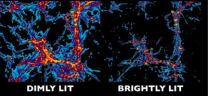
(Press-News.org) Pasadena, CA—Something is amiss in the Universe. There appears to be an enormous deficit of ultraviolet light in the cosmic budget.
The vast reaches of empty space between galaxies are bridged by tendrils of hydrogen and helium, which can be used as a precise "light meter." In a recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, a team of scientists finds that the light from known populations of galaxies and quasars is not nearly enough to explain observations of intergalactic hydrogen. The difference is a stunning 400 percent.
"It's as if you're in a big, brightly-lit room, but you look around and see only a few 40-watt lightbulbs," noted Carnegie's Juna Kollmeier, lead author of the study. "Where is all that light coming from? It's missing from our census."
Strangely, this mismatch only appears in the nearby, relatively well-studied cosmos. When telescopes focus on galaxies billions of light years away (and therefore are viewing the universe billions of years in its past), everything seems to add up. The fact that this accounting works in the early universe but falls apart locally has scientists puzzled.
The light in question consists of highly energetic ultraviolet photons that are able to convert electrically neutral hydrogen atoms into electrically charged ions. The two known sources for such ionizing photons are quasars—powered by hot gas falling onto supermassive black holes over a million times the mass of the sun—and the hottest young stars.
Observations indicate that the ionizing photons from young stars are almost always absorbed by gas in their host galaxy, so they never escape to affect intergalactic hydrogen. But the number of known quasars is far lower than needed to produce the required light.
"Either our accounting of the light from galaxies and quasars is very far off, or there's some other major source of ionizing photons that we've never recognized," Kollmeier said. "We are calling this missing light the photon underproduction crisis. But it's the astronomers who are in crisis—somehow or other, the universe is getting along just fine."
The mismatch emerged from comparing supercomputer simulations of intergalactic gas to the most recent analysis of observations from Hubble Space Telescope's Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. "The simulations fit the data beautifully in the early universe, and they fit the local data beautifully if we're allowed to assume that this extra light is really there," explained Ben Oppenheimer a co-author from the University of Colorado. "It's possible the simulations do not reflect reality, which by itself would be a surprise, because intergalactic hydrogen is the component of the Universe that we think we understand the best."
"The most exciting possibility is that the missing photons are coming from some exotic new source, not galaxies or quasars at all," said Neal Katz a co-author from the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
For example, the mysterious dark matter, which holds galaxies together but has never been seen directly, could itself decay and ultimately be responsible for this extra light.
"You know it's a crisis when you start seriously talking about decaying dark matter!" Katz remarked.
"The great thing about a 400% discrepancy is that you know something is really wrong," commented co-author David Weinberg of The Ohio State University. "We still don't know for sure what it is, but at least one thing we thought we knew about the present day universe isn't true."
Whether the explanation is exotic or not, astronomers will be working hard to shed light on the mystery.
INFORMATION:Other co-authors on the study are Francesco Haardt of the Università dell'Insubria, Romeel Davé of the University of the Western Cape, Mark Fardal of University of Massachusetts Amherst, Piero Madau of University of California Santa Cruz, Charles Danforth of the University of Colorado, Amanda Ford of University of Arizona, Molly Peeples of the Space Telescope Science Institute, and Joseph McEwen of The Ohio State University.
This work was supported by the NSF, NASA, and the Ahmanson Foundation.
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
Cosmic accounting reveals missing light crisis
2014-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More California gas stations can provide H2 than previously thought, Sandia study says
2014-07-08
LIVERMORE, Calif. — A study by researchers at Sandia National Laboratories concludes that a number of existing gas stations in California can safely store and dispense hydrogen, suggesting a broader network of hydrogen fueling stations may be within reach.
The report examined 70 commercial gasoline stations in the state of California and sought to determine which, if any, could integrate hydrogen fuel, based on the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) hydrogen technologies code published in 2011.
The study determined that 14 of the 70 gas stations involved in ...
Logging and burning cause the loss of 54 million tons of carbon a year in Amazonia
2014-07-08
A study conducted by scientists in Brazil and the United Kingdom has quantified the impact that selective logging, partial destruction by burning, and fragmentation resulting from the development of pastures and plantations have had on the Amazon rainforest. In combination, these factors could be removing nearly 54 million tons of carbon from the forest each year, introduced into the atmosphere as greenhouse gases. This total represents up to 40% of the carbon loss caused by deforestation in the region.
