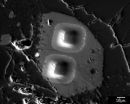
(Press-News.org) Zeolites are among the substances which can accelerate chemical reactions – they are known as catalysts. Usually applied in pellet form, the industrial production of gasoline from crude oil without zeolites is today inconceivable. The chemical reactions occur on their surface. Fortunately, these are very large for zeolites: the catalysts are interspersed with nano-sized pores and microscopic channels through which gaseous or liquid reactants penetrate and the products later can leave.
One of the main industrial problems with the use of zeolites is that the reaction side products clog the pores or block the active sites of the catalyst. Experts call such hydrocarbon deposits 'coke'. Consequently, the production needs to be interrupted at regular intervals to burn off the debris formed in the catalyst, thereby regenerating the latter. This reduces the efficiency of the process.
It all depends on the inner structure
Researchers are therefore working to make zeolite catalysts more resistant to such deposits, thereby delaying the need for regeneration and thus, extending the production cycles. Researchers from ETH Zurich headed by Javier Pérez-Ramírez, a professor of catalysis engineering, have now identified the relation between this resistance and the internal structure of a new class of zeolite catalysts combining a complex network of pores of various sizes: "It is not only about the providing the greatest number of pores, as was previously thought", says Sharon Mitchell, researcher in the group of Pérez-Ramírez. "Rather it is crucial that the nano-sized channels are well connected within the zeolite catalysts and has numerous openings to the outside." This facilitates the penetration of the chemical compounds into the catalyst even when some of the pores are blocked.
The researchers came to this realization by preparing catalysts with diverse pore structures in the laboratory. To achieve this they used different synthesis methods and conditions. The catalysts were subsequently studied in collaboration with Paolo Crivelli, researcher at the Department of Physics, with positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS). This technique measures how long the positrons reside within the catalyst. The more connected the pores are, and the greater the number of openings, the faster the positrons can escape from the zeolite. In addition, the scientists assessed how quickly coke deposits formed within the various zeolite catalysts in their laboratory.
Not only better, but also cheaper
"Interestingly, the method by which we could make the most resistant zeolites, was also the cheapest", says Pérez-Ramírez. He expects that the results of the study, published in the journal Nature Communications, will animate industry to adopt their zeolite manufacturing process.
Zeolite catalysts are currently used on a large scale in the petroleum industry to produce high-grade propellants, fuels and raw materials for the chemical industry. On the one hand, large hydrocarbon molecules in the crude oil can be broken down into more useful medium-sized molecules. On the other hand, zeolites can also be used to couple very small hydrocarbons – such as ethene and propene – to obtain higher quality products also of medium chain length. "Even as oil is gradually one day replaced by renewable feedstocks, such as biomass, zeolite catalysts will retain their importance," says Pérez-Ramírez. Premium base chemicals could be produced in an efficient manner using zeolite catalysts.
INFORMATION:
Literature reference
Milina M, Mitchell S, Crivelli P, Cooke D, Pérez-Ramírez J: Mesopore quality determines the lifetime of hierarchically-structured zeolite catalysts. Nature Communications, Advance online publication 27 May 2014, doi: 10.1038/ncomms4922 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4922]
Better catalysts for the petrochemical industry
2014-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MRI catches breast cancer early in at-risk survivors of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma
2014-05-28
(TORONTO, Canada – May 28, 2014) – The largest clinical study to evaluate breast cancer screening of female survivors of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), who are at increased risk because they received chest radiation, shows that magnetic-resonance imaging (MRI) detected invasive breast tumours at very early stages, when cure rates are expected to be excellent.
The finding, published online today in the American Cancer Society Journal Cancer (doi: doi/10.1002/cncr.28747), underscores the need for at-risk childhood HL survivors and primary care physicians to be aware ...
Fish more inclined to crash than bees
2014-05-28
Swimming fish do not appear to use their collision warning system in the same way as flying insects, according to new research from Lund University in Sweden that has compared how zebra fish and bumblebees avoid collisions. The fish surprised the researchers.
