(Press-News.org) A new study from the Swedish medical university Karolinska Institutet shows that asthma drugs are a potential treatment for aortic aneurysm. These drugs, which block cysteinyl-leukotrienes, could reduce the break down of vessel wall tissue and the dilation of the aortic wall, and thus the risk of its rupturing. This could both save lives and reduce the need for complicated and risky surgery. The results are presented in the scientific journal PNAS.
Aortic aneurism is a life-threatening disease caused by the weakening of a section of the wall of the aorta, which then dilates and, in advanced cases, risks rupturing. If the condition is discovered in time, surgery is a possible course of action, but often the disease develops unnoticed, causing death by sudden and massive internal haemorrhage when the aneurysm bursts.
Aortic aneurysms are more common in the 65-plus age group, and amongst men. One of the causes of the disease is a chronic inflammatory, multi-signal molecule process which activates enzymes that slowly break down proteins and the various components of the vessel wall tissue. This promotes the development of the disease and the eventual rupture of the aorta.
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have now discovered that the wall of an aortic aneurysm contains increased levels of enzymes able to form what scientists call cysteinyl-leukotrienes. As these biologically potent substances trigger the contraction of smooth muscle and a swelling of the airways they can cause asthma, and therefore asthma patients are often treated with drugs that block cysteinyl-leukotrienes.
"We've also found that cysteinyl-leukotrienes can stimulate the release of protein-digesting enzymes called metalloproteases, which can contribute to the weakening of the aortic wall and the development of an aneurysm," says Professor Jesper Haeggström, who led the study.
The researchers found that the introduction of an asthma drug blocked the cysteinyl-leukotrienes and thus impeded the release of the harmful metalloproteases. Their results suggest that this type of asthma drugs could be used to reduce aortic dilation and hence the danger of a ruptured aneurysm.
"These asthma drugs are both efficacious and safe, and we should soon be able to test any positive effect they might have on aortic aneurysm," says Professor Jesper Haeggström.
###
Publication: 'Increased expression of leukotriene C4 synthase and predominant formation of cysteinyl-leukotrienes in human abdominal aortic aneurysm', Di Gennaro A, Wågsäter D, Mäyränpää MI, Gabrielsen A, Swedenborg J, Hamsten A, Samuelsson B, Eriksson P, Haeggström JZ., PNAS, Epub ahead of print 15-19 Nov 2010.
Download images: http://ki.se/pressroom
For further information, please contact:
Professor Jesper Z. Haeggström
Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics
Tel: +46 (0)8-524 876 12 or +46 (0)70-277 76 12
Email: jesper.haeggstrom@ki.se
Professor Jesper Swedenborg
Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery
Tel: +46 (0)8-517 723 48 or +46 (0)70-970 80 79
Email: jesper.swedenborg@ki.se
Karolinska Institutet is one of the world's leading medical universities. Its mission is to contribute to the improvement of human health through research and education. Karolinska Institutet accounts for over 40 per cent of the medical academic research conducted in Sweden, and offers the country's broadest range of education in medicine and health sciences. Since 1901 the Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has selected the Nobel laureates in Physiology or Medicine. More information on ki.se.
END
HealthSpace, the internet-accessible personal health organiser developed as part of the National Programme for IT in the National Health Service, was significantly less popular than anticipated, a research team from the University of London has found.
Instead of the predicted 5-10% of the population signing up, only 0.13% of those invited got as far as activating the full functionality of their personal health record, according to the study published on bmj.com today.
Professor Trisha Greenhalgh from Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry led the team ...
Researchers from the Group of Applied Artificial Intelligence (GIAA) on the Colmenarejo Campus of UC3M have presented this application at the latest Salón Internacional de Material Eléctrico y Electrónico, recently held in Madrid. The participants at the stand of Infaimon, the company which has collaborated on this project, had the opportunity to test this interface with a videogame operated simply by moving ones hands as if holding a virtual steering wheel. For this purpose, the scientists have employed a time of flight camera or TOF with which they capture in 3D user's ...
An open letter from 20 consultants and a patient group published on bmj.com today, calls on the prime minister to take action over a legal loophole that allows drug companies to make easy profits by licensing existing treatments for rare (orphan) diseases.
They argue that the current situation concerning orphan drugs is not in the best interests of patients or the NHS and that the cost to the NHS is likely to be above £10m a year.
The original purpose of this legislation was to encourage drug companies to conduct research into rare diseases and develop new treatments. ...
The metallic particles in the smoke emitted by fireworks pose a health risk, particularly to people who suffer from asthma. This is the conclusion of a study led by researchers from the Institute of Environmental Assessment and Water Research (IDAEA-CSIC), published this week in the Journal of Hazardous Materials.
"The toxicological research has shown that many of the metallic particles in the smoke from fireworks are bio-reactive and can affect human health", Teresa Moreno, a researcher from the IDAEA (CSIC) and lead author of a study that has been published this week ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- University of Michigan researchers have solved the structure of a protein that is integral to processes responsible for maintaining a healthy heart and nervous system.
The protein structure in question is cystathionine beta-synthase, known as CBS. CBS uses vitamin B6 to make hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gaseous signaling molecule that helps maintain a healthy heart and nervous system. H2S also induces a state of suspended animation or hibernation in animals by decreasing body temperature and lowering metabolic rate.
The work to decode the structure ...
Arlington, Va. — New research being presented at the 2010 International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) Pharmaceutical Sciences World Congress (PSWC) in association with the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) Annual Meeting and Exposition will feature an inhalable dry powder antibiotic that when used alone or with current treatments may significantly reduce treatment for tuberculosis (TB) and multi-drug resistant TB.
There are an estimated 9.4 million new cases of TB worldwide, according to the most recent statistics from the World Health Organization. ...
Whether a small cut with a fruit knife, a surgical wound or a major injury caused by a fall – the body's defense and repair system leaps into action and tries to close the wound as quickly as possible. Small injuries usually heal within a few days, but a gaping wound will take longer to heal, and an infection can take hold even after several days. Dressings protect the site of the injury but to check the wound they have to be removed. This can be painful for the patient and moreover it risks giving germs the chance to enter and cause infection. Scientists at the Fraunhofer ...
Hair clippings, cayenne pepper and raw eggs – these are just a few of the odd ingredients recommended to keep those pesky deer away from your backyard garden. But what about farmers who have hundreds of acres of Christmas trees to protect? North Carolina State University extension specialists have now found an effective, inexpensive alternative to available commercial products to keep the deer at bay.
The NC State researchers, led by Jeff Owen, a Christmas-tree production specialist, are exploring the use of inexpensive, inedible food byproducts – such as dried blood ...
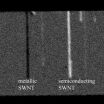
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers have demonstrated a new imaging tool for rapidly screening structures called single-wall carbon nanotubes, possibly hastening their use in creating a new class of computers and electronics that are faster and consume less power than today's.
The semiconducting nanostructures might be used to revolutionize electronics by replacing conventional silicon components and circuits. However, one obstacle in their application is that metallic versions form unavoidably during the manufacturing process, contaminating the semiconducting nanotubes.
Now ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers at Purdue University are studying the effects of fire on steel structures, such as buildings and bridges, using a one-of-a-kind heating system and a specialized laboratory for testing large beams and other components.
Building fires may reach temperatures of 1,000 degrees Celsius, or more than 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit, said Amit Varma, a Purdue associate professor of civil engineering who is leading the work.g1
"At that temperature, exposed steel would take about 25 minutes to lose about 60 percent of its strength and stiffness," he ...