo and ZSL Whipsnade Zoo. For more information visit http://www.zsl.org
Moving the fence posts
2014-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers design trees that make it easier to produce paper
2014-04-03
Researchers have genetically engineered trees that will be easier to break down to produce paper and biofuel, a breakthrough that will mean using fewer chemicals, less energy and creating fewer environmental pollutants.
"One of the largest impediments for the pulp and paper industry as well as the emerging biofuel industry is a polymer found in wood known as lignin," says Shawn Mansfield, a professor of Wood Science at the University of British Columbia.
Lignin makes up a substantial portion of the cell wall of most plants and is a processing impediment for pulp, ...
Cassini reports sub-surface ocean on Enceladus
2014-04-03
Enceladus—one of Saturn's smaller satellites—has joined the ranks of Titan and Europa as a moon that appears to have liquid water splashing around inside of it, researchers say. New gravity data from the Cassini spacecraft, which has been exploring the planet's moons for 10 years, reveal that Enceladus harbors an ocean of water beneath 18 to 24 miles (30 to 40 kilometers) of ice at its surface.
A team of Italian and American scientists led by Luciano Iess at Sapienza Università di Roma in Rome, Italy investigated the moon's gravity field and the notable asymmetry it ...
Gravity measurements confirm subsurface ocean on Enceladus
2014-04-03
In 2005, NASA's Cassini spacecraft sent pictures back to Earth depicting an icy Saturnian moon spewing water vapor and ice from fractures, known as "tiger stripes," in its frozen surface. It was big news that tiny Enceladus—a mere 500 kilometers in diameter—was such an active place. Since then, scientists have hypothesized that a large reservoir of water lies beneath that icy surface, possibly fueling the plumes. Now, using gravity measurements collected by Cassini, scientists have confirmed that Enceladus does in fact harbor a large subsurface ocean near its south pole, ...
'Unzipping' poplars' biofuel potential
2014-04-03
EAST LANSING, Mich. — What began 20 years ago as an innovation to improve paper industry processes and dairy forage digestibility may now open the door to a much more energy- and cost-efficient way to convert biomass into fuel.
The research, which appears in the current issue of Science, focuses on enhancing poplar trees so they can break down easier and thus improving their viability as a biofuel. The long-term efforts and teamwork involved to find this solution can be described as a rare, top-down approach to engineering plants for digestibility, said Curtis Wilkerson, ...
Study shows more than half of high-risk alcohol users report improvement after surgery
2014-04-03
BOSTON – Much has been reported about the potential for increased risk of alcohol misuse after weight loss surgery (WLS), with most theories pointing to lower alcohol tolerance and a longer time to return to a sober state after surgery, but a new study from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center suggests that upwards of half of high-risk drinkers are actually less likely to report high-risk drinking behavior after weight loss surgery.
The results appear in the journal, Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.
"This is the first study to show that high-risk drinking ...
Aging workforce requires new strategies for employee retention, MU researcher says
2014-04-03
COLUMBIA, Mo. – As more baby boomers reach retirement age, state governments face the likelihood of higher workforce turnover. For example, in the state of Missouri, more than 25 percent of all active state employees will be eligible to retire by 2016. Such large numbers of retirees threaten the continuity, membership and institutional histories of the state government workforce, according to Angela Curl, assistant professor in the University of Missouri School of Social Work. In a case study of the state of Missouri's Deferred Retirement Option Provision (BackDROP), Curl ...
Scientists say new computer model amounts to a lot more than a hill of beans
2014-04-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Crops that produce more while using less water seem like a dream for a world with a burgeoning population and already strained food and water resources. This dream is coming closer to reality for University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign researchers who have developed a new computer model that can help plant scientists breed better soybean crops.
Under current climate conditions, the model predicts a design for a soybean crop with 8.5 percent more productivity, but using 13 percent less water, and reflecting 34 percent more radiation back into space, ...
Dress and behavior of mass shooters as factors to predict and prevent future attacks
2014-04-03
New Rochelle, NY, April 3, 2014–In many recent incidents of premeditated mass shooting the perpetrators have been male and dressed in black, and may share other characteristics that could be used to identify potential shooters before they commit acts of mass violence. Risk factors related to the antihero, dark-knight persona adopted by these individuals are explored in an article in Violence and Gender, a new peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Violence and Gender website at http://www.liebertpub.com/vio.
In ...
Ouch! Computer system spots fake expressions of pain better than people
2014-04-03
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A joint study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, the University at Buffalo, and the University of Toronto has found that a computer–vision system can distinguish between real or faked expressions of pain more accurately than can humans.
This ability has obvious uses for uncovering pain malingering — fabricating or exaggerating the symptoms of pain for a variety of motives — but the system also could be used to detect deceptive actions in the realms of security, psychopathology, job screening, medicine and law.
The study, "Automatic ...
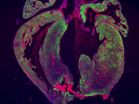
New study casts doubt on heart regeneration in mammals
2014-04-03
The mammalian heart has generally been considered to lack the ability to repair itself after injury, but a 2011 study in newborn mice challenged this view, providing evidence for complete regeneration after resection of 10% of the apex, the lowest part of the heart. In a study published by Cell Press in Stem Cell Reports on April 3, 2014, researchers attempted to replicate these recent findings but failed to uncover any evidence of complete heart regeneration in newborn mice that underwent apex resection.
"Our results question the usefulness of the apex resection model ...