The study, which was conducted by 10 researchers from 11 institutions ...
Earthquakes explained? New research shows friction and fracture are closely related
2014-07-08
Overturning conventional wisdom stretching all the way to Leonardo da Vinci, new Hebrew University of Jerusalem research shows that how things break (fracture) and how things slide (friction) are closely interrelated. The breakthrough study marks an important advance in understanding friction and fracture, with implications for describing the mechanics that drive earthquakes.
Over 500 years ago, da Vinci described how rough blocks slide over one another, providing the basis for our understanding of friction to this day. The phenomenon of fracture was always considered ...
Contradictory findings about the effect of the full moon on sleep
2014-07-08
A Swiss research study conducted last year showed that the full moon affects sleep. The findings demonstrated that people average 20 minutes less sleep, take five minutes longer to fall asleep and experience 30 minutes more of REM sleep, during which most dreaming is believed to occur.
Different outcome
Numerous studies through the years have attempted to prove or disprove the hypothesis that lunar phases affect human sleep. But results have been hard to repeat. A group of researchers at the famed Max Planck Institute and elsewhere analyzed data from more than 1,000 ...
Collisions with robots -- without risk of injury
2014-07-08
Everybody has experienced this: You aren't careful for just one moment and suddenly you run into the edge of a table. At first, it hurts. A little later, a bruise starts to appear. What falls into the category of "nothing bad, but aggravating" in the case of a table, takes on a new dimension when the colliding partner is a robot, because such a collision can injure humans seriously. That is why these mechanical assistants usually still work behind protective barriers. Since some applications require humans and robots to work hand-in-hand, though, their cooperation has become ...
Preterm babies more likely to survive in larger newborn care units
2014-07-08
Premature newborns are 32% less likely to die if they are admitted to high volume neonatal units rather than low volume, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Warwick and published in BMJ Open, analysed data from 165 neonatal units across the UK. It found babies born at less than 33 weeks gestation were 32% less likely to die if they were admitted to high volume units, compared to low volume.
For babies born at less than 27 weeks the effect was greater, with the odds of dying almost halved when they were admitted to high volume units, compared ...
New research finds working memory is the key to early academic achievement
2014-07-08
Working memory in children is linked strongly to reading and academic achievement, a new study from the University of Luxembourg and partner Universities from Brazil* has shown. Moreover, this finding holds true regardless of socio-economic status. This suggests that children with learning difficulties might benefit from teaching methods that prevent working memory overload. The study was published recently in the scientific journal "Frontiers in Psychology".
The study was conducted in Brazil on 106 children between 6 and 8 from a range of social backgrounds, with half ...
Sandalwood scent facilitates wound healing and skin regeneration
2014-07-08
Skin cells possess an olfactory receptor for sandalwood scent, as researchers at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum have discovered. Their data indicate that the cell proliferation increases and wound healing improves if those receptors are activated. This mechanism constitutes a possible starting point for new drugs and cosmetics. The team headed by Dr Daniela Busse and Prof Dr Dr Dr med habil Hanns Hatt from the Department for Cellphysiology published their report in the "Journal of Investigative Dermatology".
The nose is not the only place where olfactory receptors occur
Humans ...
Treatment-resistant hypertension requires proper diagnosis
2014-07-08
High blood pressure—also known as hypertension—is widespread, but treatment often fails. One in five people with hypertension does not respond to therapy. This is frequently due to inadequate diagnosis, as Franz Weber and Manfred Anlauf point out in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2014; 111: 425–31).
If a patient's blood pressure is not controlled by treatment, this can be due to a number of reasons. Often it is the medication the patient is on. Some patients may be taking other medicines – in addition to their antihypertensive ...
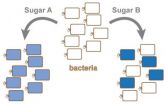
When faced with some sugars, bacteria can be picky eaters
2014-07-08
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of Minnesota have found for the first time that genetically identical strains of bacteria can respond very differently to the presence of sugars and other organic molecules in the environment, with some individual bacteria devouring the sugars and others ignoring it.
"This highlights the complexity of bacterial behaviors and their response to environmental conditions, and how much we still need to learn," says Dr. Chase Beisel, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State ...