(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – Every living cell's surface has a protein-embedded membrane that's covered in polysaccharide chains – a literal sugar coating. A new study by a Cornell University researcher found this coating is especially thick and pronounced on cancer cells and is a crucial determinant of the cell's survival.
Consisting of long, sugar-decorated molecules called glycoproteins, the coating causes physical changes in the cell membrane that make the cell better able to thrive – leading to a more lethal cancer.
Matthew Paszek, assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at Cornell and Valerie Weaver, at the University of California, San Francisco, led the study on glycoprotein-induced cancer cell survival, published online in Nature.
The researchers found that long glycoprotein chains on a cancer cell's surface cause the cell membrane to push away from its environment and bend inward. This physical change causes adhesion receptors on the cell surface called integrins to clump together. Integrins bind to protein scaffolds in their environment and regulate pretty much everything a cell does – movement, change and growth.
This clustering mechanism causes the integrins to alter the cell's normal signaling, leading to unchecked growth and survival.
"Changes to the sugar composition on the cell surface could alter physically how receptors are organized," he said. "That's really the big thing: coupling the regulation of the sugar coating to these biochemical signaling molecules."
The paper, "The cancer glycocalyx mechanically primes integrin-mediated growth and survival," was the subject of a "News and Views" feature in Nature.
INFORMATION:
For cancer patients, sugar-coated cells are deadly
2014-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clemson scientists: Kudzu can release soil carbon, accelerate global warming
2014-07-01
CLEMSON, S.C. — Clemson University scientists are shedding new light on how invasion by exotic plant species affects the ability of soil to store greenhouse gases. The research could have far-reaching implications for how we manage agricultural land and native ecosystems.
In a paper published in the scientific journal New Phytologist, plant ecologist Nishanth Tharayil and graduate student Mioko Tamura show that invasive plants can accelerate the greenhouse effect by releasing carbon stored in soil into the atmosphere.
Since soil stores more carbon than both the atmosphere ...
Cellular gates for sodium and calcium controlled by common element of ancient origin
2014-07-01
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have spotted a strong family trait in two distant relatives: The channels that permit entry of sodium and calcium ions into cells turn out to share similar means for regulating ion intake, they say. Both types of channels are critical to life. Having the right concentrations of sodium and calcium ions in cells enables healthy brain communication, heart contraction and many other processes. The new evidence is likely to aid development of drugs for channel-linked diseases ranging from epilepsy to heart ailments to muscle weakness.
"This discovery ...
Mayo Clinic: Proton therapy has advantages over IMRT for advanced head and neck cancers
2014-07-01
Rochester, Minn. -- A new study by radiation oncologists at Mayo Clinic comparing the world's literature on outcomes of proton beam therapy in the treatment of a variety of advanced head and neck cancers of the skull base compared to intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) has found that proton beam therapy significantly improved disease free survival and tumor control when compared to IMRT. The results appear in the journal Lancet Oncology.
"We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the clinical outcomes of patients treated with proton therapy ...
Video games could provide venue for exploring sustainability concepts
2014-07-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Could playing video games help people understand and address global sustainability issues such as pollution, drought or climate change? At least two researchers believe so, outlining their argument in a concept paper published in the journal First Monday.
Video games have the potential to educate the public and encourage development of creative solutions to social, economic and environmental problems, said Oregon State University's Shawna Kelly, one of the two authors of the article.
"Video games encourage creative and strategic thinking, which could ...
Studies: Addiction starts with an overcorrection in the brain
2014-07-01
The National Institutes of Health has turned to neuroscientists at the nation's most "Stone Cold Sober" university for help finding ways to treat drug and alcohol addiction.
Brigham Young University professor Scott Steffensen and his collaborators have published three new scientific papers that detail the brain mechanisms involved with addictive substances. And the NIH thinks Steffensen's on the right track, as evidenced by a $2-million grant that will help fund projects in his BYU lab for the next five years.
"Addiction is a brain disease that could be treated like ...
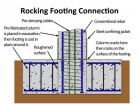
New bridge design improves earthquake resistance, reduces damage and speeds construction
2014-07-01
SEATTLE, Wash. - Researchers have developed a new design for the framework of columns and beams that support bridges, called "bents," to improve performance for better resistance to earthquakes, less damage and faster on-site construction.
The faster construction is achieved by pre-fabricating the columns and beams off-site and shipping them to the site, where they are erected and connected quickly.
"The design of reinforced concrete bridges in seismic regions has changed little since the mid-1970s," said John Stanton, a professor in the Department of Civil and Environmental ...
Chinese herbal extract may help kill off pancreatic cancer cells
2014-07-01
Bethesda, Md. (July 1, 2014) — A diagnosis of pancreatic cancer—the fourth most common cause of cancer death in the U.S.—can be devastating. Due in part to aggressive cell replication and tumor growth, pancreatic cancer progresses quickly and has a low five-year survival rate (less than 5 percent).
GRP78, a protein that protects cells from dying, is more abundant in cancer cells and tissue than in normal organs and is thought to play a role in helping pancreatic cancer cells survive and thrive. Researchers at the University of Minnesota have found triptolide, an extract ...
Tags reveal Chilean devil rays are among ocean's deepest divers
2014-07-01
Thought to dwell mostly near the ocean's surface, Chilean devil rays (Mobula tarapacana) are most often seen gliding through shallow, warm waters. But a new study by scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and international colleagues reveals that these large and majestic creatures are actually among the deepest-diving ocean animals.
"So little is known about these rays," said Simon Thorrold, a biologist at WHOI and one of the authors of the paper, published July 1, 2014, in the journal Nature Communications. "We thought they probably travelled long ...
Bringing the bling to antibacterials
2014-07-01
WASHINGTON D.C., July 1, 2014 – Bacteria love to colonize surfaces inside your body, but they have a hard time getting past your rugged, salty skin. Surgeries to implant medical devices often give such bacteria the opportunity needed to gain entry into the body cavity, allowing the implants themselves to act then as an ideal growing surface for biofilms.
A group of researchers at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics in the Chinese Academy of Sciences are looking to combat these dangerous sub-dermal infections by upgrading your new hip or kneecap in a fashion appreciated ...
Efforts to cut unnecessary blood testing bring major decreases in health care spending
2014-07-01
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center used two relatively simple tactics to significantly reduce the number of unnecessary blood tests to assess symptoms of heart attack and chest pain and to achieve a large decrease in patient charges.
The team provided information and education to physicians about proven testing guidelines and made changes to the computerized provider order entry system at the medical center, part of the Johns Hopkins Health System. The guidelines call for more limited use of blood tests for so-called cardiac biomarkers. A year after implementation, ...