All animals need some form of warning system that prevents them colliding with objects in their surroundings. The warning system helps them to continually regulate their speed and judge their distance from objects. For flying and swimming creatures this is an extra challenge because they also have to deal with winds ...
NUS researchers discover unusual parenting behavior by a Southeast Asian treefrog
2014-05-28
Researchers from the Department of Biological Sciences at the National University of Singapore (NUS) Faculty of Science have discovered that a Southeast Asian species of treefrog practices parental care to increase the likelihood of survival of its offspring. Chiromantis hansenae (C. hansenae), is currently the only species in the treefrog family in Southeast Asia that is known to exhibit such behaviour. This discovery was recently published as the cover story in a popular magazine of nature and science, Natural History, in May 2014.
The study investigates parental care ...
'Nanodaisies' deliver drug cocktail to cancer cells
2014-05-28
Biomedical engineering researchers have developed daisy-shaped, nanoscale structures that are made predominantly of anti-cancer drugs and are capable of introducing a "cocktail" of multiple drugs into cancer cells. The researchers are all part the joint biomedical engineering program at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
"We found that this technique was much better than conventional drug-delivery techniques at inhibiting the growth of lung cancer tumors in mice," says Dr. Zhen Gu, senior author of the paper and an assistant ...
Marathon runners' times develop in a U shape
2014-05-28
Spanish researchers have demonstrated that the relationship between marathon running times and the age of the athlete is U-shaped. The work shows the unusual fact that it takes an 18-year-old athlete the same amount of time to finish a marathon as a 55- or 60-year-old runner.
The 42,195 metres that are nowadays known as the marathon were run for the first time at the London Olympic Games of 1908. Since then, many athletes have completed this race and there has also been numerous scientific studies conducted on endurance runners.
Up to now, the majority of these works ...
International research group documents unique songbird diversity of the Eastern Himalayas
2014-05-28
The Eastern Himalayas are home to more than 360 different songbird species, most of which are to be found nowhere else on the planet. This makes the region extending from eastern Nepal to the borderlands of China, India, and Myanmar unique and one of the most important hot spots for biological diversity in the western hemisphere. A recent research paper describes how this impressive bird community came about millions of years ago, emphasizing both the uniqueness and biological significance of this remote area. "As the Himalayan mountain range was formed, a profusion of ...
Sneaky bacteria change key protein's shape to escape detection
2014-05-28
Every once in a while in the U.S., bacterial meningitis seems to crop up out of nowhere, claiming a young life. Part of the disease's danger is the ability of the bacteria to evade the body's immune system, but scientists are now figuring out how the pathogen hides in plain sight. Their findings, which could help defeat these bacteria and others like it, appear in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Linda Columbus and colleagues explain that the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis, one cause of meningitis, and its cousin Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is responsible ...
Artificial lung the size of a sugar cube
2014-05-28
This news release is available in German.
Lung cancer is a serious condition. Once patients are diagnosed with it, chemotherapy is often their only hope. But nobody can accurately predict whether or not this treatment will help. To start with, not all patients respond to a course of chemotherapy in exactly the same way. And then there's the fact that the systems drug companies use to test new medications leave a lot to be desired. "Animal models may be the best we have at the moment, but all the same, 75 percent of the drugs deemed beneficial when tested on animals ...
Water in moon rocks provides clues and questions about lunar history
2014-05-28
A recent review of hundreds of chemical analyses of Moon rocks indicates that the amount of water in the Moon's interior varies regionally – revealing clues about how water originated and was redistributed in the Moon. These discoveries provide a new tool to unravel the processes involved in the formation of the Moon, how the lunar crust cooled, and its impact history.
This is not liquid water, but water trapped in volcanic glasses or chemically bound in mineral grains inside lunar rocks. Rocks originating from some areas in the lunar interior contain much more water ...
Ultraviolet cleaning reduces hospital superbugs by 20 percent: Study
2014-05-28
Washington, DC, May 27, 2014 – Healthcare-associated vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile (CD), and other multidrug-resistant organisms (MDRO) were decreased among patients after adding ultraviolet environmental disinfection (UVD) to the cleaning regimen, according to a study published in the June issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
In this retrospective study led by the ...