(Press-News.org) A variant of the gene KLOTHO is known for its anti-aging effects in people fortunate enough to carry one copy. Now researchers find that it also has benefits when it comes to brain function. The variant appears to lend beneficial cognitive effects by increasing overall levels of klotho in the bloodstream and brain.
What's more, the improvements in learning and memory associated with klotho elevation aren't strictly tied to aging. They do occur in aging mice, but also in young animals, according to a report published in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports on May 8th. That means klotho works to enhance brain power, but in an unexpected way.
"Based on what was known about klotho, we expected it to affect the brain by changing the aging process," said Lennart Mucke of the Gladstone Institute and the University of California, San Francisco, who directed the study. "But this is not what we found, which suggests to us that we are on to something new and different."
Aging is a primary risk factor for cognitive decline, lead author Dena Dubal explained. The question was: Would a factor known to play a role in long life have benefits for cognition too?
Together with a large group of collaborators, Mucke and Dubal examined the question in three separate cohorts of people participating in aging studies of various kinds, adding up to more than 700 people. Their analysis showed that people with one of the life-extending variants of the KLOTHO gene scored better on cognitive tests. Because those effects were associated with higher circulating levels of klotho, the researchers turned to genetically engineered mice that express higher-than-normal levels of the life-extending substance.
Indeed, klotho worked there too. "Mice with elevated klotho performed twice as well as controls in some cognitive tests – such as remembering where a hidden platform was located in a water maze," Dubal said. In other tests, the mice did better too, but in some cases only slightly.
Elevating klotho in mice also enhanced the formation and flexibility of neural connections, the cellular basis for learning and memory. Surprisingly, the effects of klotho were evident in mice young and old. They didn't correlate with age in humans, either.
In other words, klotho appears to work in a manner independent of aging and may increase cognitive reserve at different life stages. The researchers say that in healthy, aging humans the positive cognitive effects of carrying one copy of the KLOTHO variant may even exceed the harmful effect of carrying the notorious ε4 variant of the APOE gene, best known for its contributions to Alzheimer's disease.
Mucke says that means the findings could have broad therapeutic implications. "Because cognition is a highly valued aspect of brain function that diminishes with aging and disease, the potential to enhance it even slightly is of great potential relevance to the human condition," Dubal said.
INFORMATION:
Cell Reports, Dubal et al.: "Life extension factor klotho enhances cognition."
Anti-aging factor offers brain boost too
2014-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What vigilant squid can teach us about the purpose of pain
2014-05-08
Most of us have probably felt that lasting sense of anxiety or even pain after enduring some kind of accident or injury. Now, researchers have the first evidence in any animal that there may be a very good reason for that kind of heightened sensitivity—or at least there is in the battle of squid versus fish. Squid that behave with extra vigilance after experiencing even a minor injury are more likely to live to see another day, according to a report appearing in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on May 8.
The findings suggest that behaviors that appear counterproductive ...
Antibiotic resistance genes are essentially everywhere
2014-05-08
The largest metagenomic search for antibiotic resistance genes in the DNA sequences of microbial communities from around the globe has found that bacteria carrying those vexing genes turn up everywhere in nature that scientists look for them. The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on May 8 add to evidence showing just how common and abundant those resistance genes really are in natural environments.
This big-picture, ecological view on a growing healthcare concern emphasizes the important relationship between antibiotic resistance in the clinic ...
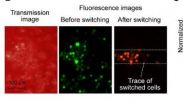
New technology using florescent proteins tracks cancer cells circulating in the blood
2014-05-08
After cancer spreads, finding and destroying malignant cells that circulate in the body is usually critical to patient survival. Now, researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Chemistry & Biology have developed a new method that allows investigators to label and track single tumor cells circulating in the blood. This advance could help investigators develop a better understanding of cancer spread and how to stop it.
Cancer spread, or metastasis, leads to up to 90% of cancer deaths. Investigators currently do not have the clinical capability to intervene and stop ...
Spurt of heart muscle cell division seen in mice well after birth
2014-05-08
The entire heart muscle in young children may hold untapped potential for regeneration, new research suggests.
For decades, scientists believed that after a child's first few days of life, cardiac muscle cells did not divide. Instead, the assumption was that the heart could only grow by having the muscle cells become larger.
Cracks were already appearing in that theory. But new findings in mice, scheduled for publication in Cell, provide a dramatic counterexample -- with implications for the treatment of congenital heart disorders in humans.
Researchers at Emory University ...
Discovery that heart cells replicate during adolescence opens new avenue for heart repair
2014-05-08
It is widely accepted that heart muscle cells in mammals stop replicating shortly after birth, limiting the ability of the heart to repair itself after injury. A study published by Cell Press May 8th in the journal Cell now shows that heart muscle cells in mice undergo a brief proliferative burst prior to adolescence, increasing in number by about 40% to allow the heart to meet the increased circulatory needs of the body during a period of rapid growth. The findings suggest that thyroid hormone therapy could stimulate this process and enhance the heart's ability to regenerate ...
Polar bear genome reveals rapid adaptation to fatty diet
2014-05-08
Polar bears adapted to life in cold Arctic climates in part by relying on a high-fat diet mainly consisting of seals and their blubber. In a study published by Cell Press May 8th in the journal Cell, researchers discovered that mutations in genes involved in cardiovascular function allowed polar bears to rapidly evolve the ability to consume a fatty diet without developing high rates of heart disease. Moreover, the study revealed that polar bears diverged from brown bears less than 500,000 years ago—much more recently than estimates based on previous genomic data.
"In ...
Using genetics to measure the environmental impact of salmon farming
2014-05-08
Determining species diversity makes it possible to estimate the impact of human activity on marine ecosystems accurately. The environmental effects of salmon farming have been assessed, until now, by visually identifying the animals living in the marine sediment samples collected at specific distances from farming sites. A team led by Jan Pawlowski, professor at the Faculty of Science of the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, analysed this type of sediment using a technique known as "DNA barcoding" that targets certain micro-organisms. Their research, which has ...
Humans may benefit from new insights into polar bear's adaptation to high-fat diet
2014-05-08
A comparison of the genomes of polar bears and brown bears reveals that the polar bear is a much younger species than previously believed, having diverged from brown bears less than 500,000 years ago.
The analysis also uncovered several genes that may be involved in the polar bears' extreme adaptations to life in the high Arctic. The species lives much of its life on sea ice, where it subsists on a blubber-rich diet of primarily marine mammals.
The genes pinpointed by the study are related to fatty acid metabolism and cardiovascular function, and may explain the bear's ...
Better cognition seen with gene variant carried by 1 in 5
2014-05-08
A scientific team led by the Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco has discovered that a common form of a gene already associated with long life also improves learning and memory, a finding that could have implications for treating age-related diseases like Alzheimer's.
The researchers found that people who carry a single copy of the KL-VS variant of the KLOTHO gene perform better on a wide variety of cognitive tests. When the researchers modeled the effects in mice, they found it strengthened the connections between neurons that make learning possible – what is known ...
Penn yeast study identifies novel longevity pathway
2014-05-08
PHILADELPHIA - Ancient philosophers looked to alchemy for clues to life everlasting. Today, researchers look to their yeast. These single-celled microbes have long served as model systems for the puzzle that is the aging process, and in this week's issue of Cell Metabolism, they fill in yet another piece.
The study, led by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, identifies a new molecular circuit that controls longevity in yeast and more complex organisms and suggests a therapeutic intervention that could mimic the lifespan-enhancing effect of caloric restriction, ...